观察者模式
发布&订阅
一对多
示例:点好咖啡之后坐等被叫
传统 UML 类图

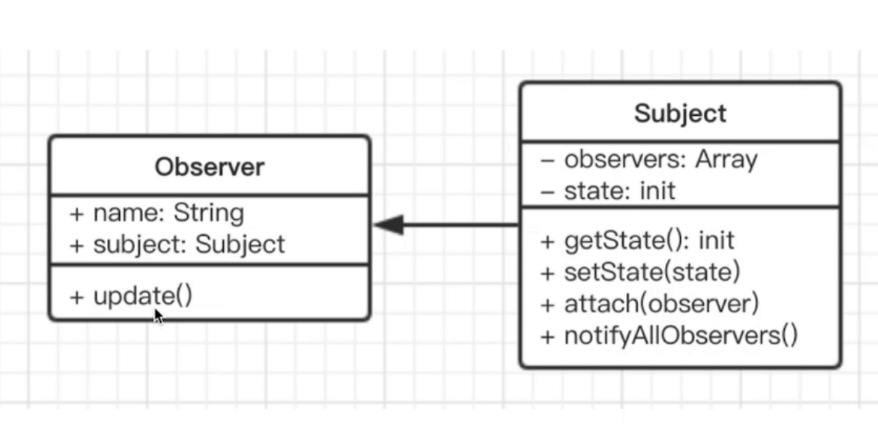
javascript 中的 UML 类图
应用场景
网页事件绑定
<button id="btn1"></button>
<script>
$("#btn1").click(function() {
console.log(1);
});
$("#btn1").click(function() {
console.log(2);
});
$("#btn1").click(function() {
console.log(3);
});
</script>promise
function loadImg(src) {
var promise = new Promise(function(reslove, reject) {
var img = document.creatElement("img");
img.onload = function() {
reslove(img);
};
img.src = src;
});
return promise;
}
var src = ".....";
var result = loadImg(src);
result
.then(function(img) {
console.log("img.width", img.width);
return img;
})
.then(function(img) {
console.log("img.height", img.height);
})
.catch(function(ex) {
console.log(ex);
});jQuery callback
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>jQuery callbacks</p>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js"></script>
<script>
var callbacks = $.Callbacks(); // 注意大小写
callbacks.add(function(info) {
console.log("fn1", info);
});
callbacks.add(function(info) {
console.log("fn2", info);
});
callbacks.add(function(info) {
console.log("fn3", info);
});
callbacks.fire("gogogo");
callbacks.fire("fire");
</script>
</body>
</html>nodejs 自定义事件
const EventEmitter = require("events").EventEmitter;
const emitter1 = new EventEmitter();
emitter1.on("some", () => {
// 监听 some 事件
console.log("some event is occured 1");
});
emitter1.on("some", () => {
// 监听 some 事件
console.log("some event is occured 2");
});
// 触发 some 事件
emitter1.emit("some");
//------------------------------------------------------------
const emitter = new EventEmitter();
emitter.on("sbowName", name => {
console.log("event occured ", name);
});
emitter.emit("sbowName", "zhangsan"); // emit 时候可以传递参数过去
//------------------------------------------------------------
// 任何构造函数都可以继承 EventEmitter 的方法 on emit
class Dog extends EventEmitter {
constructor(name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
}
var simon = new Dog("simon");
simon.on("bark", function() {
console.log(this.name, " barked");
});
setInterval(() => {
simon.emit("bark");
}, 500);nodejs 处理文件
var fs = require("fs");
var readStream = fs.createReadStream("./data/file1.txt"); // 读取文件的 Stream
var length = 0;
readStream.on("data", function(chunk) {
length += chunk.toString().length;
});
readStream.on("end", function() {
console.log(length);
});var readline = require("readline");
var fs = require("fs");
var rl = readline.createInterface({
input: fs.createReadStream("./data/file1.txt")
});
var lineNum = 0;
rl.on("line", function(line) {
lineNum++;
});
rl.on("close", function() {
console.log("lineNum", lineNum);
});其他应用场景
nodejs 中:处理 http 请求,多进程通讯
var http = require("http");
function serverCallback(req, res) {
var method = req.method.toLowerCase(); // 获取请求的方法
if (method === "get") {
}
if (method === "post") {
// 接收 post 请求的内容
var data = "";
req.on("data", function(chunk) {
// “一点一点”接收内容
console.log("chunk", chunk.toString());
data += chunk.toString();
});
req.on("end", function() {
// 接收完毕,将内容输出
console.log("end");
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-type": "text/html" });
res.write(data);
res.end();
});
}
}
http.createServer(serverCallback).listen(8081); // 注意端口别和其他 server 的冲突
console.log("监听 8081 端口……");// parent.js
var cp = require("child_process");
var n = cp.fork("./sub.js");
n.on("message", function() {
console.log("PARENT got message: " + m);
});
n.send({ hello: "word" });
//sub.js
process.on("message", function() {
console.log("CHILD got message: " + m);
});
process.send({ foo: "bar" });vue 和 react 组件生命周期出发
class Login extends React.Component {
constructor(props, context) {
super(props, context);
this.shouldComponentUpdate = PureRenderMixin.shouldComponentUpdate.bind(
this
);
this.state = {
checking: ture
};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Header title="开始" history={this.props.history} />
</div>
);
}
componentDidMount() {
// 判断是否已经登陆
this.doCheck();
}
}
vue watch
var vm = new vue({
el: "#demo",
data: {
firstNameL: "Foo",
lastName: "bar",
fullName: "Foo Bar"
},
watch: {
firstName: function(val) {
this.fullName = val + " " + this.firstName;
},
lastName: function(val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + " " + val;
}
}
});设计原则验证
- 主题和观察者分离,不是主动触发而是被动监听,两者解耦
- 符合开放和封闭原则