文章目录
从redis源码看数据结构(一)链表
作者今年大三,正在准备明年的春招,文章中有写得不对的,希望大家及时指出文章中的错误的地方,欢迎互粉,大家一起努力!
一,redis数据类型
redis的数据类型有5种:
- 列表(list)
- 哈希表(hash)
- 集合(set)
- 字符串(String)
- 有序集合(zset)
二,redis底层列表实现
以下代码均是redis源码,我已经放到我的github上,有意者可以前往拉取
1.列表底层数据结构
关于redis列表底层实现在src/adlist.c,adlist.h
链表节点源码:
/*
* 链表节点
*
* 【从链表节点这个结构体可以看出,redis的链表的数据类型底层是一个双向链表的实现】
*/
typedef struct listNode {
// 前驱节点
struct listNode *prev;
// 后继节点
struct listNode *next;
// 值
void *value;
} listNode;
链表源码:
/*
* 链表
*/
typedef struct list {
// 表头指针
listNode *head;
// 表尾指针
listNode *tail;
// 节点数量
unsigned long len;
// 复制函数
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
// 释放函数
void (*free)(void *ptr);
// 比对函数
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
} list;
链表迭代器:
/*
* 链表迭代器
*/
typedef struct listIter {
// 下一节点
listNode *next;
// 迭代方向
int direction;
} listIter;
从以上列表节点源码中可以看出,redis列表底层是使用链表中的双向链表实现的。
本文是题目是从redis中看数据结构,所以,我们本文的重点还是放在数据结构的复习上,刚刚既然提到了链表,好,我们开始对链表来一个大体的复习
2.redis双向链表操作
新建链表
/*
* 创建一个新列表
*
* 创建成功时返回列表,创建失败返回 NULL
*
* T = O(1)
*/
list *listCreate(void)
{
struct list *list;
// 为列表结构分配内存,创建失败返回null
if ((list = zmalloc(sizeof(*list))) == NULL)
return NULL;
// 初始化属性
//头结点和未节点均为null
list->head = list->tail = NULL;
//长度为0
list->len = 0;
list->dup = NULL;
list->free = NULL;
list->match = NULL;
return list;
}
删除链表
删除链表就是从头结点开始,一个节点一个节点的释放内存
/*
* 释放整个列表(以及列表包含的节点)
*
* T = O(N),N 为列表的长度
*/
void listRelease(list *list)
{
unsigned long len;
listNode *current, *next;
//当前节点
current = list->head;
//当前节点长度
len = list->len;
//遍历链表,一个节点一个节点的释放内存,直到长度为0
while(len--) {
next = current->next;
// 如果列表有自带的 free 方法,那么先对节点值调用它
if (list->free) list->free(current->value);
// 之后再释放节点,zfree()是redis自己实现的内存释放函数
zfree(current);
current = next;
}
zfree(list);
}
添加结点
添加头结点
添加头结点可以总结为:
- 1.新建并初始化节点
- 2.建立新建节点和原头结点的指针指向关系
- 3.重新指定头节点

/*
* 新建一个给定 value 的节点,并将它加入到列表的头部
*
* 出错时,返回 NULL ,不执行动作。
* 成功时,返回传入的列表
*
* T = O(1)
*/
list *listAddNodeHead(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
//先新建节点,新建失败返回null
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//初始化节点值
node->value = value;
//判断链表长度
if (list->len == 0) {
//该链表如果是一个空链表,则新建节点既是头结点也是尾节点
list->head = list->tail = node;
//前驱和后继指针均指向为空
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
//该链表不是空链表
//因为是要插入头结点,所以该链表的前驱一定指向为空
node->prev = NULL;
//后继指针指向头结点head
node->next = list->head;
//原头结点head的前驱节点指向新建节点node
list->head->prev = node;
//指向关系确定好后,指定新的头结点为node
list->head = node;
}
//长度+1
list->len++;
//返回
return list;
}
添加尾节点
添加尾节点可以总结为:
- 1.新建并初始化节点
- 2.建立新建节点和原尾结点的指针指向关系
- 3.重新指定尾节点

/*
* 新建一个包含给定 value 的节点,并将它加入到列表的表尾
*
* 出错时,返回 NULL ,不执行动作。
* 成功时,返回传入的列表
*
* T = O(1)
*/
list *listAddNodeTail(list *list, void *value)
{
listNode *node;
//先新建节点,新建失败返回null
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//初始化节点值
node->value = value;
//判断链表长度
if (list->len == 0) {
//该链表如果是一个空链表,则新建节点既是头结点也是尾节点
list->head = list->tail = node;
//前驱和后继指针均指向为空
node->prev = node->next = NULL;
} else {
//该链表至少一个节点
//指定新建节点的前驱节点指向原链表的尾节点
node->prev = list->tail;
//新建节点的后继节点指向为空,因为是插入尾节点
node->next = NULL;
//原链表的尾节点tail的后继节点指向新的尾节点,即新建节点
list->tail->next = node;
//指向关系明确后,指定新的尾节点为新建节点
