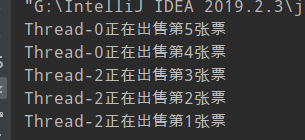
1.线程安全问题代码实现
- 概述:多线程访问了共享的数据,会产生线程安全问题
- 代码实现:
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
int tacket =5;
@Override
public void run() {
while (tacket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tacket + "张票");
tacket--;
}
}
};
Thread one = new Thread(run);
Thread two = new Thread(run);
Thread three = new Thread(run);
one.start();
two.start();
three.start();
}
}
三个窗口共同卖5张票(共享数据),出现了三个窗口一起卖同一张票,或者卖不存在的票的情况
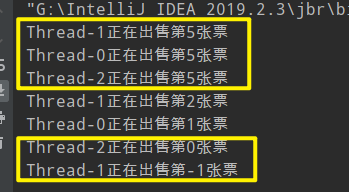
2.线程安全问题产生原理

-
产生不存在的票的原因:
-
one抢占cpu执行权,执行
run()方法,进入while循环,碰到sleep()方法,进入睡眠,失去CPU执行权 -
two抢占cpu执行权,执行
run()方法,进入while循环,碰到sleep()方法,进入睡眠,失去CPU执行权 -
three抢占cpu执行权,执行
run()方法,进入while循环,碰到sleep()方法,进入睡眠,失去CPU执行权,此时3个线程全部睡眠. -
one经过1000ms睡醒后执行卖票,打印Thread-0正在出售第1张票,变量
tacket-1=0 -
two经过1000ms睡醒后执行卖票,此时变量
tacket-1=0,所以打印Thread-1正在出售第0张票,变量tacket-1=-1 -
three经过1000ms睡醒后执行卖票,此时变量
tacket-1=-1,所以打印Thread-2正在出售第-1张票 -
卖出重复的票原因:
3个线程同时执行到卖票(输出语句),这时候的ticket--还没有执行到.
3.线程安全问题解决(一)之同步代码块
- 格式
synchronized(同步锁对象){
可能会出现线程安全问题的代码;
}
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
int tacket = 5;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (obj) {
if (tacket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tacket + "张票");
tacket--;
}
}
}
}
};
Thread one = new Thread(run);
Thread two = new Thread(run);
Thread three = new Thread(run);
one.start();
two.start();
three.start();
}
}
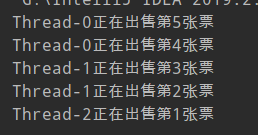
- 原理:
- one抢占cpu执行权,执行
run()方法,进入while循环,遇到synchronized,此时one会检查synchronized是否有锁对象,发现有,会获取锁对象,继续向下执行 - two抢占cpu执行权,执行
run()方法,进入while循环,遇到synchronized,此时one会检查synchronized是否有锁对象,发现没有,锁对象已经被one获取,进入阻塞状态,直到one执行完毕,归还锁对象 - 缺点:
程序不断获取锁对象,判断锁对象,归还锁对象,会使得程序执行效率低
4.线程安全问题解决(二)之同步方法
- 格式:
public synchronized void 方法名(){
可能产生线程安全问题的代码;
}
public static synchronized void 方法名(){
可能产生线程安全问题的代码;
}
接口实现类中写同步方法:
public class ImplRunnable implements Runnable {
int tacket = 5;
public synchronized void paytakcet() {
if (tacket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tacket + "张票");
tacket--;
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
paytakcet();
}
}
}
main()主程序中创建对象使用:
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
Runnable run = new ImplRunnable();
Thread one = new Thread(run);
Thread two = new Thread(run);
Thread three = new Thread(run);
one.start();
two.start();
three.start();
}
}
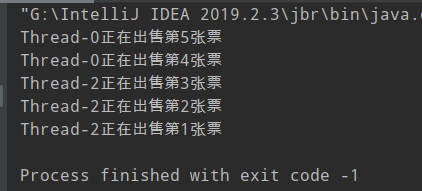
法二:
public class ImplRunnable implements Runnable {
static int tacket = 5;
public static synchronized void paytacketstatic(){
if (tacket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tacket + "张票");
tacket--;
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
paytacketstatic();
}
}
}
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
Runnable run = new ImplRunnable();
Thread one = new Thread(run);
Thread two = new Thread(run);
Thread three = new Thread(run);
one.start();
two.start();
three.start();
}
}

5.线程安全问题解决(三)之Lock锁
- 步骤
- 在成员位置创建一个
Lock 对象名 = new ReentrantLock(); - 在可能出现安全问题的位置前使用
lock()方法获取锁 - 在可能出现安全问题的位置后使用
unlock()方法释放锁
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ImplRunnable implements Runnable {
int tacket = 5;
Lock l = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
l.lock();
if (tacket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tacket + "张票");
tacket--;
}
l.unlock();
}
}
}
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
Runnable run = new ImplRunnable();
Thread one = new Thread(run);
Thread two = new Thread(run);
Thread three = new Thread(run);
one.start();
two.start();
three.start();
}
}