Flask介绍
Flask作为轻便小巧的web开发框架,极大的简化了web service服务的开发周期,个人感觉比较适用于小巧的web service服务接口的开发,当然django也是不错的选择。接下来介绍下web service开发中不同请求方式,python urllib库的处理。
需要使用到的基本类
import urllib.request, urllib.parse, urllib.response
- urllib.request: 客户请求类
request.args.get: 针对显式的get方式,获取请求参数
request.form.get: 针对POST和隐私的get方式,获取请求参数
request.values.get: 适用于任何形式的请求方式
request.get_data():获取通过request body传的byte类型的字符串
- urllib.response: 请求返回的响应类
response.read().decode('utf-8'):获取请求返回的内容
- urllib.parse: 请求参数转化类
data = { 'ip':'35.1.32.84', 'hostname':'非车核保 +', 'cpu':90, 'mem':90, 'curtime':'2018-05-04 17:40:00'}
'''
urlencode对query的dict参数进行拼接,转化为:key=value&key=value&key=value 的格式,返回string字符串
注意:改函数默认编码为 encoding='utf-8'
会将空格' '替换为'+'
'''
post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8') # 提交类型不能为str,需要为byte类型
【显式Get请求方式】
将请求参数直接跟在服务地址后,如:
http://34.1.32.136:8001/monitor/host/param?ip=34.1.32.136&hostname=%E9%9D%9E%E8%BD%A6%E6%A0%B8%E4%BF%9D
客户端
