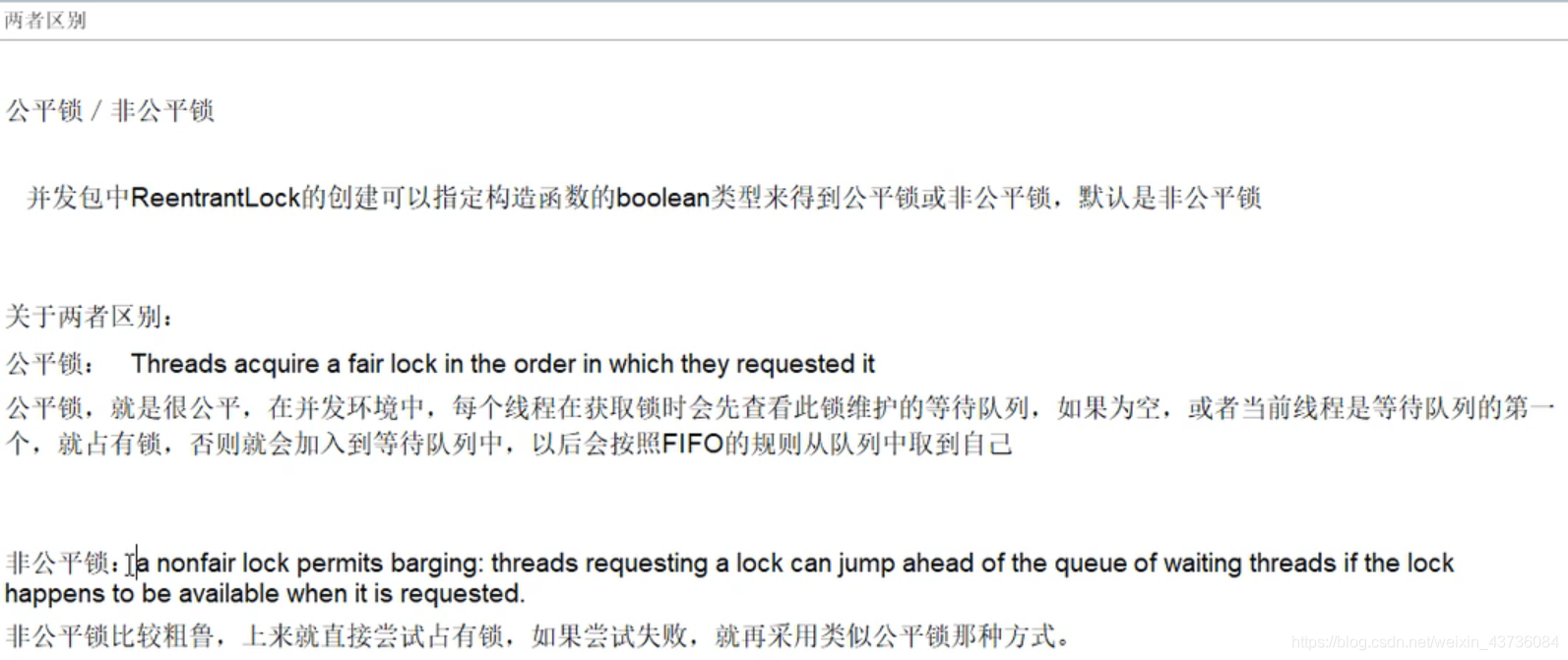
1.公平锁、非公平锁

2.可重入锁(递归锁)

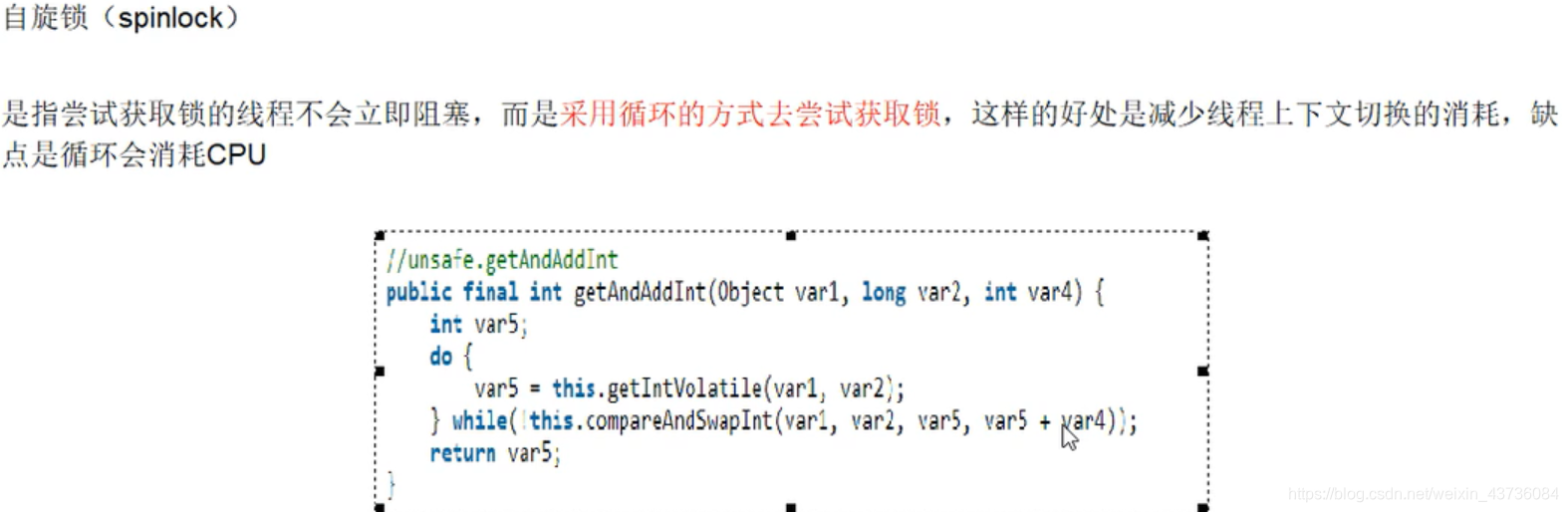
3.自旋锁
AtomicReference atomicReference = new AtomicReference();//原子引用线程
下面代码5秒钟自旋了10万次,还是很消耗CPU的
package HighConcurrency;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class SpinLockDemo {
//原子引用线程
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
public void myLock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t come in");
while(!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null,thread)){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程自旋。。。");
}
}
public void myunLock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread,null);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t invoked myUnLock");
}
public static void main(String []args){
SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo();
new Thread(()->{
spinLockDemo.myLock();
//暂停线程一会
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
spinLockDemo.myunLock();
},"AA").start();
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
new Thread(()->{
spinLockDemo.myLock();
spinLockDemo.myunLock();
},"BB").start();
}
}
4.独占锁(写锁)|共享锁(读锁)
独占锁:指该锁一次只能被一个线程持有,ReentrantLock和synchronized都是独占锁
共享锁:可被多个线程所持有。对ReentrantReadWriteLock其读锁是共享锁,其写锁是独占锁。
读锁的共享锁可保证高并发读是非常都效的
class MyCache{ //资源类
private volatile Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
private ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
//写缓存框架,读、写、清空
public void get(String key,Object value){ //读
rwLock.readLock().lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 正在读取:");
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Object object = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 读取完成" + object);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
rwLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
public void put(String key,Object value){ //写
rwLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 正在写入" + key);
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t 写入完成");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
rwLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
}
public class ReadWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache = new MyCache();
//线程操作资源类
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int tempInt = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.put(tempInt+"",tempInt+"");
},"线程"+String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int tempInt = i;
new Thread(() -> {
myCache.get(tempInt+"",tempInt+"");
},"线程"+String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