list->tail = node;
}
//长度+1
list->len++;
//返回
return list;
}
在指定节点前或后插入节点
- 1.新建并初始化节点
- 2.判断指定节点是否是头尾节点
- 3.如果是头尾节点就根据上文提到的流程走
- 4.如果不是头尾节点则指定节点和新建节点建立好对应的指向关系

/*
* 创建一个包含值 value 的节点
* 并根据 after 参数的指示,将新节点插入到 old_node 的之前或者之后
*
* T = O(1)
*/
list *listInsertNode(list *list, listNode *old_node, void *value, int after) {
listNode *node;
//新建节点,创建节点出错则返回null
if ((node = zmalloc(sizeof(*node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
//初始化节点value
node->value = value;
//根据 after 参数的指示,将新节点插入到 old_node 的之前或者之后
if (after) {
// 插入到 old_node 之后
//则node的前驱指向old_node
node->prev = old_node;
//node的后继指针指向old_node的后继节点
node->next = old_node->next;
//如果old_node本来就是该链表的尾节点,则相当于node要称为该链表的新的尾节点
if (list->tail == old_node) {
list->tail = node;
}
} else {
//逻辑差不多。就不多详细注释了
// 插入到 old_node 之前
node->next = old_node;
node->prev = old_node->prev;
// 处理表头节点
if (list->head == old_node) {
list->head = node;
}
}
// 更新前置节点和后继节点的指针
if (node->prev != NULL) {
node->prev->next = node;
}
if (node->next != NULL) {
node->next->prev = node;
}
// 更新列表节点数量
list->len++;
return list;
}
删除节点
删除给定节点
- 判断给定节点是否是头尾节点,如果是则删除后重新指定后继或者前驱节点为新的头结点或者尾节点
- 不是的话,则删除节点的前驱和后继节点建立起指向关系
/*
* 释放列表中给定的节点
* 清除节点私有值(private value)的工作由调用者完成
*
* T = O(1)
*/
void listDelNode(list *list, listNode *node)
{
// 处理前驱节点的指针
if (node->prev)
node->prev->next = node->next;
else
//node是头结点,则直接删除头结点
list->head = node->next;
// 处理后继节点的指针
if (node->next)
node->next->prev = node->prev;
else
//node是尾结点,则直接删除头结点
list->tail = node->prev;
// 释放节点值
if (list->free) list->free(node->value);
// 释放节点
zfree(node);
// 更新列表节点数量
list->len--;
}
获取节点
通过索引获取节点
- 1.redis中根据索引查找节点,索引可以是正数,也可以是负数
- 2.正数从 0 开始计数,由表头开始;负数从 -1 开始计数,由表尾开始。
/*
* 根据给定索引,返回列表中对应的节点
*
* 索引可以是正数,也可以是负数。
* 正数从 0 开始计数,由表头开始;负数从 -1 开始计数,由表尾开始。
*
* 如果给定索引超出列表的返回,返回 NULL 。
*
* T = O(N),N 为列表的长度
*/
listNode *listIndex(list *list, long index) {
listNode *n;
//如果索引是负数,
if (index < 0) {
//负数从 -1 开始计数,由表尾开始。
index = (-index)-1;
n = list->tail;
//从表尾开始遍历
while(index-- && n) n = n->prev;
} else {
//索引是整数,则从0开始计数
n = list->head;
//从表头开始遍历查找
while(index-- && n) n = n->next;
}
//返回
return n;
}
获取迭代器当前节点
/*
* 返回迭代器的当前节点
*
* 可以使用 listDelNode() 删除当前节点,但是不可以删除其他节点。
*
* 函数要么返回当前节点,要么返回 NULL ,因此,常见的用法是:
*
* iter = listGetIterator(list,<direction>);
* while ((node = listNext(iter)) != NULL) {
* doSomethingWith(listNodeValue(node));
* }
*
* T = O(1)
*/
listNode *listNext(listIter *iter)
{
listNode *current = iter->next;
if (current != NULL) {
// 根据迭代方向,选择节点
if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD)
iter->next = current->next;
else
iter->next = current->prev;
}
return current;
}
三,java链表实现
本文作者的目标是希望通过redis底层数据结构来进行相应的数据结构的复习,包括哈希表,链表,集合等,都会在后边更新,说完redis源码后,这一部分基本就是自己手动实现相关数据结构,可能文字描述并不多
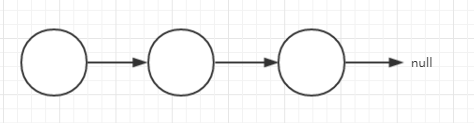
1.单链表
单链表是由后继指针和数值域构成的
public class MyList {
/**
* 单链表实现
*/
private static class Node{
//后继指针
private Node next;
//数值域
private int value;
public Node(Node next, int value) {
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value){
this(null,value);
}
//省略get set
}
//头结点
private Node head;
//节点数量
private int size;
public MyList() {
head = null;
size = 0;
}
//.....
