首先说一下,教科书上的扫描线算法确实是用c++很好实现,而且网上有很多源码,而java实现的基本没有(可能是我没看到),所以肖先生还是打算自己码(实验作业写这个而自己又个是写java的猿0.0)。
对于扫描线的实现过程,我只在这里大概讲下书本上的内容(自己去看),主要还是讲一下自己实现时算法的改动和实现方法。
扫描线算法:顾名思义,就是从Ymin开始扫描,然后构建出NET,之后根据NET建立AET。
贴个图:
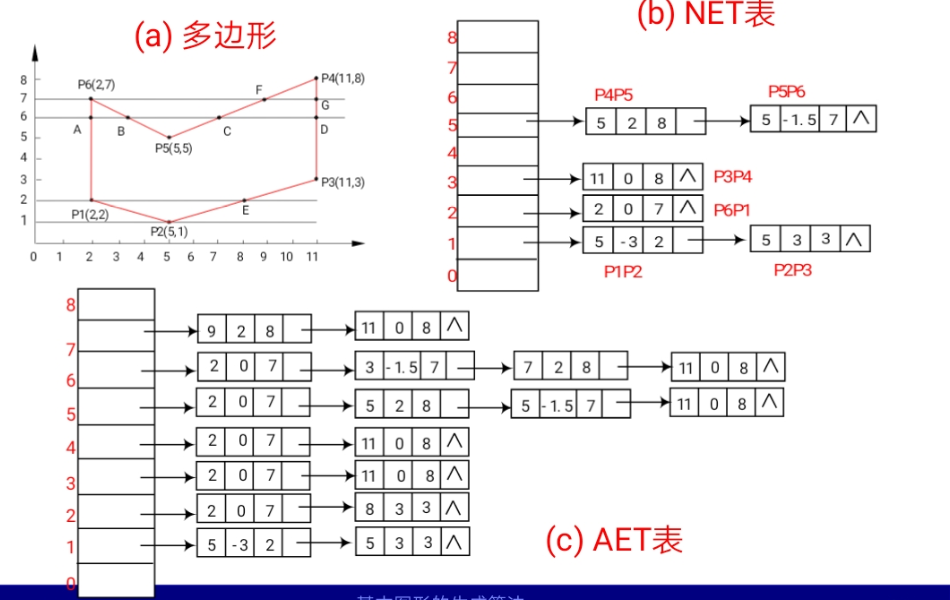

实现的时候首先是构造NET,因为对于java来说不能像c++一样直接用指针所以我用对象数组和Node类(如下代码)构造了类似数组+指针的数据结构。在实现了NET后开始通过NET实现AET,在这里我改变了一种实现方式,教科书上是一次次遍历扫描线,然后将NET插入AET后进行排序等一系列操作,而我因为是自己写的数据结构,如果说再建个表按书上的方式来最后还得自己实现链表排序等一系列操作。所以我这里直接用一个包含Arraylist的对象数组代替了。我的方法是:直接从NET开始遍历每个节点,得到节点后将它以及它自己之后会引申出的插入AET的节点(比如当前扫描线y=0 节点 X:1 dx:-1 Ymax:3 那之后会插入AET的就是 0 -1 1 和 -1 -1 2 )将这些节点不论顺序的先插入AET对应扫描线位置的对象数组的list中,将NET中节点全部遍历完之后再最后对AET中每个对象数组的list进行排序。最后得到了NET在进行打印。
贴个代码(仅供参考学习交流):
package PolygonScanningAndFilling; public class Node { //新编表记录x,dx,yMax public int x; public float dx; public int yMax; public Node next; public int ymin; public Node(int x, int dx, int yMax){ this.x=x; this.dx=dx; this.yMax=yMax; } public void getYmin(int Ymin){ this.ymin=Ymin; } }
package PolygonScanningAndFilling; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class classAndArray { public List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); public classAndArray(){ } public void listSort() { Collections.sort(list); } }
package PolygonScanningAndFilling; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; import java.awt.event.KeyListener; import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter; import java.awt.event.MouseEvent; import java.io.IOException; public class PolygonScanning extends JPanel { static int X0; static int Y0; static int X1; static int Y1; static int a[]=new int [10]; //保存点击的10个x坐标 static int b[]=new int [10]; //保存点击的10个y坐标 static int index=0; static int time=0; @Override protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) { super.paintComponent(g); this.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() { public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) { time++; repaint(); } }); Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g; int Ymax=0; for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++) { if(Ymax<b[i]) Ymax=b[i]; } // System.out.println("Ymax"+Ymax); /* * 画出多边形 */ int Sum=0; for(;Sum<=index;Sum++) { if(Sum==index-1) { g2d.drawLine(a[Sum], b[Sum], a[0],b[0]); break; } else { g2d.drawLine(a[Sum], b[Sum], a[Sum+1],b[Sum+1]); } } if(time!=0) { Node [] head =new Node [Ymax]; //建立对应扫描边数的链表长度 for(int i=0;i<index-1;i++) { if(b[i]<b[i+1]) //从第一个点开始若前一个点小于后一个点 { if(head[b[i]]==null) head[b[i]]=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[i]].ymin=b[i]; if(head[b[i]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点 { head[b[i]].next=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[i]].next.x=a[i]; head[b[i]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i]].next.yMax=b[i+1]; //ymax为后一点的y } else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点 if(head[b[i]].next.next==null) head[b[i]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0); if((float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1])<head[b[i]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小 { head[b[i]].next.next.x=head[b[i]].next.x; head[b[i]].next.next.dx=head[b[i]].next.dx; head[b[i]].next.next.yMax=head[b[i]].next.yMax; head[b[i]].next.x=a[i]; head[b[i]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i]].next.yMax=b[i+1]; } else { head[b[i]].next.next.x=a[i]; head[b[i]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i]].next.next.yMax=b[i+1]; } } } else { if(head[b[i+1]]==null) head[b[i+1]]=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[i+1]].ymin=b[i+1]; if(head[b[i+1]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点 { head[b[i+1]].next=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[i+1]].next.x=a[i+1]; head[b[i+1]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i+1]].next.yMax=b[i]; //ymax为后一点的y } else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点 if(head[b[i+1]].next.next==null) head[b[i+1]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0); if((float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1])<head[b[i+1]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小 { head[b[i+1]].next.next.x=head[b[i+1]].next.x; head[b[i+1]].next.next.dx=(float)head[b[i+1]].next.dx; head[b[i+1]].next.next.yMax=head[b[i+1]].next.yMax; head[b[i+1]].next.x=a[i+1]; head[b[i+1]].next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i+1]].next.yMax=b[i]; } else { head[b[i+1]].next.next.x=a[i+1]; head[b[i+1]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[i]-a[i+1])/(b[i]-b[i+1]); head[b[i+1]].next.next.yMax=b[i]; } } } } if(index>0) { if(b[0]<b[index-1]) //从第一个点到最后一个点 { if(head[b[0]]==null) head[b[0]]=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[0]].ymin=b[0]; if(head[b[0]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点 { head[b[0]].next=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[0]].next.x=a[0]; head[b[0]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[0]].next.yMax=b[index-1]; //ymax为后一点的y } else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点 if(head[b[0]].next.next==null) head[b[0]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0); if((float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1])<head[b[0]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小 { head[b[0]].next.next.x=head[b[0]].next.x; head[b[0]].next.next.dx=head[b[0]].next.dx; head[b[0]].next.next.yMax=head[b[0]].next.yMax; head[b[0]].next.x=a[0]; head[b[0]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[0]].next.yMax=b[index-1]; } else { head[b[0]].next.next.x=a[0]; head[b[0]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[0]].next.next.yMax=b[index-1]; } } } else { if(head[b[index-1]]==null) head[b[index-1]]=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[index-1]].ymin=b[index-1]; if(head[b[index-1]].next==null) //该点是第一个插入的节点 { head[b[index-1]].next=new Node(0,0,0); head[b[index-1]].next.x=a[index-1]; head[b[index-1]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[index-1]].next.yMax=b[0]; //ymax为后一点的y } else { //该点不是第一个插入的节点 if(head[b[index-1]].next.next==null) head[b[index-1]].next.next=new Node(0,0,0); if((float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1])<head[b[index-1]].next.dx) //当前插入x比之前存在的节点x小 { head[b[index-1]].next.next.x=head[b[index-1]].next.x; head[b[index-1]].next.next.dx=head[b[index-1]].next.dx; head[b[index-1]].next.next.yMax=head[b[index-1]].next.yMax; head[b[index-1]].next.x=a[index-1]; head[b[index-1]].next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[index-1]].next.yMax=b[0]; } else { head[b[index-1]].next.next.x=a[index-1]; head[b[index-1]].next.next.dx=(float)(a[0]-a[index-1])/(b[0]-b[index-1]); head[b[index-1]].next.next.yMax=b[0]; } } } } for(int i=0;i<Ymax;i++) if(head[i]!