使用的是[email protected]版本
首先安装 npm install create-react-app -g
然后创建文件 create-react-app react-test
进入文件
cd react-test
运行npm run eject让文件吧webpack相关配置暴露出来,之后删除node-modules (把不需要的包去掉),重新安装一次npm install
跨环境变量使用cross-env 安装(npm install cross-env --save-dev)
package.json配置
"scripts": {
"dev:test": "cross-env REACT_APP_SECRET_API='dev_test' node scripts/start.js",
"dev:build": "cross-env REACT_APP_SECRET_API='dev_build' node scripts/start.js",
"build:test": "cross-env REACT_APP_SECRET_API='build_test' node scripts/build.js",
"build": "cross-env REACT_APP_SECRET_API='production' node scripts/build.js",
"test": "node scripts/test.js"
},
找到config文件里的env.js,找到这个函数getClientEnvironment
function getClientEnvironment(publicUrl) { const raw = Object.keys(process.env) .filter(key => REACT_APP.test(key)) .reduce( (env, key) => { env[key] = process.env[key]; return env; }, { // Useful for determining whether we’re running in production mode. // Most importantly, it switches React into the correct mode. NODE_ENV: process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development', REACT_APP_SECRET_API:process.env.REACT_APP_SECRET_API,//加入自己的环境变量 // Useful for resolving the correct path to static assets in `public`. // For example, <img src={process.env.PUBLIC_URL + '/img/logo.png'} />. // This should only be used as an escape hatch. Normally you would put // images into the `src` and `import` them in code to get their paths. PUBLIC_URL: publicUrl, } );
创建你自己不用环境变量不同域名
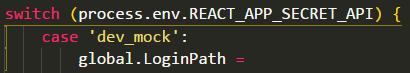
在入口index.js里面引入你自己定的文件名称
import './utils/initEnv';
然后就可以使用全部变量global了
然后就可以使用全部变量global了