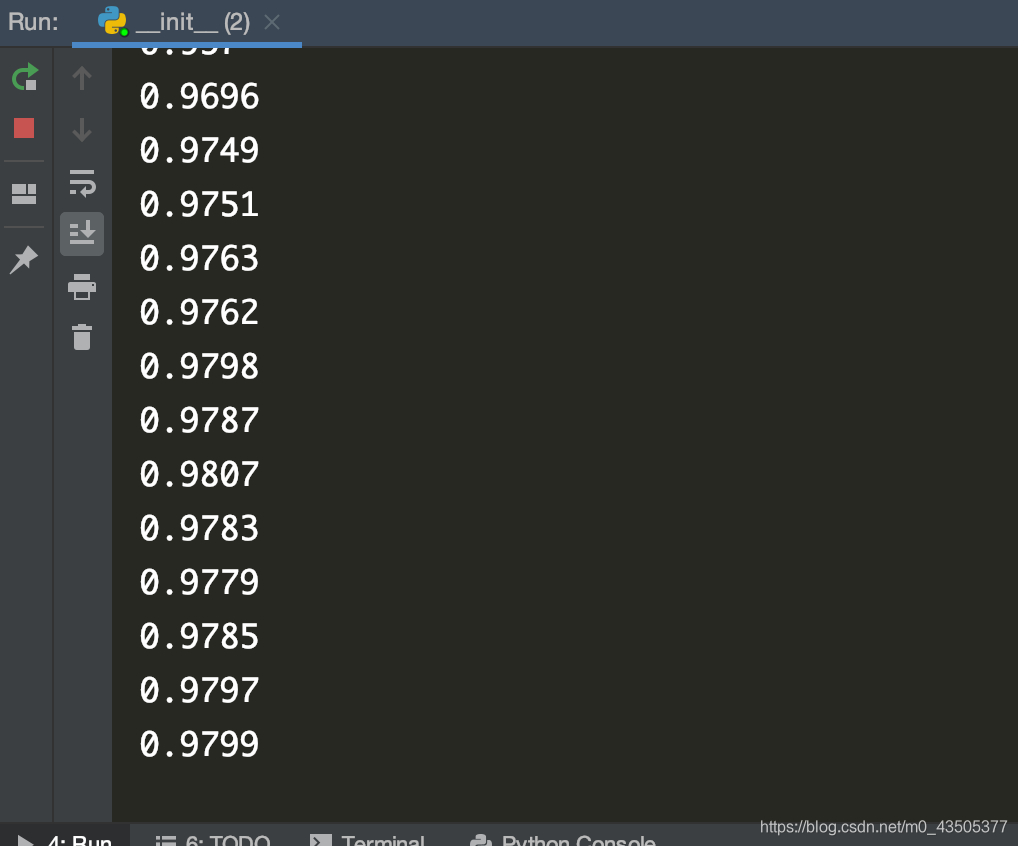
点击图片进行查看
一、什么是滑动平均?
- 滑动平均法(moving average)又称移动平均法。在简单平均数法基础上,通过顺序逐期增减新旧数据求算移动平均值,借以消除偶然变动因素,找出事物发展趋势,并据此进行预测的方法。
- 简单来说就是 参数变化 时 滑动平均(影子值),跟随参数的变化 进行缓慢追随。
- 滑动平均(exponential moving average),或者叫做指数加权平均,可以用来估计变量的局部均值,使得变量的更新与一段时间内的历史取值有关。
二、滑动平均的作用:
- 滑动平均可以使模型在测试数据上更健壮(robust)。采用随机梯度下降算法训练神经网络时,使用滑动平均在很多应用中都可以在一定程度上提高最终模型在测试数据上的表现。
- 记录了一段时间内模型中所有参数 w 和 b 各自的平均值。利用滑动平均值可以增强模型的泛化能力。
- 滑动平均可以看作是变量的过去一段时间取值的均值,相比对变量直接赋值而言,滑动平均得到的值在图像上更加平缓光滑,抖动性更小,不会因为某次的异常取值而使得滑动平均值波动很大。
三、滑动平均在神经网络的具体应用:
-
计算公式:
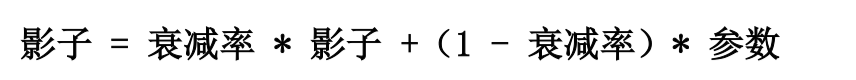
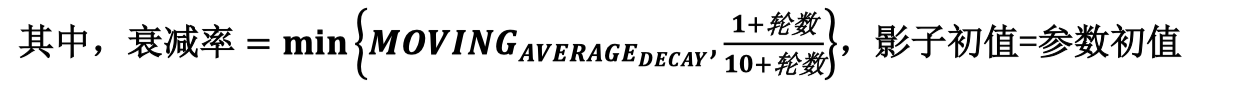
- MOVING AVERAGE DECAY 决定了影子变量的更新速度,DECAY越大影子变量越趋于稳定。在实际运用中,decay一般会设成非常接近 1 的数(比如0.999或0.9999)。
-
TensorFlow下的使用:
- ema=tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY,global_step)
其中,MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY 表示滑动平均衰减率,一般会赋接近 1 的值,global_step 表示当前 训练了多少轮。 - ema_op = ema.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
其中,ema.apply()函数实现对括号内参数求滑动平均,tf.trainable_variables()函数实现把所有待训练参数(学习参数)汇总为列表。
- ema=tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY,global_step)
with tf.control_dependencies([train_step, ema_op]):
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train')
其中,该函数实现将滑动平均和训练过程同步运行。
查看模型中参数的平均值,可以用 ema.average()函数。

四、实例展示:
我们用熟悉的手写字识别来演示:
import tensorflow as tf
import pretty_errors
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data as data
import numpy as np
# 解析数据集
mnist = data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
def layer(w, x, b=0, n=1): # 定义运算函数
if n == 1:
y = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, w) + b)
else:
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, w))
return y
# 设置神经网络基本参数
train_steps = 20000 # 训练轮数
learning_rate = 0.1 # 初始学习率
decay_rate = 0.9 # 学习率衰减指数
decay_steps = 500 # 衰减频率控制
scale = 0.1 # 正则率
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.99 #滑动平均衰减率
# decay_steps控制衰减速度
# 如果decay_steps大一些,(global_step / decay_steps)就会增长缓慢一些
# 从而指数衰减学习率decayed_learning_rate就会衰减得慢一些
# 否则学习率很快就会衰减为趋近于0
# 定义输入节点
X = tf.placeholder(shape=(None, 784), dtype=tf.float32, name="X")