=null) while(head[i].next!=null) { System.out.println("新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.yMax); if(head[i].next.next!=null) { System.out.println("多的"+"新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.next.yMax); } break; } int YMIN=b[0]; for(int i=0;i<b.length;i++) { if(YMIN>b[i]&&b[i]!=0) YMIN=b[i]; } classAndArray [] ca=new classAndArray [Ymax]; for(int i=YMIN;i<Ymax;i++) ca[i]=new classAndArray(); //一个点一个点的全装入ca中再排序打印出点 for(int i=0;i<Ymax;i++) { if(head[i]!=null) if(head[i].next!=null) { //System.out.println("新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.yMax); for(int j=head[i].ymin;j<head[i].next.yMax;j++) { ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.add(head[i].next.x+(int)(0.5+((j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.dx))); //System.out.print("ca[i+j-head[i].ymin]为"+(i+j-head[i].ymin)+"值为"+ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.toString()); //System.out.println("Ymin为"+i+" x为"+(head[i].next.x+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.dx)); } if(head[i].next.next!=null) { for(int j=head[i].ymin;j<head[i].next.next.yMax;j++) { ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.add(head[i].next.next.x+(int)(0.5+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.next.dx)); //System.out.print("next中ca[i+j-head[i].ymin]为"+(i+j-head[i].ymin)+"值为"+ca[i+j-head[i].ymin].list.toString()); //System.out.println("Ymin为"+i+" x为"+head[i].next.next.x+(j-head[i].ymin)*head[i].next.next.dx); } //System.out.println("多的"+"新编表y"+head[i].ymin+"新编表x"+head[i].next.next.x+"新编表dx"+head[i].next.next.dx+"新编表yMax"+head[i].next.next.yMax); } } } // for(int i=YMIN;i<Ymax;i++) { ca[i].listSort(); for (int j = 0; j < ca[i].list.size(); j++) { if(j%2==0||(j==0)) { g2d.drawLine(ca[i].list.get(j), i, ca[i].list.get(j+1), i); } } System.out.println(ca[i].list.toString()); } } } private static void createAndShowGUI() { JFrame frame = new JFrame(); frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); frame.setLayout(null); JPanel jp=new JPanel(); frame.setContentPane(jp); frame.setVisible(true); frame.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() { }); jp.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() { public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) { if(e.getButton() == e.BUTTON1) {a[index]=e.getX(); b[index]=e.getY(); System.out.println("坐标为("+a[index]+","+b[index]+")"); index++; frame.setVisible(true); } if(e.getButton() == e.BUTTON3) { frame.setContentPane(new PolygonScanning()); frame.setVisible(true); } } } ); frame.setSize(600, 600); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); frame.setVisible(true); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { createAndShowGUI(); } }
效果截图(先在面板里点击点,右键出现所需填充的轮廓,鼠标移出面板填充)

