结对成员 3117004646 陈浩民
3117004676 叶剑庭
一、Github项目地址:https://github.com/silakami/Myapp.exe
二、PSP表格
| Planning | 计划 | 40 | 35 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 40 | 35 |
| Development | 开发 | 1480 | 1585 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 | 150 | 150 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 80 | 65 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 60 | 70 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 | 30 | 30 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 90 | 90 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 900 | 1000 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 80 | 90 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 90 | 90 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 150 | 150 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 70 | 70 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 40 | 40 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 40 | 40 |
| 合计 | 1670 | 1770 |
三、效能分析
在优化之前,生成10000条算式的时间:
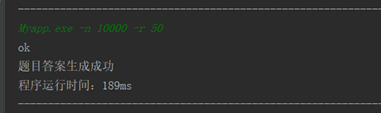

优化之后,生成10000条算式的时间
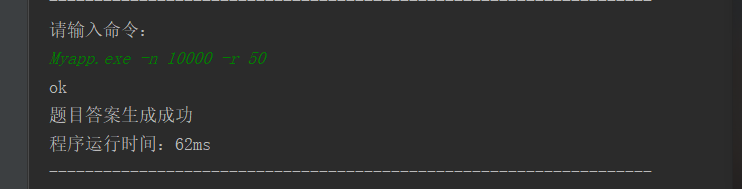
优化内容:
在原来生成题目中,括号的数量是通过随机生成得到的,但必须要生成该数量的括号,由于是随机生成,所以可能需要很多次都生成出相同的或者是位置不正确的括号,需要删掉重新再生成,后来将括号生成改成了同样是随机生成,但是不需要一定生成这个数量的括号,一旦生成失败就跳过,直到循环结束,这样能使循环的次数减少,提升运行速度,但是降低了括号嵌套的概率。
四、设计实现过程
流程图
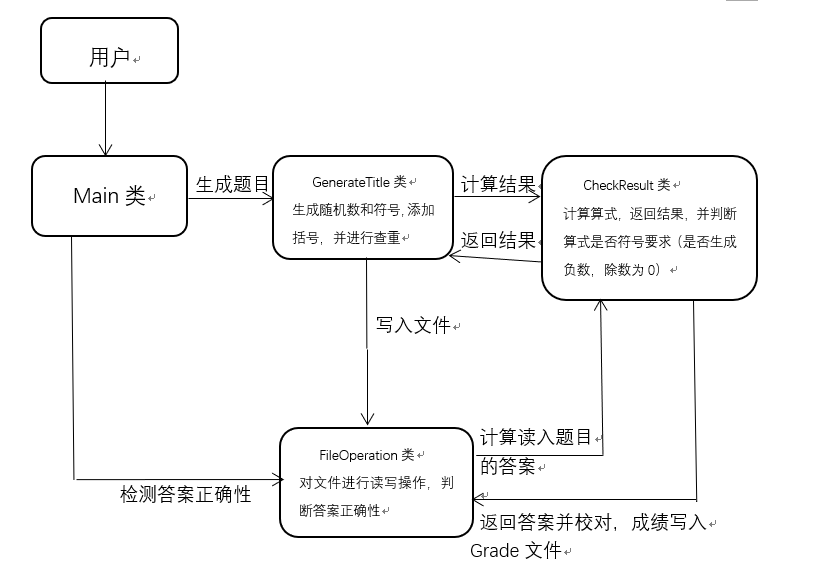
对于这个题目,我们将其分成了四个类:Main类,FileOperation类,GenerateTitle类,CheckResult类。
1、Main类:用正则表达式对输入进行检测,接收用户输入。
2、FileOperation类:对文件进行读写操作,并且对读入的文件进行答案校对。
3、GenerateTitle类:使用随机数,生成题目,并且对其添加括号和查重。
4、CheckResult类:专门负责计算题目的答案。
五、代码说明
1、GenerateTitle类
这部分最主要是插入括号和查重,其他生成操作数和操作符是通过随机数生成,然后将它们放到两个数组中,这样方便构建算式和查重,其他生成随机数,真分数都不难,化简只需要求出最大公因数,然后约分就行了。
括号方法,我们的思路是不管怎样先生成随机生成左括号,然后再随机生成右括号。在生成左括号时,要判断这个地方是否已经生成过左括号了,这里就要分两类讨论:①此处没有生成过左括号,则在生成右括号时,需要判断生成右括号的位置是否存在左括号或者左括号位置是否有右括号,如果有,则需要重新生成右括号。②此处已经生成过左括号,则在生成右括号时,需要判断该位置是否有右括号,如果有,那肯定是两个括号括住同一条式子,则需要重新生成,最后还是要判断生成右括号的位置是否存在左括号或者左括号位置是否有右括号。这样才能保证括号的正确加入。
但是这里有个缺陷,这里生成的括号不一定有意义,如1+(2+3),我们没有做到将这种没有意义的括号去除方法,因为要保证不能把程序写死,要保留扩展性,这样做这个确实很难,但是如果能做完,查重就变得简单很多了。