添加节点
/**
* 头部添加节点
* @param value
*/
public void addFirst(int value){
Node node = new Node(value);
node.next = this.head;
this.size++;
this.head = node;
}
/**
* 尾部添加节点
* @param value
*/
public void addLast(int value){
add(this.size,value);
}
/**
* 在指定索引下添加指定节点
* @param index
* @param value
*/
public void add(int index,int value){
if(index < 0 || index > this.size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index greater list.size");
} else if(index == 0){
addFirst(value);
}else{
Node cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0; i< index - 1;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
Node node = new Node(value);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
this.size++;
}
}
删除节点
/**
* 删除指定下标的链表元素
* @param index
*/
public void remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > this.size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index greater list.size");
}else if(this.head == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("list is null list");
}else if(index == 0){
//删除头结点
Node deleteNode = this.head;
//指定新的头结点
this.head = deleteNode.next;
deleteNode.next = null;
this.size--;
}else{
//找出指定下标的节点
Node cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index - 1;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
Node deleteNode = cur.next;
cur.next = deleteNode.next;
deleteNode.next = null;
this.size--;
}
}
判断是否包含指定节点
/**
* 判断是否包含指定节点
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(int value){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.value == value){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyList myList = new MyList();
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++){
myList.addLast(i);
}
System.out.println(myList.size);
System.out.println(myList.contains(5));
System.out.println(myList.contains(2));
myList.add(1,5);
System.out.println(myList.contains(5));
System.out.println(myList.head.value);
myList.add(0,9);
System.out.println(myList.head.value);
}

2.双向链表
链表和节点结构
public class MyLinkedList {
//头结点
private Node head;
//尾节点
private Node tail;
//节点数量
private int size;
/**
* 节点类
*/
private class Node{
//前驱
private Node pre;
//后继
private Node next;
//数值域
private int value;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
//省略get set
}
public MyLinkedList(){
head = tail = null;
size = 0;
}
//....
添加节点
/**
* 头部添加
*/
public void addFirst(int value){
Node node = new Node(value);
Node head = this.head;
this.head = node;
if(head == null){
this.tail = node;
}else{
head.pre = node;
node.next = head;
}
this.size++;
}
/**
* 尾部添加
* @param value
*/
public void addLast(int value){
Node node = new Node(value);
Node tail = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
}else{
tail.next = node;
node.pre = tail;
}
this.size++;
}
/**
* 指定索引添加指定节点
* @param index
* @param value
*/
public void add(int index,int value){
if(index < 0 || index > this.size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index greater list.size");
}else if (index == this.size){
addLast(value);
}else if(index == 0){
addFirst(value);
}else{
Node cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index - 1;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
Node node = new Node(value);
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
node.pre = cur;
next.pre = node;
node.next = next;
this.size++;
}
}
删除节点
public void removeFirst(){
if(this.head == null){
return;
}
Node deleteHead = this.head;
this.head = deleteHead.next;
deleteHead.next = null;
this.size--;
}
public void removeLast(){
if(this.tail == null){
return;
}
Node deleteHead = this.tail;
this.tail = deleteHead.pre;
deleteHead.pre = null;
this.size--;
}
/**
* 删除指定下标的链表元素
* @param index
*/
public void remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index > this.size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index greater list.size");
}else if(this.head == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("list is null list");
}else if(index == 0){
removeFirst();
}else if(index == this.size){
removeLast();
}else{
//找出指定下标的节点
Node cur = this.head;
for(int i = 0;i < index - 1;i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
Node deleteNode = cur.next;
Node next = deleteNode.next;
cur.next = next;
next.pre = cur;
deleteNode.pre = null;
deleteNode.next = null;
this.size--;
}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
for(int i = 0; i<5;i++){
myLinkedList.addLast(i);
}
System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(2));
System.out.println(myLinkedList.head.value);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.tail.value);
myLinkedList.remove(3);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(3));
myLinkedList.remove(0);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.head.value);
}

