一、简介
Android android.graphics.Matrix 类是一个3 x 3的矩阵(方阵),上一张几乎所有介绍Matrix的文章都会引用的Matrix内容图:
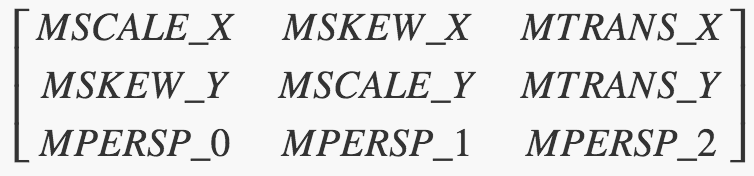
二、相关方法
1、equals
比较两个矩阵是否相等。
Matrix matrix1 = new Matrix(); Matrix matrix2 = new Matrix(); matrix1.setTranslate(1,2); matrix2.setTranslate(2,2); // 输出:matrix1 == matrix2:false System.out.println("matrix1 == matrix2:" + matrix1.equals(matrix2)); 2、+号相连/toString/toShortString
将矩阵转换为字符串。
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // 输出:+号相连:Matrix{[1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]} System.out.println("+号相连:" + matrix); // 输出:Matrix{[1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0]} System.out.println("toString:" + matrix.toString()); // 输出:[1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0] System.out.println("toShortString:" + matrix.toShortString()); 3、getValues()、setValues()
当我们调用Matrix类的getValues(float[] values)、setValues(float[] values)方法时,可以将这个矩阵转换成一个数组进行操作。转换后的数组为:
[ MSCALE_X, MSKEW_X, MTRANS_X, MSKEW_Y, MSCALE_Y, MTRANS_Y, MPERSP_0, MPERSP_1, MPERSP_2]
为了方便操作这个数组,在android.graphics.Matrix类中,定义了MSCALE_X、MSKEW_X...变量,分别代表各自功能在数组中对应的下标,具体内容如下:
public static final int MSCALE_X = 0; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MSKEW_X = 1; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MTRANS_X = 2; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MSKEW_Y = 3; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MSCALE_Y = 4; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MTRANS_Y = 5; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MPERSP_0 = 6; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MPERSP_1 = 7; //!< use with getValues/setValues public static final int MPERSP_2 = 8; //!< use with getValues/setValues 方法示例:
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // matrix = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0][0.0, 1.0, 0.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0] System.out.println("matrix = " + matrix.toShortString()); float[] values = new float[9]; matrix.getValues(values); // matrix转换成数组后 = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0] System.out.println("matrix转换成数组后 = " + Arrays.toString(values)); // 为matrix赋值 values [Matrix.MTRANS_X] = 2; values [Matrix.MTRANS_Y] = 3; matrix.setValues(values); // matrix = [1.0, 0.0, 2.0][0.0, 1.0, 3.0][0.0, 0.0, 1.0] System.out.println("matrix = " + matrix.toShortString()); 4、setXXX/preXXX/postXXX
XXX可以是Translate、Scale、Rotate、Skew和Concat。其中Concat参数为Matrix,表示直接操作Matrix。由于缩放、旋转、错切可以绕中心操作,如果指定了中心,则变换步骤为:
- 将原点平移到该点。
- 做缩放、错切、旋转操作。
- 原点平移到原来的原点处。
方法参数转换成了一个怎样的矩阵?
// 下面代码中参数(2,2) 转换后的矩阵为
// [2.0, 0.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 2.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
// 即根据XXX代表的功能修改矩阵中对应功能位置的值即可 matrix.postScale(2,2); setXXX
首先会将该Matrix重置为单位矩阵,即相当于首先会调用reset()方法,然后再设置该Matrix中对应功能的值。例:
// [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] // [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] matrix.setValues(new float[]{2.0f,3.0f, 4.0f, 2.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,1.0f,1.0f}); // [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [2.0, 2.0, 0.0] -> [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [0.0, 2.0, 0.0] // [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] matrix.setScale(2,2); preXXX
不会重置Matrix,相当于当前操作矩阵(A)左乘参数矩阵(B),即AB。例:
// [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] // [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] matrix.setValues(new float[]{2.0f,3.0f, 4.0f, 2.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,1.0f,1.0f}); // [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] [4.0, 6.0, 4.0] // [2.0, 0.0, 0.0](matrix) * [0.0, 2.0, 0.0] = [4.0, 0.0, 0.0](matrix) // [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [2.0, 2.0, 1.0] matrix.preScale(2,2); postXXX
不会重置Matrix,相当于当前操作矩阵(A)右乘参数矩阵(B),即BA,例:
