概述:
hibernate-validator是Hibernate项目中的一个数据校验框架,是Bean Validation 的参考实现,hibernate-validator除了提供了JSR 303规范中所有内置constraint 的实现,还有一些附加的constraint 。使用hibernate-validator能够将数据校验从业务代码中脱离出来,增加代码可读性,同时也让数据校验变得更加方便、简单。
实践步骤;
添加依赖:
<!--参数校验框架依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
hibernate-validator常用注解
| Constraint | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| @Valid | 被注释的元素是一个对象,需要检查此对象的所有字段值 |
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max, min) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(value) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
| 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 | |
| @Length | 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @NotEmpty | 被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @Range | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
| @NotBlank | 被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=) | 被注释的字符串必须是一个有效的url |
| @CreditCardNumber | 被注释的字符串必须通过Luhn校验算法,银行卡,信用卡等号码一般都用Luhn计算合法性 |
自定义校验结果返回类型:
package com.miaoshaproject.validator;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* @Description: 自定义校验结果返回类型格式
* @Package: com.miaoshaproject.validator
* @author: FLy-Fly-Zhang
* @Date: 2019/7/29
* @Time: 11:59
*/
public class ValidationResult {
//校验结果是否有错
private boolean hasError;
//存放校验信息
private Map<String,String> errorMsgMap;
public ValidationResult(){
this.errorMsgMap=new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* 通过格式化字符串信息获取错误结果的msg
* @return
*/
public String getErrorMsg(){
//组装错误信息并用逗号隔开
return StringUtils.join(errorMsgMap.values().toArray(),",");
}
public boolean isHasError() {
return hasError;
}
public void setHasError(boolean hasError) {
this.hasError = hasError;
}
public Map<String, String> getErrorMsgMap() {
return errorMsgMap;
}
public void setErrorMsgMap(Map<String, String> errorMsgMap) {
this.errorMsgMap = errorMsgMap;
}
}
自定义实现校验类
package com.miaoshaproject.validator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @Created with IntelliJ IDEA
* @Description: 校验器
* @Package: com.miaoshaproject.validator
* @author: FLy-Fly-Zhang
* @Date: 2019/7/29
* @Time: 12:07
*/
@Component
public class ValidatorImpl implements InitializingBean {
//java实现
private Validator validator;
public ValidationResult validate(Object bean){
ValidationResult result=new ValidationResult();
//bean中参数违背了validator定义的规则的话,错误就会出现在集合中
Set<ConstraintViolation<Object>> constraintViolationSet=validator.validate(bean);
//有错误
if(!constraintViolationSet.isEmpty()){
result.setHasError(true);
// Iterator<ConstraintViolation<Object>> iterator=constraintViolationSet.iterator();
// while(iterator.hasNext()){
// ConstraintViolation<Object> constraintViolation=iterator.next();
// //错误信息
// String errMsg=constraintViolation.getMessage();
// //错误属性
// String properyName=constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().toString();
// result.getErrorMsgMap().put(errMsg,properyName);
// }
constraintViolationSet.forEach(constraintViolation->{
//错误信息
String errMsg=constraintViolation.getMessage();
//错误属性
String properyName=constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().toString();
result.getErrorMsgMap().put(properyName,errMsg);
});
}
return result;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//将hibernate valitator通过工厂的初始化方式使其实例化。
this.validator=Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory().getValidator();
}
}
注解添加:
- message为错误信息。
public class UserModel {
private Integer id;
@NotBlank(message = "用户名为空") //NotBlank校验当前字符串属性不能为空字符串,也不能为null
private String name;
@NotNull(message = "性别为空") //校验普通对象空指针
private String gender;
@NotNull(message = "年龄为空")
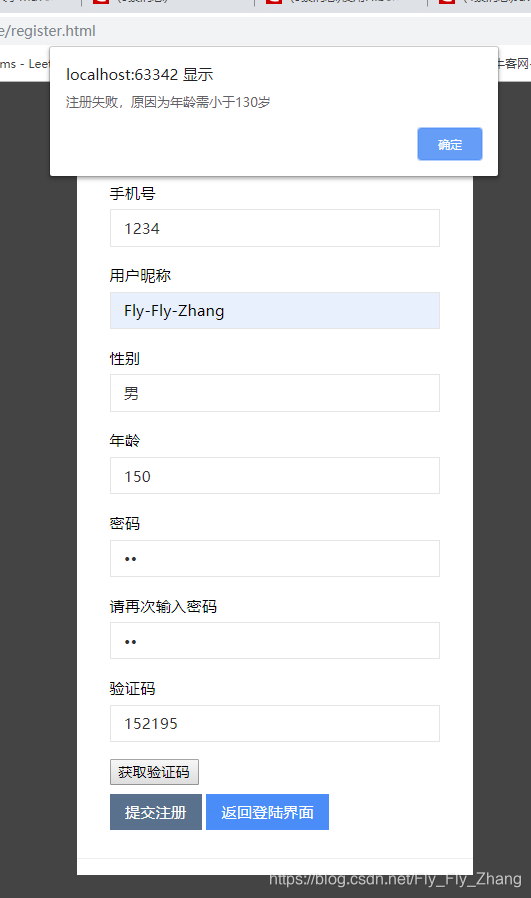
@Min(value = 0,message = "年龄需大于0岁") //可以用来校验和指定参数范围
@Max(value = 150,message = "年龄需小于130岁")
private Integer age;
@NotBlank(message = "手机号为空")
private String telphone;
private String registerMode;
private String thirdPartyId;
@NotBlank(message = "密码为空")
private String encrptPassword; //加密密码
}
校验:
//使用validator校验userModel
ValidationResult result=validator.validate(userModel);
//有异常,直接抛出
if(result.isHasError()){
throw new BusinessException(EnumBusinessError.PARAMETER_VALIDATION_ERROR,result.getErrorMsg());
}
结果演示: