4292: Count the Trees 
总提交: 15 测试通过:6
描述
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two child nodes, usually distinguished as "left" and "right". A subtree of a tree T is a tree consisting of a node in T and all of its descendants in T. Two binary trees are called identical if their left subtrees are the same(or both having no left subtree) and their right subtrees are the same(or both having no right subtrees).
According to a recent research, some people in the world are interested in counting the number of identical subtree pairs, each from the given trees respectively.
Now, you are given two trees. Write a program to help to count the number of identical subtree pairs, such that the first one comes from the first tree and the second one comes from the second tree.
输入
There are multiple test cases. The first line contains a positive integer T (T ≤ 20) indicating the number of test cases. Then T test cases follow.
In each test case, There are two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100000) indicating the number of nodes in the given two trees. The following n lines describe the first tree. The i-th line contains two integers u and v (1 ≤ u ≤ n or u = -1, 1 ≤ v ≤ n or v = -1) indicating the indices of the left and right children of node i. If u or v equals to -1, it means that node i don't have the corresponding left or right child. Then followed by m lines describing the second tree in the same format. The roots of both trees are node 1.

输出
For each test case, print a line containing the result.
样例输入
2
2 2
-1 2
-1 -1
2 -1
-1 -1
5 5
2 3
4 5
-1 -1
-1 -1
-1 -1
2 3
4 5
-1 -1
-1 -1
-1 -1
样例输出
1
11
提示
The two trees in the first sample look like this.
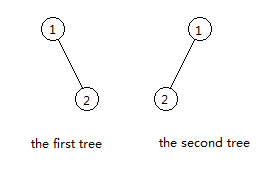
解题思路: 求子树相等总共有多少个 树hash

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define ll long long 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int t; 6 int n,m,jishu,flag; 7 const int maxn=1e5+5; 8 int tree[maxn][2]; 9 int num[maxn]; 10 map<pair<int,int>,int>ma; 11 ll res; 12 13 int dfs(int ee){ 14 int ls=-1,rs=-1,t; 15 if(tree[ee][0]!=-1) ls=dfs(tree[ee][0]); 16 if(tree[ee][1]!=-1) rs=dfs(tree[ee][1]); 17 if(!flag){ 18 if(!ma.count({ls,rs})) ma[{ls,rs}]=++jishu; //hash 19 num[t=ma[{ls,rs}]]++; //计数 20 } 21 else{ 22 if(ma.count({ls,rs})) res+=num[t=ma[{ls,rs}]]; 23 else t=0; 24 } 25 return t; 26 } 27 28 int main(){ 29 scanf("%d",&t); 30 while(t--){ 31 ma.clear(); 32 memset(num,0,sizeof(num)); 33 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 34 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 35 scanf("%d%d",&tree[i][0],&tree[i][1]); 36 } 37 flag=0,jishu=0; 38 dfs(1); 39 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ 40 scanf("%d%d",&tree[i][0],&tree[i][1]); 41 } 42 res=0,flag=1,dfs(1); 43 printf("%lld\n",res); 44 } 45 return 0; 46 }