// [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); // [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] // [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] matrix.setValues(new float[]{2.0f,3.0f, 4.0f, 2.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,1.0f,1.0f}); // [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] [4.0, 6.0, 8.0] // [0.0, 2.0, 0.0] * [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] (matrix) = [4.0, 0.0, 0.0](matrix) // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] matrix.postScale(2,2); setContact
关于setContact(Matrix m1,Matrix m2)方法,需要单独说下,它的参数为两个Matrix对象,计算规则为:当前操作的Matrix对象 = m1 * m2;
例:
// [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]
// [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); Matrix matrix1 = new Matrix(); Matrix matrix2 = new Matrix(); // [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] // [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [2.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] matrix1.setValues(new float[]{2.0f,3.0f, 4.0f, 2.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,1.0f,1.0f}); // [1.0, 0.0, 0.0] [2.0, 5.0, 4.0] // [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] -> [3.0, 0.0, 0.0] // [0.0, 0.0, 1.0] [1.0, 2.0, 1.0] matrix2.setValues(new float[]{2.0f,5.0f, 4.0f, 3.0f,0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,2.0f,1.0f}); // [2.0, 3.0, 4.0] [2.0, 5.0, 4.0] [17.0, 18.0, 12.0] // [2.0, 2.0, 0.0](matrix1) * [3.0, 0.0, 0.0](matrix2) = [4.0, 10.0, 8.0 ] (matrix) // [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] [1.0, 2.0, 1.0] [6.0, 7.0, 5.0 ] matrix.setConcat(matrix1,matrix2); 5、mapRadius/mapPoints/mapRect/mapVectors
可翻译为将矩阵映射到(作用于)点、矩形、半径、向量。
mapRadius
半径的计算。例:
// 一个半径为100.0f的圆,放大1倍后,半径也将增大一倍。据说用在画布中的圆随画布大小变化时
float radius = 100.0f; float radiusAfterMatrix; Matrix matrixRadius = new Matrix(); matrixRadius.setScale(2,2); radiusAfterMatrix = matrixRadius.mapRadius(radius); // 输出:radius=200.0 System.out.println("radius=" + radiusAfterMatrix); mapPoints
此方法有3个重载方法。点数组各值分别代表pts[x0,y0,x1,y1 ... xn,yn],因为一个点的确定需要x坐标和y坐标两个值,所以,pts数组的长度一般为偶数,如果为奇数,则最后一个值不参与计算(长度为1将不计算)。下面给出具体例子,例子中将会详细说明mapPoints方法。
// =======================
// mapPoints(float[] pts)
// =======================
// 运算后的结果会保存在pts数组中,原pts数组中的内容会被覆盖
// 1.《点的移动》,对于任意点(Xn,Yn),x轴方向平移dx,y轴方向平移dy后有: // Xn = Xn + dx // Yn = Yn + dy float[] ptsTrans = {6,2}; Matrix matrixTrans = new Matrix(); matrixTrans.setTranslate(-2,2); matrixTrans.mapPoints(ptsTrans); // 输出:trans=[4.0, 4.0] System.out.println("trans=" + Arrays.toString(ptsTrans)); // 2.《点的放大》,对于任意点(Xn,Yn),绕点(px,py)x轴、y轴方向分别放大sx倍、sy倍后,有: // Xn = Xn * sx + (px - px * sx) // Yn = Yn * sy + (py - sy * py) float[] ptsScale = {2,3}; Matrix matrixScale = new Matrix(); matrixScale.setScale(3,6,2,2); matrixScale.mapPoints(ptsScale); // 输出:scale=[2.0, 8.0] System.out.println("scale=" + Arrays.toString(ptsScale)); // 3.《点的旋转》,对于任意点(Xn,Yn),绕点(px,py)旋转a度后,有: // Xn = (Xn - px) * cos(a) - (Yn - py) * sin(a) + px // Yn = (Xn - px) * sin(a) + (Yn - py) * cos(a) + py float[] ptsRotate = {6,6}; Matrix matrixRotate = new Matrix(); matrixRotate.preRotate(90,2,3); matrixRotate.mapPoints(ptsRotate); // 输出:rotate=[-1.0,7.0] System.out.println("rotate=" + Arrays.toString(ptsRotate)); // 4.《点的错切》,对于任意点(Xn,Yn),绕点(px,py)x轴、y轴方向分别错切kx、ky后,有: // Xn = Xn + kx(Yn - py) // Yn = Yn + ky(Xn - px) float[] ptsSkew = {3,2}; Matrix matrixSkew = new Matrix(); matrixSkew.setSkew(2,3,6,8); matrixSkew.mapPoints(ptsSkew); // 输出:skew=[-9.0,-7.0] System.out.println("skew=" + Arrays.toString(ptsSkew)); // =================================== // mapPoints(float[] dst, float[] src) // =================================== // 运算后的结果保存在dst数组中,原src数组中的内容会保留 float[] src = {2,3,3,3}; float[] dst = new float[src.length]; Matrix matrixDstSrc = new Matrix(); matrixDstSrc.setTranslate(2,