一、什么是BIO
BIO是传统的通信技术,在BIO通信模型中,客户端发送请求给服务器,服务器每次都是会单独创建一个线程来监控客户端的请求,会为每个客户端创建一个线程来处理请求。当前服务器处理完成后,通过原来的输出流返回处理结果给到客户端。如图:
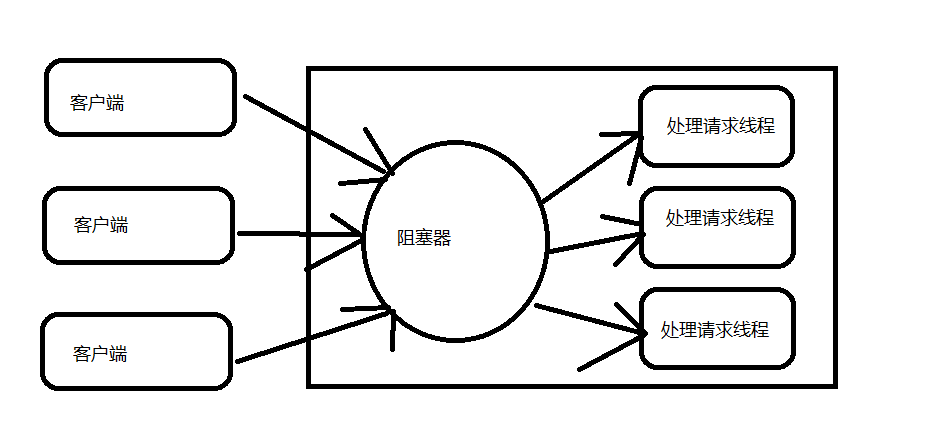
二、JDK实现BIO的案例
按照上面的图,我们知道至少需要三给类来完成,一个客户端,一个服务端,一个服务端逻辑处理:
服务器代码:
/** * 服务端代码 */ public class BioServer { //端口号 private final static int port = 8080; public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个ServerSocket对象,作为服务器 ServerSocket server = null; try { server = new ServerSocket(port); System.out.println("服务器启动,端口号为:" + port); Socket socket = null; while (true) { //阻塞服务器,等待客户端发送数据 socket = server.accept(); //客户端发送了数据,开始处理 new Thread(new BioServerShow(socket)).start(); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (server != null) { System.out.println("The time server close"); try { server.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } server = null; } } } }
服务器逻辑处理类:
/** * 服务器处理数据逻辑类 */ public class BioServerShow implements Runnable{ private Socket socket; public BioServerShow(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } @Override public void run() { //输入流的内容表示客户端带来的消息 BufferedReader in = null; //输出流的内容表示服务器要发送给客户端的内容 PrintWriter out = null; try { in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(this.socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(this.socket.getOutputStream(), true); String body = null; while (true) { body = in.readLine(); if (body == null) break; System.out.println("客户端发生的请求是: " + body); out.println("你好"); } } catch (Exception e) { if (in != null) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } if (out != null) { out.close(); out = null; } if (this.socket != null) { try { this.socket.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } this.socket = null; } } } }
客户端代码:
/** * 客户端代码 */ public class BioClient { public static void main(String[] args) { int port = 8080; //创建一个socke对象,连接服务器,IP和端口必须一致 Socket socket = null; //输入流的内容表示服务端带来的消息 BufferedReader in = null; //输出流的内容表示客户端要发送给服务端的请求 PrintWriter out = null; try { socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", port); System.out.println("客户端启动"); in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true); out.println("你好,我是客户端"); String resp = in.readLine(); System.out.println("服务器的消息是: " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { if (out != null) { out.close(); out = null; } if (in != null) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } in = null; } if (socket != null) { try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } socket = null; } } } }
测试:
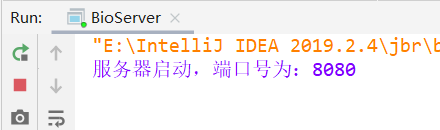
我们先运行服务端代码:
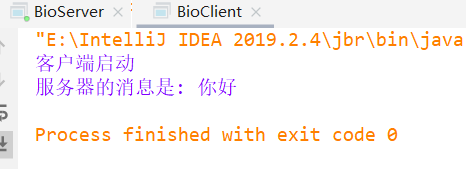
然后运行客户端代码:
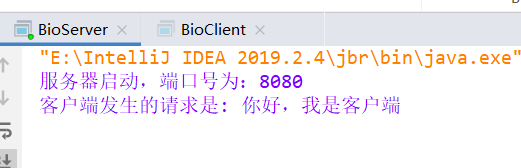
接下来我们在看服务端的控制台,发现有客户端的数据打印出来:
三、BIO通信的优点与缺点
先说优点:
1.模型简单,这个从上面的那张图就可以明白,BIO的模型是很简单的:客户端发送请求,服务器阻塞分发请求到处理的线程,最后将结果返回给客户端。
2.编码简单,这个也能从我们的代码中看见,编码逻辑都很简易的。
再说说缺点:
由于BIO的模型,我们就能发现这个模型最大的缺点就是性能太低,特别是在请求数过多的高并发下,服务器CPU的上下文切换太耗费资源,就是线程的创建与销毁。