data = { 'ip':'35.1.32.84', 'hostname':'非车核保 +', 'cpu':90, 'mem':90, 'curtime':'2018-05-04 17:40:00'}
'''
urlencode对query的dict参数进行拼接,转化为:key=value&key=value&key=value 的格式,返回string字符串
注意:改函数默认编码为 encoding='utf-8'
会将空格' '替换为'+'
'''
post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8') # 提交类型不能为str,需要为byte类型
geturl = url+"?"+urllib.parse.urlencode(data)
print(geturl)
request = urllib.request.Request(geturl, method='GET')
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
#返回hostname 非车核保
if (content):
print(content)
服务器端
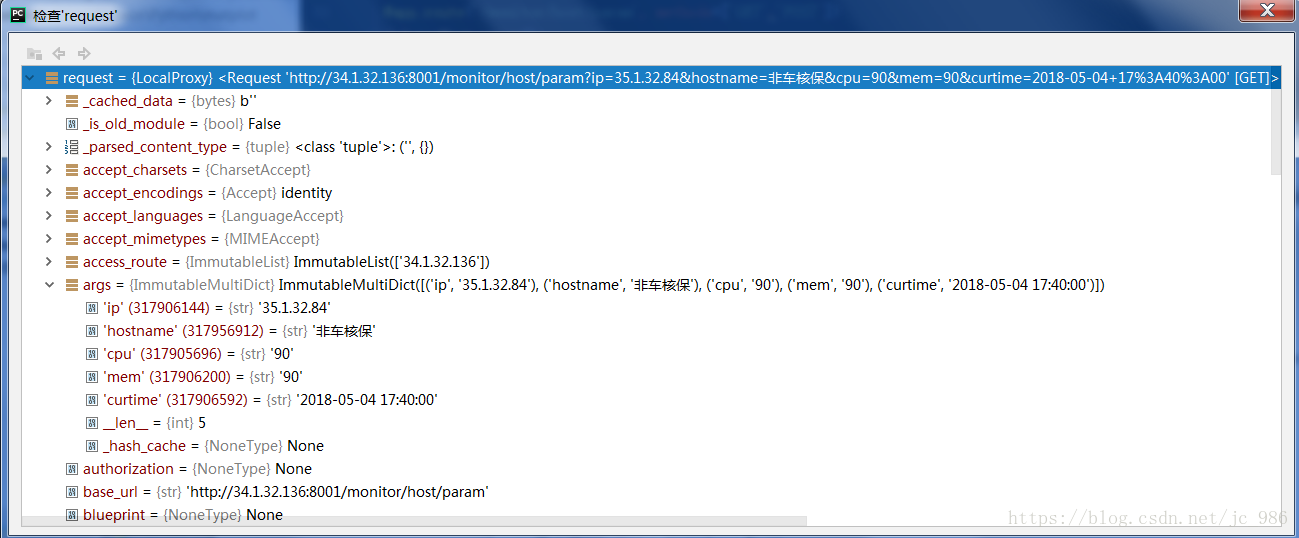
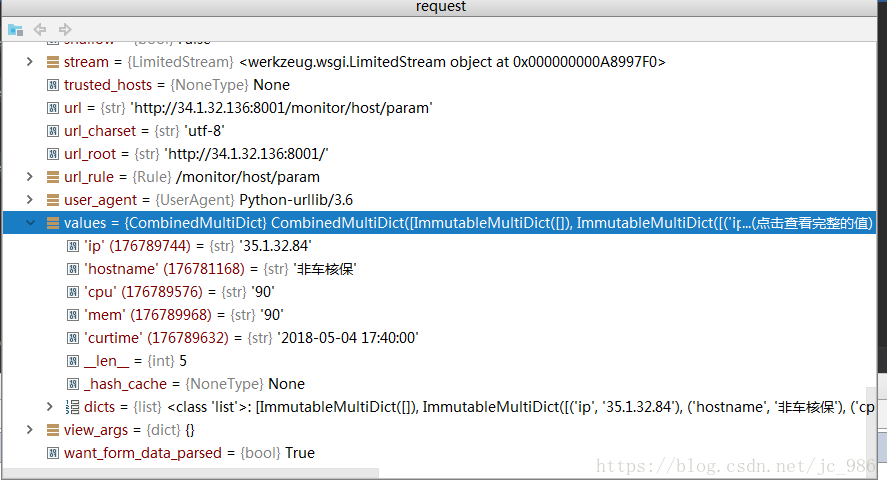
args = request.args.get("hostname", type=str) print(args)
可以在args中获取到请求参数
values中也可以获取到参数
args = request.values.get("hostname", type=str) print(args)
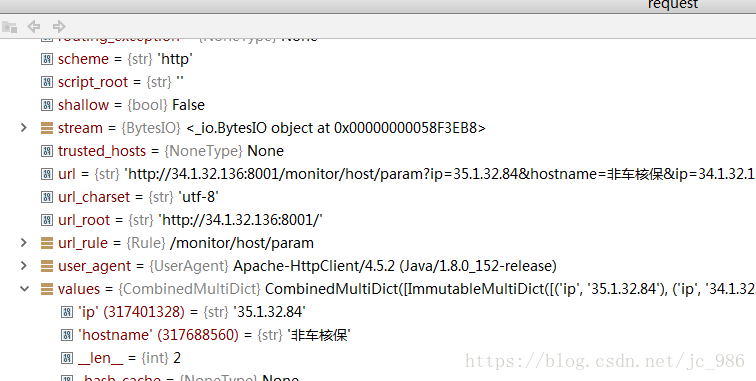
【隐藏式Get请求方式】
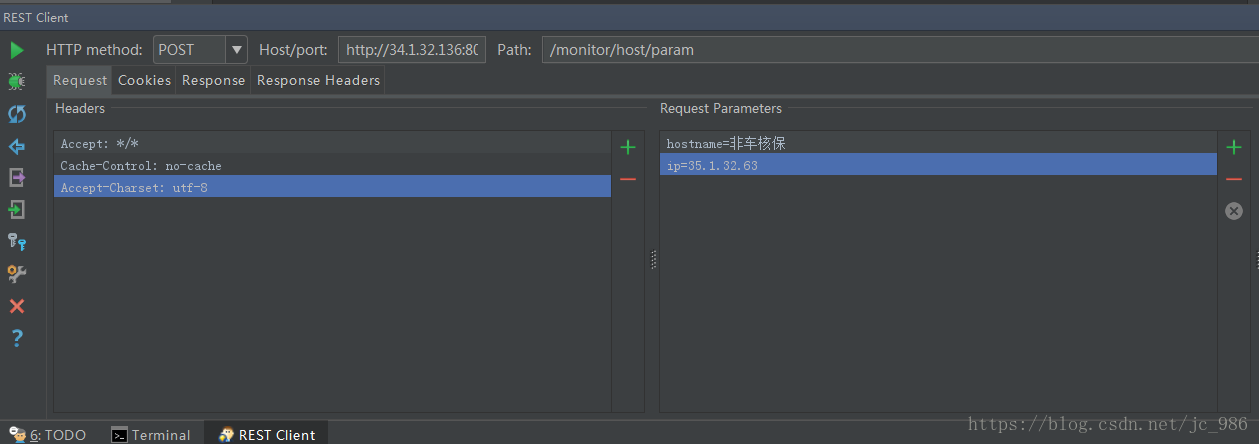
即请求的参数不是显式的以“?”开始跟在请求地址后面,而是隐藏式的通过request parameter方式进行传递。
客户端
data = { 'ip':'35.1.32.84', 'hostname':'非车核保', 'cpu':90, 'mem':90, 'curtime':'2018-05-04 17:40:00'}
