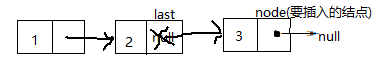
关于表的概念:
1.线性表: (linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表/链表/栈/队列/字符串···
2.顺序表: 顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下,采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储
动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储
3.链表: 链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续,非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链表依次实现的。
4.顺序表和链表的优缺点: ①顺序表:优点:空间连续,支持随机访问
缺点:中间或前面部分的插入删除时间复杂度O(N);增容的代价比较大
②链表:优点:在任意位置插入删除时间复杂度为O(1);没有增容问题,插入一个开辟一个空间
缺点:以结点为单位存储,不支持随机访问
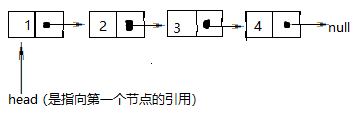
学习链表前先了解一下这张图↓

链表: 逻辑上有前后关系,物理上不保证前后关系
链表的头插: 前提:链表中一定有至少一个结点
①若要插入的数据没有结点,先给它装入一个结点
Node node=new Node();
node.value=0;//value是结点名,0是要插入的数据
②让原来的第一个结点,成为新结点的下一个结点
node.next=head;//head是原来的第一个结点
③更新最新的第一个结点为新结点
head=node;
链表的尾插: 要考虑是否是空链表
1>空链表的情况:让新结点成为第一个结点
2>非空链表的情况:
①若没在结点中,装到结点后,让新结点的next=null
Node node=new Node(val);//构造方法中已经让.next=null了
②找到倒数第一个结点,找到.next==null的结点
Node last=head; //从头开始找
while(last.next!=null){last=last.next;}//一直找到最后一个结点,然后进行尾插
③让原来的倒数第一个结点的下一个为新结点
last.next=node;
//完整的链表尾插代码
private static Node PushBack(Node head,int value){
Node node=new Node(val);
if(head==null){
return node;
}else{
Node last=head;
while(last.next!=null){
last=last.next;
}
last.next=node;
return head;
}
}
链表的头删:
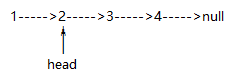
head=head.next ;//让第一个结点的下一个结点成为头结点
链表的尾删: 看是否有>=1个结点
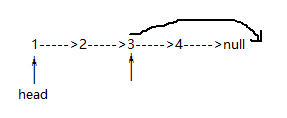
1>只有一个结点:head=null;
2>大于一个结点:
①找到倒数第二个结点:
lastSecond.next.next==null; //相当于找到了倒数第二个结点
②让倒数第二个结点的next=null
③原来最后一个结点因为没有引用指向而被回收
遍历打印链表:
Node cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.println(cur.val);
cur=cur.next;
}
**反转链表的大体思想:**不断从原来链表中取出结点,头插到一个新链表上
class Node {
int val; // data | element 要插入的数据
Node next; // 如果 next == null 表示是最后一个结点
public Node(int val) { //构造方法
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
public String toString() { //普通方法
return String.format("Node(%d)", val);
}
}
public class myLinkedList{
private static void print(Node head) {
System.out.println("打印链表:");
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
System.out.print(cur + " --> ");
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// 头插
// head: 原来的第一个结点
// val:要插入的值
// 返回:新的第一个结点
private static Node pushFront(Node head, int val) {
// 1. 结点
Node node = new Node(val);
// 2. 让原来的 head 成为 node 的下一个结点
node.next = head;
// 3. 更新第一个结点的引用
return node;
}
//尾插
private static Node pushBack(Node head, int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if (head == null) {
return node;
} else {
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null) {
last = last.next;
}
last.next = node;
return head;
}
}
//头删
private static Node popFront(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
System.err.println("空链表无法删除");
return null;
}
// 原来第一个结点,会因为没有引用指向而被回收
return head.next;
}
//尾删
private static Node popBack(Node head) {
if (head == null) { //空链表
System.err.println("空链表无法删除");
return null;
}
if (head.next == null) { //只有一个结点
return null;
} else { //有一个以上个结点
Node lastSecond = head;
while (lastSecond.next.next != null) {
lastSecond = lastSecond.next;
}
lastSecond.next = null;
return head;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node head = null;
// head 的意思是链表的第一个结点
// 通过第一个结点,就可以找到完整的链表的所有结点
// 所以,链表的第一个结点往往代表整个链表
// 空的链表,就是一个结点都没有的链表
// 也就没有第一个结点
// head == null 表示第一个结点不存在
// 也就是整个链表为空
// 头插
/*
int val = 0;
// 1. 结点
Node node = new Node(val);
// 2. 让原来的 head 成为 node 的下一个结点
node.next = head;
// 3. 更新第一个结点的引用
head = node;
pushFront(head, 0);
*/
head = pushFront(head, 0);
head = pushFront(head, 1);
head = pushFront(head, 2);
// 打印
print(head); // 2 1 0
// 头删
head = popFront(head);
print(head); // 1 0
//尾插
head = pushBack(head, 10);
head = pushBack(head, 20);
head = pushBack(head, 30);
print(head); // 1 0 10 20 30
//尾删
head = popBack(head);
head = popBack(head);
head = popBack(head);
head = popBack(head);
head = popBack(head);
head = popBack(head); // 报错
print(head); // 空
head = pushBack(head, 100); //尾插
print(head); // 100
}
}