参考mysql5.7 en manual,对列id的解释:
The SELECT identifier. This is the sequential number of the SELECT within the query. The value can be NULL if the row refers to the union result of other rows. In this case, the table column shows a value like <unionM,N> to indicate that the row refers to the union of the rows with id values of M and N.
翻译:SELECT标识符,它是查询里的SELECT的顺序编号,如果这行涉及其他行联合的结果,这个值可能是NULL。在这种情况下,explain输出列中的table列会展示一个像<unionM,N>的值来指出该行涉及带id值为M和N的行的联合。
示例
# 快速创建三个表tb1, tb2, tb3
# 创建tb1
mysql> create table tb1(
-> id int unsigned not null primary key auto_increment comment '主键,自增',
-> name varchar(30) not null default '' comment '姓名'
-> ) engine=innodb auto_increment=1 default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_general_ci;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
# 创建tb2
mysql> create table tb2 like tb1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
# 创建tb3
mysql> create table tb3 like tb1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)一,id相同,按table列由上至下顺序执行
# id都是1,值相同,执行顺序是从上至下依次是tb1, tb2, tb3
mysql> explain select tb2.* from tb1, tb2, tb3 where tb1.id=tb2.id and tb1.id=tb3.id and tb1.name='jerry';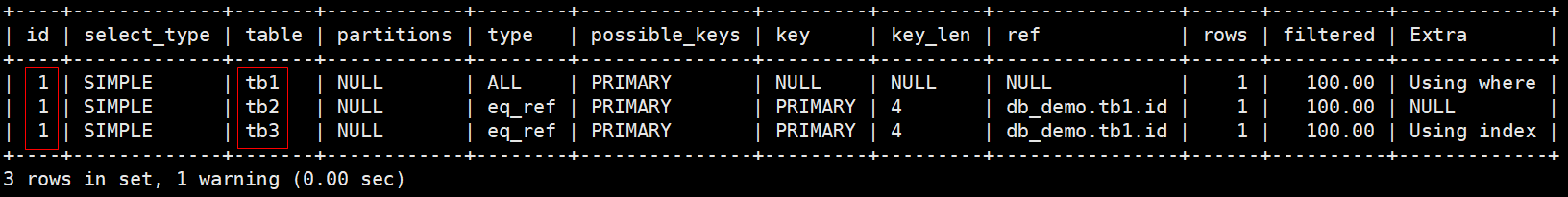
二,id不同,如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id的值越大优先级越高,越先被执行
# 分别向三个表中插入记录
mysql> insert into tb1 values(null, 'tom');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into tb2 select * from tb1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> insert into tb3 select * from tb1;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from tb1, tb2, tb3;
+----+------+----+------+----+------+
| id | name | id | name | id | name |
+----+------+----+------+----+------+
| 1 | tom | 1 | tom | 1 | tom |
+----+------+----+------+----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
# id不相同并且子查询的id是递增的,此时table列的执行顺序是tb3, tb1, tb2
# tb3的id是3优先被执行,其次是tb1, tb2
mysql> explain select tb2.* from tb2 where id=(select id from tb1 where id=(select tb3.id from tb3 where tb3.name='tom'));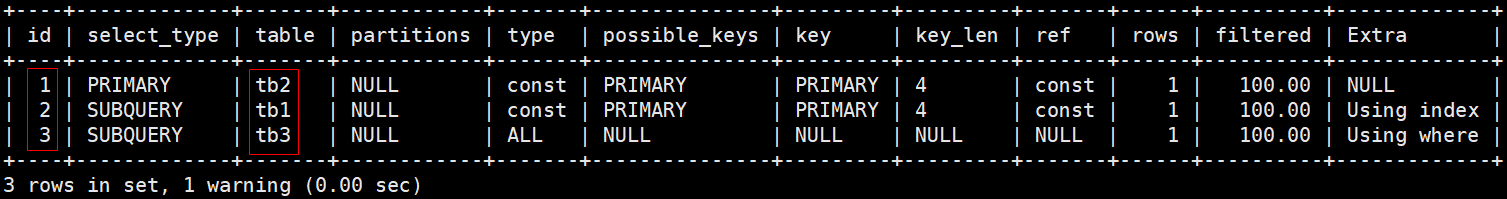
三,id相同不同,同时存在
# id相同都是1,顺序执行依次是tb3, tb2
mysql> explain select tb2.* from (select tb3.id from tb3 where tb3.name='') as n1, tb2 where n1.id=tb2.id;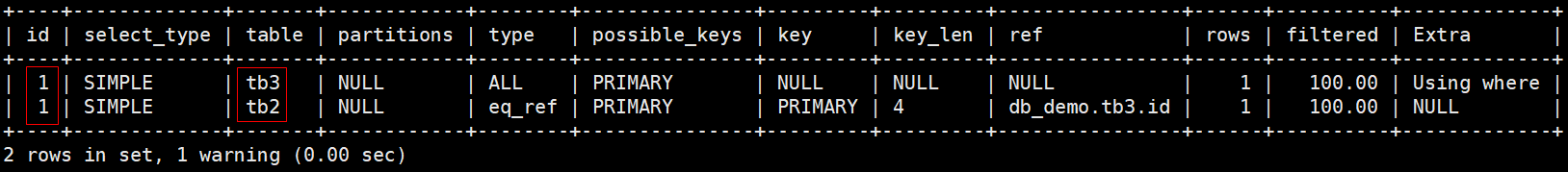
在上面的例子中没有模拟出id相同不同混合的情况,可以看下下面的截图

如上图所示,id如果相同,可以认为是一组,(本组内)从上往下顺序执行;在所有组中,id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行。
四,对于使用union的情况
# id有相同也有不同,相同id为一组,所以执行顺序为tb1, tb2, tb3
mysql> explain select tb3.* from tb3 union select tb2.* from (select tb1.* from tb1) as n1, tb2;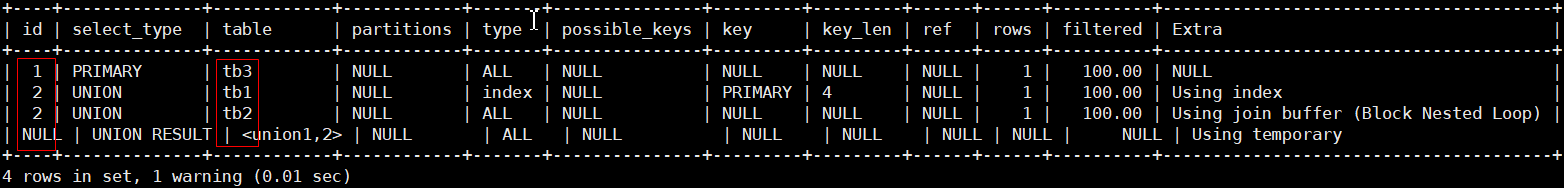
总结

注意:以上示例显示的结果是在centos7和mysql5.7.26上测试所得,其他mysql版本或环境结果可能会有所不同。