#针对dict类型数据进行拼接 b'ip=35.1.32.84&hostname=%E9%9D%9E%E8%BD%A6%E6%A0%B8%E4%BF%9D&cpu=90&mem=90&curtime=2018-05-04+17%3A40%3A00'
post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8') # 提交类型不能为str,需要为byte类型
request = urllib.request.Request(url, post_data, method='GET')
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
#返回hostname 非车核保
if (content):
print(content)
服务器端
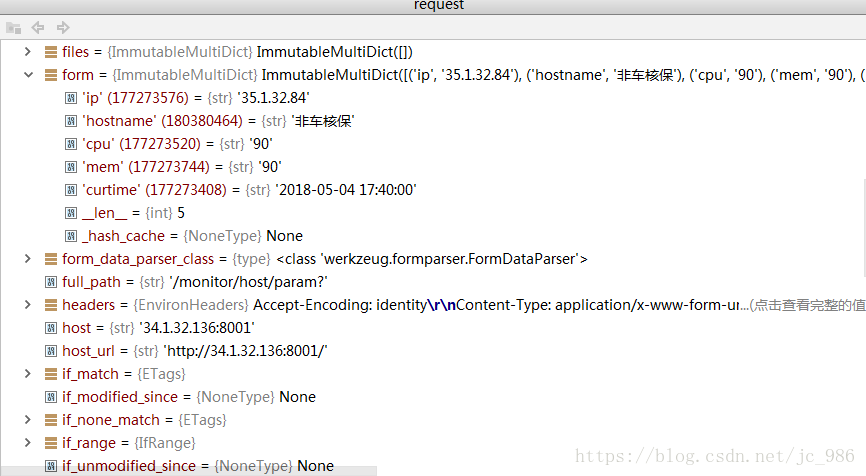
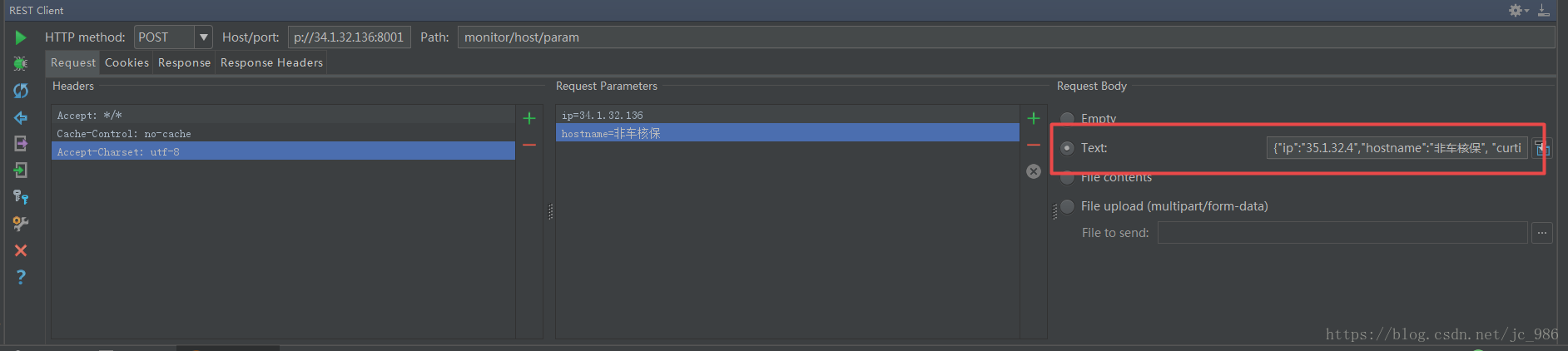
【Post请求方式】
客户端请求 -- 通过 request paramter 传值
data = { 'ip':'35.1.32.84', 'hostname':'非车核保', 'cpu':90, 'mem':90, 'curtime':'2018-05-04 17:40:00'}
#针对dict类型数据进行拼接 b'ip=35.1.32.84&hostname=%E9%9D%9E%E8%BD%A6%E6%A0%B8%E4%BF%9D&cpu=90&mem=90&curtime=2018-05-04+17%3A40%3A00'
post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode(data).encode('utf-8') # 提交类型不能为str,需要为byte类型
request = urllib.request.Request(url, post_data, method='POST')
