代码来源:java知音
一、lambda表达式&stream能做什么
- 替代匿名类,简化代码:创建线程、Comparator实现比较接口
- 简化集合的遍历,
- 集合元素筛选:(filter 条件过滤,Predicate 多条件过滤)
- limit截取元素
- sorted 快速排序
- max 返回集合最大值,min 返回集合最小值
- map 对集合中元素进行特定操作
二、定义:代码考入idea就会了,不会看开头连接
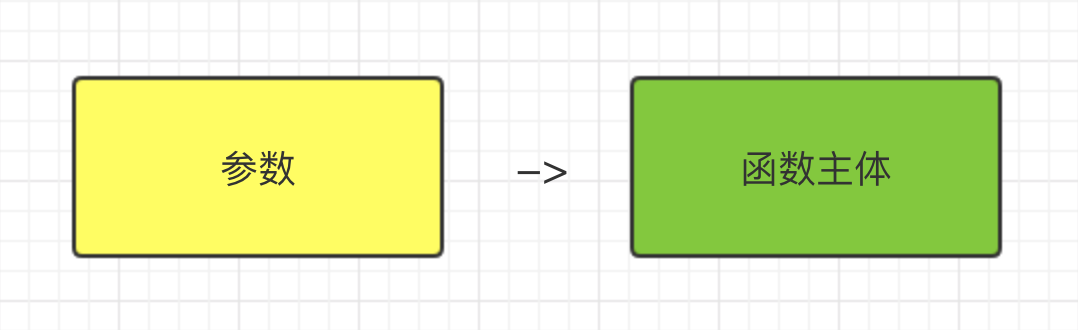
由1、参数;2、->;3、函数主体组成
能够使用 Lambda 表达式的必须是一个函数接口,函数接口是指该接口中只包含一个方法,如 Runnable 接口。超过两个方法的接口,不能使用lambda表达式;
@FunctionalInterface public interface Runnable { /** * When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used * to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's * <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing * thread. * <p> * The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may * take any action whatsoever. * * @see java.lang.Thread#run() */ public abstract void run(); }接口可以包含参数,也可以不包含参数,有返回值,也可以没有返回值;
package lamda; /** * @author Levi * @date 2019/12/26 19:32 */ public class TestLambda { public static void main(String[] args){ /** * 普通方式创建线程 */ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("thread start ..."); } }).start(); /** * lambda方式创建线程 */ new Thread(()-> System.out.println("lambda thread start...")).start(); TestLambda test = new TestLambda(); //无参数 test.test(()-> System.out.println("333")); //有参数 test.test2((int x,int y)-> System.out.println("传入的参数是:"+x+" "+y)); //有参数,有返回值 int result = test.test3((x,y)->x+y); System.out.println("test3结果"+result); } //带参数 public interface InterfaceOne { public void test1(); } //调用方法test1 public void test(InterfaceOne myInterface){ myInterface.test1(); } //带参数 public interface InterfaceTwo{ public void test2(int x,int y); } //调用方法test2 public void test2(InterfaceTwo interfaceTwo){ int x =10; int y = 15; interfaceTwo.test2( x, y); } //带参数,有返回值 public interface InterfaceThree { public int test2(int x,int y); } //调用方法test3 public int test3(InterfaceThree myInterface2){ int x =10; int y = 15; return myInterface2.test2( x, y); } }运行结果:

测试用People类:
package test;
/**
* @author Levi
* @date 2019/11/13 9:27
*/
public class People implements Comparable<People>{
String name;
int num;
public People(String name,int num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
People() {}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(People o) {
return 0;
}
}
测试代码
package lamda;
import test.People;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author Levi
* @date 2019/12/26 19:32
*/
public class TestLambda2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//如果函数接口的方法体包含多条语句,需要在 {} 中添加相关语句
List<People> pl = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <5 ; i++) {
People people = new People("姓名"+i,i);
pl.add(people);
}
pl.forEach(people -> {
System.out.println("姓名"+people.getName());
});
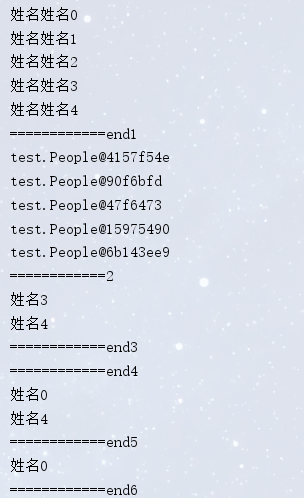
System.out.println("============end1");
//双冒号 :: 表示方法引用,可以引用其他方法。
pl.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("============2");
//筛选出num大于5的
pl.stream().filter(people -> people.getNum()>2).forEach(people -> System.out.println(people.getName()));
System.out.println("============end3");
//多条件过滤:除了上述方法,
Predicate<People> pd1 = people -> people.getName().endsWith("4");
Predicate<People> pd2 = people -> people.getNum()<1;
pl.stream()
.filter(pd1)
.filter(pd2)
.forEach(people -> System.out.println(people.getName()));
System.out.println("============end4");
//也可以调用 Predicate 对象的 and() 方法,对多个 Predicate 对象进行且运算,或者用 or() 进行或运算
pl.stream().filter(pd1.or(pd2)).forEach(people -> System.out.println(people.getName()));
System.out.println("============end5");
//limit截取,功能和 SQL 语句的 limit 一致
pl.stream().filter(pd1.or(pd2)).limit(1).forEach(people -> System.out.println(people.getName()));
System.out.println("============end6");
//sorted排序
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,6,2,3,5,4);
list.stream()
.sorted()
.forEach(num-> System.out.println(num));
System.out.println("============end7");
//默认是升序排列,可通过添加 Comparator.reverseOrder() 进行降序排列,如下所示。
list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
.forEach(num-> System.out.println(num));
System.out.println("============end8");
/**
* 需要注意的是 max() 和 min() 的返回值是 Optional 类型,Optional 也是 Java8 提 供的新特性,
* Optional 类是一个可以为 null 的容器对象,需要调用 get() 方法取出容器内的数据,
*/
System.out.println(list.stream().max(Integer::compareTo).get());
System.out.println(list.stream().min(Integer::compareTo).get());
System.out.println("============end9");
pl.stream()
.map(people->people.getNum()+10)
.forEach(people-> System.out.println(people));
System.out.println("============end10");
/**
* reduce() 和 map() 一样,都可以对集合中元素进行操作,区别在于 reduce() 是将所有元素按照传入的逻辑进行处理,
* 并将结果合并成一个值返回,如返回集合所有元素之和,reduce() 的返回值是 Optional 类型,需要调用 get() 方法取出容器内的数据
*/
System.out.println(list.stream().reduce((sum,num)->sum+num).get());
System.out.println("============end11");
/**
* collection 基于目标集合的元素生成新集合,从目标集合中取出所有的奇数生成一个新的集合,
* 即在前面的筛选输出中使用它,生成筛选后的符合条件的集合
*/
List<People> newPl = pl.stream().filter(pd1.or(pd2)).collect(Collectors.toList());
newPl.forEach(people -> System.out.println(people.getName()));
System.out.println("============end12");
}
}