/** * 生成括号 * @param num 操作数数组 * @param op 操作符数组 * @param operatorNum 操作数个数 * @return */ public String Cover(String[] num, String[] op,int operatorNum){ String title = null; int i, j, k, judge, lPoint, rPoint,midel,judge_left,judge_right; Random ra = new Random(); if(operatorNum == 1) title = num[0] + " " +op[0] + " " + num[1]; //只有一个操作符,不能生成括号 else{ k = ra.nextInt(operatorNum); //随机生成括号数量 if(k >= operatorNum) //括号数量需要小于等于操作符数量减1,否则括号生成位置会出错 k = ra.nextInt(operatorNum); if(k == 0) { //不生成括号,直接组装算式 title = num[0]; for (i = 1; i < operatorNum + 1; i++) title = title + " " + op[i - 1] + " " + num[i]; } else{ //采用两个数组,长度为操作数个数,用来标志左右括号的位置 int[] leftBracket = new int[operatorNum + 1]; //左括号,元素值为该位置左括号数量 int[] rightBracket = new int[operatorNum + 1]; //右括号,元素值为该位置右括号数量 for(i = 0;i < operatorNum+1;i++) { //需要赋初值 leftBracket[i] = 0; rightBracket[i] = 0; } for(i = 0;i < k;i++){ //生成括号 lPoint = ra.nextInt(operatorNum); //随机生成左括号位置 judge = 0; //标志作用 //判断该位置是否有左括号 if(leftBracket[lPoint] == 0) { midel = 0; //标志该位置没有左括号 leftBracket[lPoint]++; } else{ midel = 1; //标志该位置存在左括号 leftBracket[lPoint]++; } rPoint = ra.nextInt(operatorNum) + 1; //随机生成右括号 while(rPoint <= lPoint || (lPoint == 0 && rPoint == operatorNum)) //该右括号不能在左括号左边,且不能和左括号在同一位置 rPoint = ra.nextInt(operatorNum) + 1; if(midel == 0){ //该位置上没有左括号 if(leftBracket[rPoint] != 0) { //判断在右括号的位置上是否存在左括号 while (leftBracket[rPoint] != 0 || (lPoint == 0 && rPoint == operatorNum) || rPoint <= lPoint) { //随机再产生右括号,若当跳出循环前都没有合适的右括号,则去掉左括号 rPoint = ra.nextInt(operatorNum) + 1; judge++; //防止出现死循环 if(judge == operatorNum) //跳出循环 break; } if(rightBracket[lPoint] != 0 || leftBracket[rPoint] != 0 || judge == operatorNum) { //避免先生成左括号再生成右括号或者反过来生成的情况,即左括号位置有右括号或者右括号位置有左括号,如(3+(4)+5+6) leftBracket[lPoint]--; //去掉该左括号 continue; } rightBracket[rPoint]++; //添加右括号 } else rightBracket[rPoint]++; //添加右括号 } else{ //在生成左括号位置已经有左括号 if(rightBracket[rPoint] != 0) { //右括号位置已经存在右括号,这种情况不合法,需要重新生成,如((3+4))+5 while (rightBracket[rPoint] != 0 || (lPoint == 0 && rPoint == operatorNum) || rPoint <= lPoint) { rPoint = ra.nextInt(operatorNum) + 1; judge++; //防止死循环 