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
#返回hostname 非车核保
if (content):
print(content)
服务器端响应 -- urllib.request
当客户端通过post请求方式,将请求参数传递在request parameter中时,如以下方式:
ip=35.1.32.84&hostname=非车承保
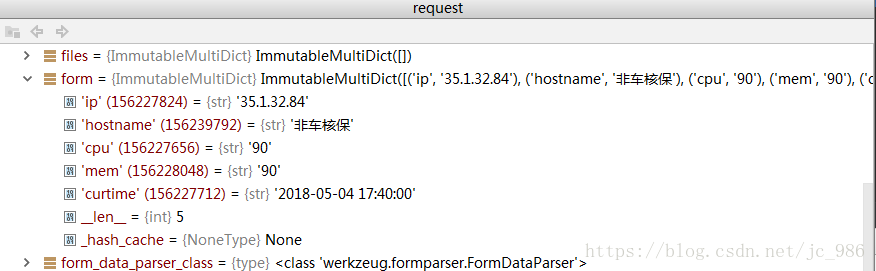
在服务器端的request.form中可以获取到相应的dict格式的参数
args = request.args.get("hostname", type=str)
同样的,在values中也可以获取到请求的参数
args = request.values.get("hostname", type=str)
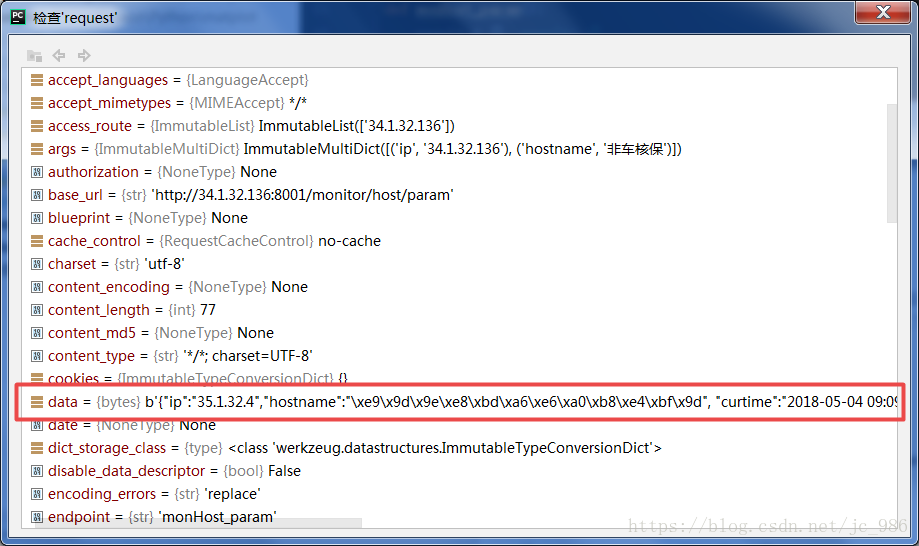
客户端--通过request body传值
path = '/monitor/host/json' url = host + path # request = urllib.request.Request(url, b'{"ip":"35.1.32.4","hostname":"非车核保"}') post_data = bytes('{"ip":"35.1.32.4","hostname":"非车核保","mem":90, "curtime":"2018-05-04 09:09:09"}', encoding='utf-8') request = urllib.request.Request(url, post_data, method='post') response = urllib.request.urlopen(request) content = response.read().decode('utf-8') if (content): print(content)
客户端直接传的byte字符串
服务器端
data = request.get_data(as_text=True) obj = json.loads(data) print(obj['ip'])