Y_ = tf.placeholder(shape=(None, 10), dtype=tf.float32, name="Y_")
# 定义神经网络中的学习参数
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([784, 100], stddev=0.1)) # 正态分布随机数
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([100, 50], stddev=0.1))
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([50, 10], stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([100]))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([50]))
# 定义运算
y1 = layer(w1, X, b1)
y2 = layer(w2, y1, b2)
y3 = layer(w3, y2, n=False)
# 使用正则化
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.WEIGHTS, w1)
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.WEIGHTS, w2)
tf.add_to_collection(tf.GraphKeys.WEIGHTS, w3)
regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(scale)
regTerm = tf.contrib.layers.apply_regularization(regularizer)
# 定义损失函数
loss = -tf.reduce_sum(Y_ * tf.math.log(y3)) + regTerm
# loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=tf.argmax(y4,1,output_type=tf.float32),
# labels=tf.argmax(Y_,1,output_type=tf.float32))
# 设置指数衰减学习率
learning_ratea = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate,
train_steps,
decay_steps,
decay_rate)
# 设置优化器 梯度下降
trainOtimaize = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_ratea).minimize(loss)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False) #建立训练计数器
ema=tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY,global_step) #设置滑动平均
ema_op = ema.apply(tf.trainable_variables()) #所有变量都进行滑动平均
with tf.control_dependencies([trainOtimaize, ema_op]): #进行绑定操作
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train') #设置绑定对象,以及名称
# 初始化所有变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) # 进行初始化
for i in range(train_steps):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) # 每次取出100张图片数据
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: batch_xs, Y_: batch_ys}) # 进行训练,完成前向和方向传播,并修改学习参数
# print("loss:",sess.run(loss,feed_dict={X:batch_xs,Y_:batch_ys}))
if i % 1000 == 0:
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y3, 1), tf.argmax(Y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y_: mnist.test.labels}))