Basic Concepts
Probability concepts
Terms
- Random variable
- A quantity whose possible values are uncertain.
- Outcomes
- The possible values of a random variable.
- Event
- A specified set of outcomes.
Properties
- 0 <= P(E) <=1

Events

Odds (赔率)
Odds for the event E
- P(E)/[1-P(E)]
Odds against the event E
- [1-P(E)]/P(E)
Example
- Goven (horse will win the race) = 1/8, what are the odds for or against the horse will win the race?
- Odds for horse will win the race = (1/8) / (1-1/8) = 1/7
- Odds against horse will win the race = (1-1/8) / (1/8) = 7/1
Rule
Multplication rule **
- P(A|B) = P(AB)/P(B)
- P(AB) = P(B)xP(A|B) = P(A)xP(B|A)
- For mutually exclusive enents: P(AB) = 0
- For independent events: P(AB) = P(A)P(B)
Addition rule
- P(A+B) = P(A)+P(B)-P(AB)
- For mutually exclusive events: P(A+B) = P(A)+P(B)
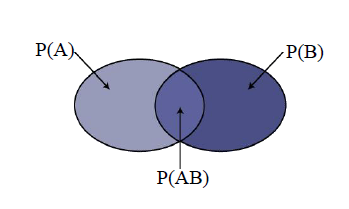
- 含义:
- P(A|B) : 在B发生的条件下A发生;
- P(B|A): 在A发生的条件下B发生;
- P(AB): A发生且B也发生.
Total probability rule (全概率法则)
- 全概率法则, 包含了所有可能发生的情况
- Definition
- explains the unconditional probability of the event in terms of probabilities conditional on the scenarios.
- Formula
- P(A) = P(A|S1)P(S1) + P(A|S2)P(S2)... + P(A|Sn)P(Sn)
- where S1,S2...Sn are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
- 其实就是乘法法则 P(A|S1)P(S1) = P(AS1)

-
- 其实就是乘法法则, P(AS1)+P(AS2)+P(AS3)+P(AS1=4)
- P(AS1)= PS1(PA|S1)
- 其实就是乘法法则, P(AS1)+P(AS2)+P(AS3)+P(AS1=4)
Baye's formula (贝叶斯公式)
- Definition
- given a prior probabilities P(A) for an event, if you receiv new information (B), the rule for updating your probability(posterior probability, P(A|B)) of the event.
- forula:
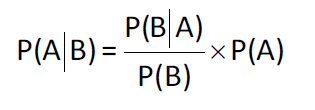
Probability Statistics
Expected value **
- Definition
- the probability-weighted average of the possible outcomes of the random variable(X)
- Calculation
- E(X) = P(X1)X1 + P(X2)X2 ... + P(Xn)Xn
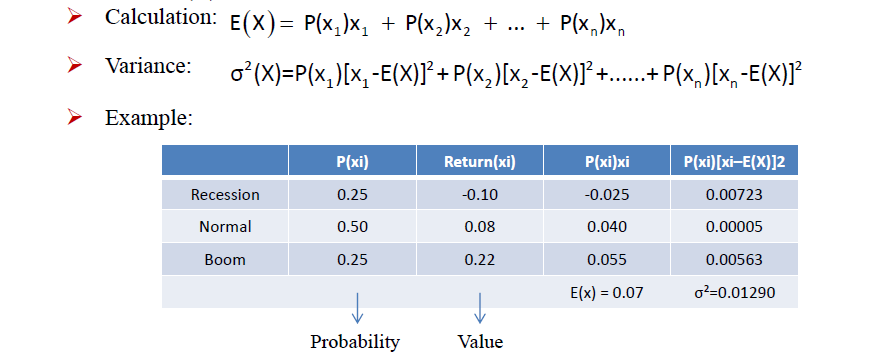
插入老师手写板书 - Variance 插入公式, 例题; 插入老师的手写板书.
- 其实求方差也是在求加权平均
- 算期望就是算加权平均. 相当于基于概率的加权平均. 所以计算期望需要两个值, probability和value.
Covariance (协方差) ***
- Definition
- A easure of how two variables move together. 两个随机变量变动的方向性.
- Calculation
-
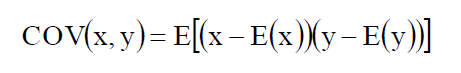
- Characteristics
- Positive covariance: the two variables tend to move together. 你涨我也涨,你跌我也跌.
- Negative covariance: the two variables tend to move in apposite direction. 你涨我跌.
- Valuses range from minus infinity to positive infinity
- Units of covariance difficult to interpret (比如若是人的平方, 这样的单位没有任何意义)
- Autocovariance is equal to the variance? 这句话怎么理解?
插入老师手书, 因为协方差是衡量两个变量,所以把其中一个x换成了y 插入例题
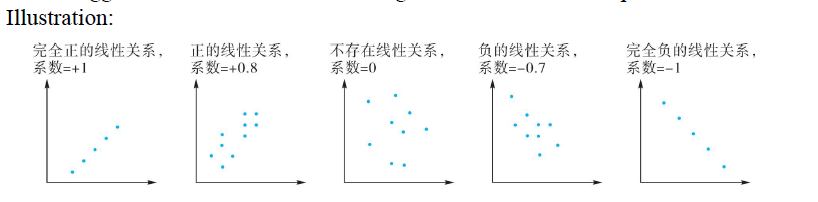
Correlation (相关系数,相关性) ***
- Definition
- A standardized measure of linear relationship between two variables.
- Calculation
- Characteristics
- Values range from -1 (perfect negative correlation) to +1 (perfect positive correlation)
- A correlation of 0 indicates an absence of any linear(straight-line) relationship and doesn't indicate independence (相关系数是0只说明两个变量没有线性关系, 不代表两个变量互不影响. 比如y=x*x,虽然不是线性关系, 但是抛物线)
- The bigger the absolute value, the stronger the linear relationship.