B、happy card
列出所有条件:人数 n,总的快乐牌 num,限制手牌 m
我们可以 DP 的是:前 i 个人在总牌数为 j 的情况下,第 i个人拿 k 张牌的最大幸福值。想想似乎和01背包有点儿类似,那么状态转移方程也就不难写出来了:
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i−1][j−k]+h[k],dp[i-1][j])
当然我们的第一维其实可以直接滚动掉的。。
其实算法还可以再进行时间的优化,将其化为
n^2 算法。
实际上人数是一个无用条件,我们知道总的快乐牌数,那么人数一定会大于等于这个数。这种情况的所有必要条件就是:总的快乐牌
num,限制牌堆 m ,那么可以化成以下情景:知道总的牌数 num,
问在限制每堆最大牌数为 m 时,堆成几堆牌能够使得快乐值最大。其方程式为:
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j−i]+h[i]);
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j−i]+h[i]);

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <time.h> 13 14 #define LL long long 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define ls nod<<1 17 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 18 19 const int maxn = 1e6 + 10; 20 const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; 21 22 LL cnt; 23 int n,k,s; 24 LL dp[1010]; 25 26 27 28 int main() { 29 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&s); 30 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 31 int val; 32 scanf("%d",&val); 33 if (val == s) 34 cnt++; 35 } 36 for (int i = 1;i <= k;i++) { 37 int val; 38 scanf("%d", &val); 39 for (int j = 0;j <= cnt;j++) { 40 if (j >= i) 41 dp[j] = std::max(dp[j],dp[j-i]+val); 42 } 43 } 44 printf("%lld\n",dp[cnt]); 45 return 0; 46 }
D、巫妖王的远征
典型的 BFS 的题目,主要问题是如何处理 传送门 和 休息时间 的问题 。
传送门: 就是如果到了可以传送的地方我们就把它传送后的地点直接入队就好了
休息时间: 最后找到了直接统一处理就好了

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <time.h> 13 14 #define LL long long 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define ls nod<<1 17 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 18 19 const int maxn = 3e5 + 10; 20 const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; 21 22 char map[1010][1010]; 23 int vis[1010][1010]; 24 int trans[1010][1010]; 25 int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1}; 26 int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0}; 27 int sx,sy,ex,ey; 28 29 struct Node { 30 int x,y,step; 31 }a,b; 32 33 std::queue<Node> q; 34 int main() { 35 int n,m; 36 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 37 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) 38 scanf("%s",map[i]+1); 39 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 40 for (int j = 1;j <= m;j++) { 41 if (map[i][j] == 'S') { 42 a.x = i; 43 a.y = j; 44 a.step = 0; 45 q.push(a); 46 } 47 if (map[i][j] == 'T') { 48 ex = i; 49 ey = j; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 int k; 54 scanf("%d",&k); 55 for (int i = 1;i <= k;i++) { 56 scanf("%d%d%d%d",&trans[i][0],&trans[i][1],&trans[i][2],&trans[i][3]); 57 if (trans[i][0] <= 0 || trans[i][0] > n || trans[i][1] <= 0 || trans[i][1] > m || trans[i][2] <= 0 || trans[i][2] > n || trans[i][3] <= 0 || trans[i][3] > m) 58 { 59 trans[i][0] = -1; 60 trans[i][2] = -1; 61 } 62 else if (map[trans[i][0]][trans[i][1]] == '#' || map[trans[i][2]][trans[i][3]] == '#') 63 { 64 trans[i][0] = -1; 65 trans[i][2] = -1; 66 } 67 } 68 for (int i = 1;i <= k;i++) { 69 if ((a.x == trans[i][0] && a.y == trans[i][1]) && (ex == trans[i][2] && ey == trans[i][3])) 70 { 71 printf("0\n"); 72 return 0; 73 } 74 else if ((a.x == trans[i][2] && a.y == trans[i][3]) && (ex == trans[i][0] && ey == trans[i][1])) 75 { 76 printf("0\n"); 77 return 0; 78 } 79 } 80 bool flag = false; 81 int ans = 0; 82 while (!q.empty()) { 83 a = q.front(); 84 q.pop(); 85 if (a.x == ex && a.y == ey) { 86 flag = true; 87 ans = a.step + a.step / 8; 88 if (a.step % 8 == 0) 89 ans--; 90 printf("%d\n",ans); 91 break; 92 } 93 for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) { 94 int x = a.x + dx[i]; 95 int y = a.y + dy[i]; 96 if (x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x > n || y > m || vis[x][y] || map[x][y] == '#') 97 continue; 98 for (int j = 1;j <= k;j++) { 99 if (x == trans[j][0] && y == trans[j][1]) 100 { 101 b.x = trans[j][2]; 102 b.y = trans[j][3]; 103 b.step = a.step + 1; 104 q.push(b); 105 vis[b.x][b.y] = 1; 106 } 107 else if (x == trans[j][2] && y == trans[j][3]) 108 { 109 b.x = trans[j][0]; 110 b.y = trans[j][1]; 111 b.step = a.step + 1; 112 q.push(b); 113 vis[b.x][b.y] = 1; 114 } 115 } 116 vis[x][y] = 1; 117 b.x = x; 118 b.y = y; 119 b.step = a.step + 1; 120 q.push(b); 121 } 122 } 123 if (!flag) 124 printf("-1\n"); 125 return 0; 126 }
I、洛克王国之域外大逃杀
http://acm.csust.edu.cn/problem/3021
我们可以先只考虑暴力,也就是先20遍bfs遍历所有的魔物,然后在地图上记录一下每个魔物抵达的时间和该时间点的最大攻击。
接下来由于最多只有两个宠物,我们跑4次bfs就好了,洛克到1号宠物再到2号,洛克到2号再到1号。于是这题就愉快的暴力掉了4000ms+。然后就是考虑优化了。
其实也不需要优化太多,我们可以将所有魔物全部放进队列中一起跑,然后稍微剪个枝就可以过了。我们知道如果一个魔物后抵达A,而它的攻击又弱于或者等于前一个抵达的魔物,那么我们就可以将这个状态给舍弃掉了。1500ms
总结下这道题目:
主要的难点我觉得还是在处理魔物的移动,某个位置可以让两个不同的魔物跑,怎么去避免去重的时候出错。
然后就是第二个 bfs 的时候,处理洛克的时候,官方给的 code 处理的也很巧妙
然后能用 bool 类型就用 bool ,不要乱开 int 会爆内存

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <time.h> 13 14 #define LL long long 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define ls nod<<1 17 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 18 19 const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; 20 const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; 21 22 int n,m,stak; 23 int cnte,cnta; 24 char mp[1010][1010]; 25 int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1}; 26 int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0}; 27 bool vis[1010][1010][25]; 28 bool visa[1010][1010]; 29 30 struct node1 { 31 int x,y,atk,p; 32 }evil[25],ang[20]; 33 34 struct node2 { 35 int x,y,atk,p,t; 36 }; 37 38 struct node3 { 39 int t,atk; 40 }ev[1010][1010][25]; 41 42 bool ok(int x,int y) { 43 if (x>=1 && x<=n && y>=1 && y<=m) 44 return true; 45 return false; 46 } 47 48 void bfs() { 49 std::queue<node2> q; 50 int t = 0; 51 for (int i = 1;i <= cnte;i++) { 52 node2 now; 53 now.x = evil[i].x; 54 now.y = evil[i].y; 55 now.p = evil[i].p; 56 now.atk = evil[i].atk; 57 now.t = t; 58 q.push(now); 59 ev[now.x][now.y][i].t = 0; 60 ev[now.x][now.y][i].atk = now.atk; 61 } 62 while (!q.empty()) { 63 node2 now = q.front(); 64 q.pop(); 65 int x = now.x,y = now.y,p = now.p; 66 if (vis[x][y][p]) 67 continue; 68 vis[x][y][p] = 1; 69 for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) { 70 int xx = x + dx[i]; 71 int yy = y + dy[i]; 72 t = now.t + 2; 73 if (!ok(xx,yy)) 74 continue; 75 if (vis[xx][yy][p]) 76 continue; 77 int j; 78 for (j = 1;j <= cnte;j++) { 79 if (ev[xx][yy][j].atk >= now.atk && ev[xx][yy][j].t <= t) 80 break; 81 } 82 if (j <= cnte) 83 continue; 84 node2 now2 = now; 85 now2.t = t; 86 now2.x = xx; 87 now2.y = yy; 88 ev[xx][yy][p].atk = now.atk; 89 ev[xx][yy][p].t = t; 90 q.push(now2); 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 95 node3 bfs2(int sx,int sy,int ex,int ey,int id,int stk,int base) { 96 if (sx == ex && sy == ey) 97 return {0,stk}; 98 std::queue<node2> q; 99 node2 now; 100 now.x = sx; 101 now.y = sy; 102 now.atk = stk; 103 now.t = base; 104 q.push(now); 105 memset(visa,0, sizeof(visa)); 106 while (!q.empty()) { 107 now = q.front(); 108 q.pop(); 109 int x = now.x,y = now.y; 110 if (visa[x][y]) 111 continue; 112 visa[x][y] = 1; 113 for (int i = 0;i < 4;i++) { 114 int xx = x + dx[i]; 115 int yy = y + dy[i]; 116 if (visa[xx][yy]) 117 continue; 118 if (!ok(xx,yy)) 119 continue; 120 int j; 121 for (j = 1;j <= cnte;j++) { 122 if (ev[xx][yy][j].t <= now.t+1 && now.atk <= ev[xx][yy][j].atk) 123 break; 124 } 125 if (j <= cnte) 126 continue; 127 if (xx == ex && yy == ey) 128 return {now.t+1,now.atk+ang[id].atk}; 129 node2 now2 = now; 130 now2.x = xx; 131 now2.y = yy; 132 now2.t += 1; 133 q.push(now2); 134 } 135 } 136 return {INF,0}; 137 } 138 139 140 int main() { 141 std::cin >> n >> m >> stak; 142 int sx,sy; 143 cnte = 1,cnta = 1; 144 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 145 for (int j = 1;j <= m;j++) { 146 std::cin >> mp[i][j]; 147 if (mp[i][j] == '*') { 148 evil[cnte].x = i; 149 evil[cnte].y = j; 150 evil[cnte].p = cnte; 151 evil[cnte++].atk = 0; 152 } 153 if (mp[i][j] == '#') { 154 ang[cnta].x = i; 155 ang[cnta].y = j; 156 ang[cnta].p = cnta; 157 ang[cnta++].atk = 0; 158 } 159 if (mp[i][j] == 'L') { 160 sx = i; 161 sy = j; 162 } 163 } 164 } 165 cnte--; 166 cnta--; 167 for (int i = 1;i <= cnte;i++) { 168 int val; 169 std::cin >> val; 170 evil[i].atk = val; 171 } 172 for (int i = 1;i <= cnta;i++) { 173 int val; 174 std::cin >> val; 175 ang[i].atk = val; 176 } 177 if (!cnta) { 178 printf("0\n"); 179 return 0; 180 } 181 bfs(); 182 node3 s1,s2,s3,s4; 183 s1.atk = s2.atk = s3.atk = s4.atk = 0; 184 s1.t = s2.t = s3.t = s4.t = INF; 185 if (cnta) { 186 if (cnta >= 1) 187 s1 = bfs2(sx,sy,ang[1].x,ang[1].y,1,stak,0); 188 if (cnta > 1) { 189 s2 = bfs2(ang[1].x,ang[1].y,ang[2].x,ang[2].y,2,s1.atk,s1.t); 190 s3 = bfs2(sx,sy,ang[2].x,ang[2].y,2,stak,0); 191 s4 = bfs2(ang[2].x,ang[2].y,ang[1].x,ang[1].y,1,s3.atk,s3.t); 192 } 193 } 194 int ans = INF; 195 if (cnta > 1) 196 ans = std::min(s2.t,s4.t); 197 else 198 ans = s1.t; 199 if (ans >= INF) 200 printf("you die!\n"); 201 else 202 printf("%d\n",ans); 203 return 0; 204 }
J、jcc爱踢球
思维题。如果可以想到满二叉树的话那么这题应该就比较简单了。
由于每轮都是偶数只队伍,那么这就相当于一颗满二叉树了,我们经常看电视的时候每次比赛都基本会出现树状图。
我们每次只记录叶节点的编号(假设为 i ),那么下一次的新叶节点编号(即旧叶节点的父亲)为(i+1)/2
如图所示:
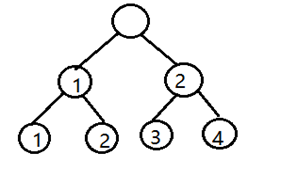
那么他们相遇也就是父节点相同的时候,而每找一次父节点计数器加一,则最后的计数器的值(记为 S )就是树的深度-1,也是比赛是场数,最后如果 2^S 为总的队伍数,则说明决赛相遇。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <time.h> 13 14 #define LL long long 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define ls nod<<1 17 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 18 19 const int maxn = 1e6 + 10; 20 const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; 21 22 int n,a,b; 23 24 25 int main() { 26 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&a,&b); 27 if (a > b) 28 std::swap(a,b); 29 int s = 1; 30 while (a != b-1 || a % 2 == 0) { 31 a = (a + 1) / 2; 32 b = (b + 1) / 2; 33 s++; 34 } 35 if (n == pow(2,s)) 36 printf("Final!\n"); 37 else 38 printf("%d\n",s); 39 return 0; 40 }
L、这是最难的题
典型的直接对答案进行二分的题目,然后直接检查正确性就好了

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <vector> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <stack> 8 #include <set> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <math.h> 11 #include <cstdio> 12 #include <time.h> 13 14 #define LL long long 15 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 16 #define ls nod<<1 17 #define rs (nod<<1)+1 18 19 const int maxn = 3e5 + 10; 20 const LL MOD = 1e9 + 7; 21 22 23 int n,m; 24 int a[maxn]; 25 26 bool check(int k) { 27 LL sum = 0; 28 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 29 sum += std::min(k,a[i]); 30 } 31 return sum >= (LL)k * m; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 36 for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) 37 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 38 std::sort(a+1,a+1+n); 39 int l = 0,r = 1e9; 40 int ans = 0; 41 while (l <= r) { 42 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 43 if (check(mid)) { 44 ans = mid; 45 l = mid + 1; 46 } 47 else 48 r = mid - 1; 49 } 50 printf("%d\n",ans); 51 return 0; 52 }
