目的和数组一样,存储数据,底层是Objet的数组
ArrayList // 底层就是数组,java帮我们封装了
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // ()里可以给长度但是没有用
list.size() // 集合长度 注意:数组.length属性 String是.length()方法
集合名.add( 增加内容 );
list.add(111);
// 指定位置添加:
list.add(下标,添加内容);
list.add(2,654); //不能超出原来集合的最大长度
集合名.get( 下标 );
list.get(aaaa)
查找集合中的某个值
list.indexof("aaa");
// .indexof 返回指定数据第一次出现在集合中的下标,没找到返回-1
// .lastIndexof 返回指定数据最后一次出现在集合中的下标,没找到返回-1
// .contains 返回一个boolean类型, 查到/没查到。true/false
集合名.remove( 删除内容 );
list.remove("aaaa")
集合名.remove( int类型的对象 );
list.remove(new Integer(111));
list.set(下标,添加内容); //也会越界
list.set(2,5555);
list.isEmpty(); //true为空
list.size(); //0为空
list.clear();
List<Student> lists = new ArrayList<>(sets);
//把sets当做参数传入,实现转换
< > 泛型
< > 泛型 基本数据类型不是objte
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
// 父类指向子类对象,2种方式都可以
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
List<Student> list = new LinkedList<>();
//基本数据类型的泛型集合,必须使用包装类
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
集合长度增加原理
new——>长度 == 0 // 创建集合时长度为0
增——>长度 == 10 // 当在集合增加内容时默认给长度10
判断长度 if 10 - 10 > 0 // 每次添加时判断长度,当大于0时,调用grow方法
grow方法 10 = 10 + >>1 // 集合长度 = 集合长度 + 长度 >> 1 (10的话就是5)
使用copyof方法拷贝复制新数组,copyof( 原数组 ,15 )
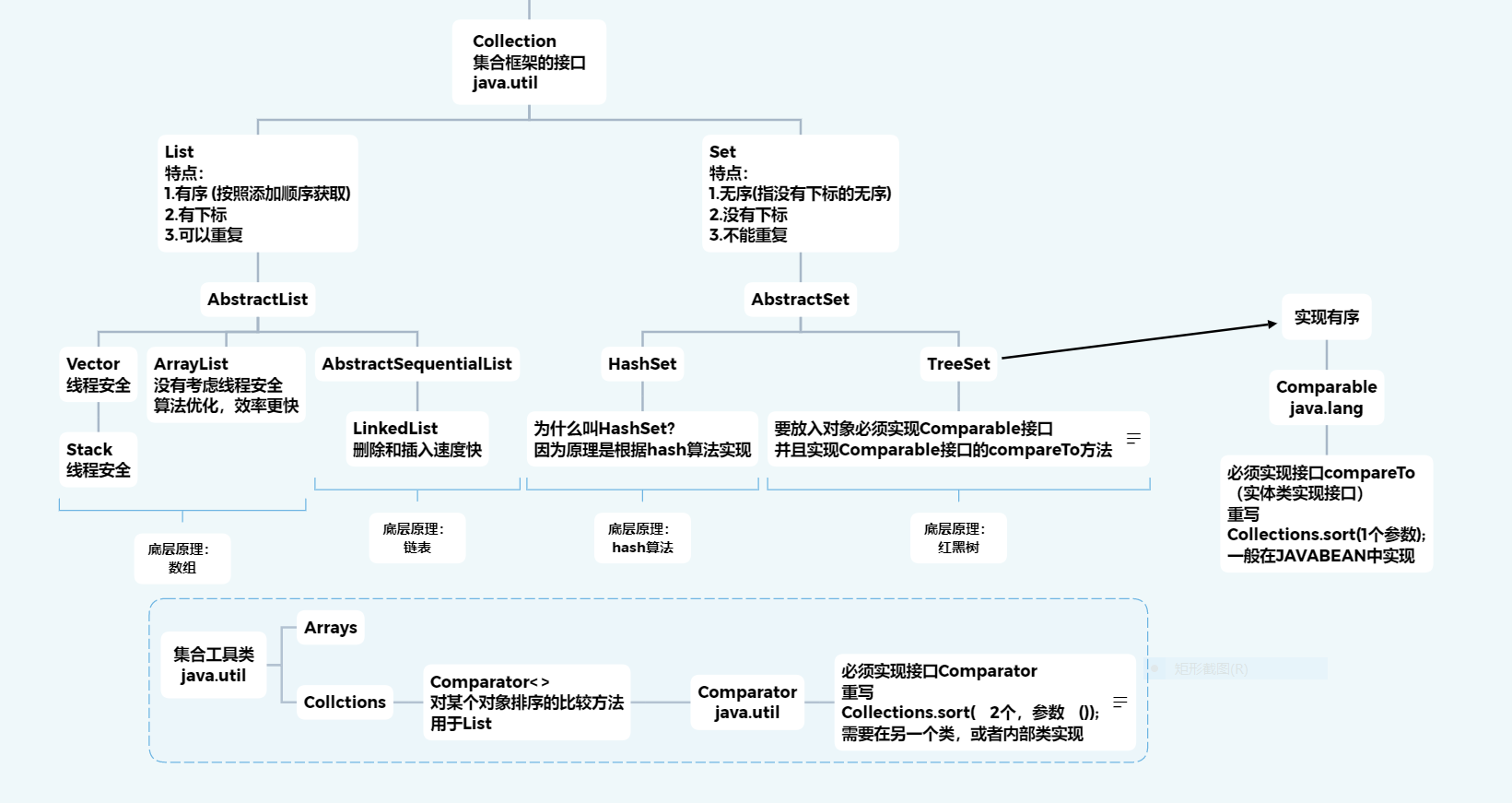
特点:
List接口:
1.都是有序的 (按照添加的顺序获取)
2.都有下标
Set接口:
特点:
1.不能重复,如果有重复后面的会覆盖前面重复的
2.没有下标,没有.get方法
3.无序的
Vector vector = new Vector()
ArrayList 和Vector有什么区别
ArrayList的方法和实现基本上和Vector一样,底层都是数组的实现
但是Vector的方法都是线程安全的,ArrayList没有考虑线程安全的问题
ArrayList在一些算法上做了优化,效率更高
Stack stack = new Stack(); 和Vector一样都是线程安全
