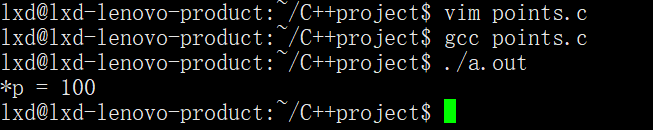
1.二级指针做形参
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void fun(int **temp) { *temp=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)); **temp=100; //可以,但是变量前两个*不常见,常用下面这种
//int *p=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
//*p=100;
//*temp=p; } int main() { int *p=NULL; fun(&p); printf("*p=%d\n",*p); free(p);
p=NULL; return 0; }


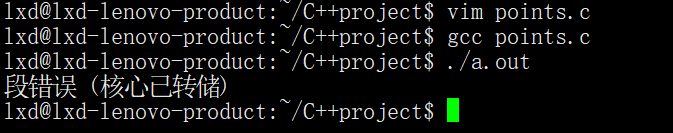
2.值传递1
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void fun(int *tmp) { tmp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); *tmp = 100; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int *p = NULL; fun(p); //值传递,形参修改不会影响实参 printf("*p = %d\n", *p);//err,操作空指针指向的内存 return 0; }
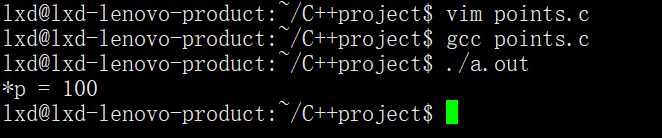
值传递2
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 void fun(int *tmp) 5 { 6 *tmp = 100; 7 } 8 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 9 { 10 int *p = NULL; 11 p=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); 12 fun(p); //值传递,形参修改不会影响实参 13 printf("*p = %d\n", *p); 14 free(p); 15 p=NULL; 16 return 0; 17 }
返回堆区地址
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int *fun() { int *tmp = NULL; tmp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); *tmp = 100; return tmp;//返回堆区地址,函数调用完毕,不释放 } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int *p = NULL; p = fun(); printf("*p = %d\n", *p);//ok //堆区空间,使用完毕,手动释放 if (p != NULL) { free(p); p = NULL; } return 0; }