文章目录
leetcode栈和队列专题
本人大三,目前在准备明年的春招,有问题欢迎及时指出,希望跟大家一起进步
1.栈相关
最小栈

使用双栈来实现最小栈,其中,一个数据栈保存push的所有数据,一个最小栈保存最小元素
当push时,数据栈每次都会将push的元素push到数据栈中,但是minstack却不一定,当一开始,最小栈是空栈的话,就会将元素push到最小栈,之后每次push新元素时,除了会将该元素push到数据栈,对于最小栈,如果当前要push的元素小于最小栈的栈顶元素,就将该元素push到最小栈,有些情况下,最小栈会只维护一个最小数,也就是说,每次新的最小值要push进栈时,都要将旧的最小值pop出去

实现:
/**
* 最小栈
*/
class MinStack{
// 数据栈
private Stack<Integer> stack;
// 最小栈
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(minStack.isEmpty() || minStack.peek() >= x){
minStack.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
int val = stack.pop();
if(minStack.peek() == val){
minStack.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
二叉树遍历
在二叉树遍历中,我们在非递归遍历二叉树的时候经常会使用到栈
二叉树前序遍历

/*非递归实现*/
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return list;
}
二叉树中序遍历

/*非递归实现*/
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
cur = node.right;
}
}
return list;
}
二叉树后序遍历
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KFvEEw9I-1573451714428)(C:\Users\12642\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20191110233558206.png)]
后序遍历和中序遍历的不同在于,需要判断当前节点是否是从右子节点回来再访问一次的
/*非递归实现*/
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal1(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode r = null;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null){
if(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else {
cur = stack.peek();
if(cur.right == null || cur.right == r){
list.add(cur.val);
r = cur;
stack.pop();
cur = null;
}else{
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
return list;
}
逆序栈元素
将一个栈中的所有元素实现逆序存放,如:

我们可以使用递归,不断删除栈底元素,然后将删除的栈底元素重新进栈,从而实现逆序栈
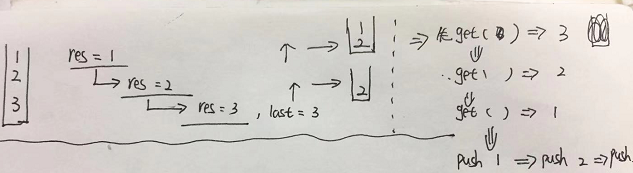
/**
* 递归删除栈底元素并返回
* @param s
* @return
*/
public int get(Stack<Integer> s){
int res = s.pop();
if(s.isEmpty()){
return res;
}else{
int last = get(s);
s.push(res);
return last;
}
}
/**
* 逆序栈
* @param s
*/
public void revserse(Stack<Integer> s){
if(s.isEmpty()){
return;
}else{
int i = get(s);
revserse(s);
s.push(i);
}
}
排序栈
双栈实现栈元素排序,从栈顶到栈底实现从小到大的顺序
/**
* 双栈实现栈元素排序,从栈顶到栈底实现从小到大的顺序
* @param stack
*/
public void sort(Stack<Integer> stack){
Stack<Integer> tmp = new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int cur = stack.pop();
while(!tmp.isEmpty() && tmp.peek() <= cur){
stack.push(tmp.pop());
}
tmp.push(cur);
}
while(!tmp.isEmpty()){
stack.push(tmp.pop());
}
}
括号匹配问题

基于计数法
遍历统计左括号left和右括号right,如果刚好匹配全部括号,则left + right = 0
public int minAddToMakeValid(String S) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < S.length();i++){
if(S.charAt(i) == '('){
//接收到(
left++;
}else{
//接收到)
if (left > 0) {
//可以匹配一个(
left--;
} else{
//不可匹配
right++;
}
}
}
return left + right;
}
基于栈
public int minAddToMakeValid(String S) {
Stack<Character> s = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < S.length(); i++){
if(s.isEmpty() || s.peek() == ')'){
s.push(S.charAt(i));
}
else {
if(S.charAt(i) == '(') {
s.push(S.charAt(i));
} else{
s.pop();
}
}
}
return s.size();
}
验证栈序列

使用 j 指针指向pop序列,指示当前要pop出栈的元素,遍历push序列依次进栈,当栈顶元素 == pop[j]时需要将栈顶元素pop出,依次执行,最后看 j 指针是否达到push序列的长度,即是否将push的元素全部pop出
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
int len = pushed.length;
int j = 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i : pushed){
stack.push(i);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && j < len && stack.peek() == popped[j]){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return j == len;
}
2.队列相关
设计循环队列

//数组实现循环队列
Integer[] list;
//头指针 -- 指向队列头部
int head;
//尾指针 -- 指向队列尾部
int tail;
//数组元素个数
// int size;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k.
*/
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
list = new Integer[k];
//初始化循环队列时,头指针和尾指针都指向同一处
head = 0;
tail = 0;
//size = 0;
}
/**
* Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
} else {
list[tail] = value;
//为什么需要取模? ---> 因为要实现在数组中循环,对+1后数组长度取模,就相当于求出了经过一次循环后的下标
//新的尾坐标
tail = (tail + 1) % list.length;
return true;
}
}
/**
* Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
list[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % list.length;
return true;
}
}
/**
* Get the front item from the queue.
*/
public int Front() {
return isEmpty() == true ? -1 : list[head];
}
/**
* Get the last item from the queue.
*/
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
if (tail != 0) {
//循环队列未满
return list[tail - 1];
} else {
//循环队列已满
return list[list.length - 1];
}
}
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
* 循环队列为空 ---> 如果头指针和尾指针指向同一处 && 头指针指向元素为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (head == tail && list[head] == null) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
* 循环队列已满 ---> 如果头指针和尾指针指向同一处 && 头指针指向元素不为空
*/
public boolean isFull() {
if (head == tail && list[head] != null) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
3.组合设计
栈实现队列

使用双栈实现FIFO的队列
class MyQueue{
private Stack<Integer> stackPush;
private Stack<Integer> stackPop;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stackPop = new Stack<>();
stackPush = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stackPush.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
while(!stackPush.isEmpty()){
stackPop.push((stackPush.pop()));
}
int i = stackPop.pop();
while(!stackPop.isEmpty()){
stackPush.push((stackPop.pop()));
}
return i;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
while(!stackPush.isEmpty()){
stackPop.push((stackPush.pop()));
}
int i = stackPop.peek();
while(!stackPop.isEmpty()){
stackPush.push((stackPop.pop()));
}
return i;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stackPush.isEmpty() && stackPop.isEmpty();
}
}
队列实现栈

/**
* <h>队列实现栈</h>
* <li>push(x) -- 元素 x 入栈</li>
* <li>pop() -- 移除栈顶元素</li>
* <li>top() -- 获取栈顶元素</li>
* <li>empty() -- 返回栈是否为空</li>
*/
//基于双向链表linkedList实现栈,linkedList尾部就是栈顶
//也可以基于双端队列实现,deque实际上是由双向链表组成的双端队列 Linkedist implements Deque<T>
Deque<Integer> deque;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public MyStackOfDeque() {
deque = new LinkedList<>();
}
/**
* Push element x onto stack.
*/
public void push(int x) {
deque.addLast(x);
}
/**
* Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
*/
public int pop() {
return deque.removeLast();
}
/**
* Get the top element.
*/
public int top() {
return deque.getLast();
}
/**
* Returns whether the stack is empty.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return deque.isEmpty();
}