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
LinkedList 和 ArrayList的区别:
1.ArrayList底层是数组的实现,LinkedList底层是链表的实现
2.ArrayList查找速度快,但是删除和插入的速度慢
3.LinkedList删除和插入的速度快,但是查询速度较慢
4.LinkedList有自己独有的addFirst,addLast,removeLast,removeFirst的方法
链表:
在java中链表就是自己实现了一个类,在类中记录了前一个和后一个的地址 每次查找都需要找到前一个或者后一个才能往前或者往后找到
双向循环链表,里面记录了下一个和上一个的地址
linkedList.First(" "); // 首
linkedList.Last(" ") // 尾
Set为什么叫HashSet
底层原理通过hash算法实现
HashSet set = new HashSer();
重写前根据内存生成hash值
object重写后: hash值为—根据内容(属性)hash值拼接。
equals重写: 比较内容。
通过重写boject只要他们内容一样 hash值就一样(没重写前object只有指向的对象地址一样hash值才一样,根据内存生成hash值)
重写equals只要他们内容一样就为true(没重写前对比的是引用类型变量指向的对象地址)
3种集合循环
for(Object obj:set){
syso(obj); //无序输出
}
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();
syso(obj); //有序输出
}
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
// 有序输出
}
TreeSet<Stdent> treeSet = new TreeSet<Stdent>(); //声明一个TreeSet类型
List<Student> lists = new ArrayList<>(sets); //转换为List类型
Collections.sort(lists); // Comparable接口 java.lang包
要实现有序,加入TreeSet的元素必须实现comparable接口的compareTo方法,通常写在JAVABEAN中。
Comparable:
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if(this.id > o.id) {
return 1;
}
else if(this.id < o.id){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
}
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(); //声明一个List类型
Collections.sort(list, new StudentCompare()); // Comparator接口 java.util
Comparator:
public class StudentCompare implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1 ==null || o2 == null) {
return 0;
}
return o1.getId() - o2.getId();
}
}