if(judge == operatorNum) break; } if(rightBracket[lPoint] != 0 || leftBracket[rPoint] != 0 || judge == operatorNum) { leftBracket[lPoint]--; continue; } rightBracket[rPoint]++; } else rightBracket[rPoint]++; } judge_left = 0; judge_right = 0; //由于为了避免增加复杂情况来进行判断,不同情况用不同的生成方法(从内向外,从外向内) //这样减少了括号嵌套的概率,但使代码变简单 for(j = lPoint;j <= rPoint;j++){ if(leftBracket[j]!=0) //遇到左括号,加该位置左括号个数 judge_left+=leftBracket[j]; if(rightBracket[j]!=0) //加右括号 judge_right+=rightBracket[j]; } if(judge_left!=judge_right){ //如果左括号数量不等于右括号,则不生成括号 rightBracket[rPoint]--; leftBracket[lPoint]--; continue; } //添加括号 num[lPoint] = "(" + num[lPoint]; num[rPoint] = num[rPoint] + ")"; } } title = num[0]; for(i = 1;i < operatorNum+1;i++) title = title + " " + op[i - 1] + " " + num[i]; return title; } return title; }
查重方法
为何这里要注释掉呢,因为这个查重方法实在是太糟糕了,我们没有想到更优的算法来实现查重,只能够用最白痴的算法来做,它的复杂度是O(n^2),实际上算上外循环是O(n^3),这效率不敢想象,我们生成10000道题需要50s的时间才能生成完,如果没有优化这个算法就不能实际用在我们的程序中,这就是没用数据结构的悲哀。但是在查重时还需要考虑很多效率问题,当-r参数很大的时候,基本上是不会出现重复的,但是-n大于一定值的时候,就有很大可能或者一定会出现重复,我们需要花很大的精力去重新生成一个不重复的式子,甚至进入死循环,这两种情况相当影响算法的效率。
/* else { //检查重复的算式 checkCopy = "no"; if(judgement == "yes" && i != 0) for(k = 0;k < i;k++){ checkCop = answer[k].split(Integer.toString(k+1)+". "); if(checkCop[1].equals(checkOut)){ //减少检测数量,检测答案相同的式子 checkCop = title[k].split(Integer.toString(k+1)+". "); w = 0; //检测长度相同的式子 if(!checkCop[1].contains(num[0]) && checkCop[1].split(" ").length == (operationNumber + operatorNum)) continue; while(w < operatorNum){ //检测式子内部内容 if(!checkCop[1].contains(num[w+1])) break; else if(!checkCop[1].contains(operator[w])) break; w++; } checkCopy = "yes"; break; } else checkCopy = "no"; } if(checkCopy == "no") { answer[i] = Integer.toString(i + 1) + ". " + checkOut; title[i] = Integer.toString(i + 1) + ". " + title[i]; } else i--; }*/
2、CheckResult类
这个类和GenetateTitle类是这个程序的两大核心,而这个类的核心是计算,计算的方法也是相当经典,使用后缀表达式来计算,实际上这个算法思路并不难,关键是具体实现的方法问题,这里我们用了一个技巧,将自然数都当成分数(分母为1)来计算,这样极大地方便程序的设计。
/** * 采用后缀表达式计算生成的式子,具体思路参照逆波兰式算法 * @param str 题目 * @return */ public String Calc(String str){ GenerateTitle gen = new GenerateTitle(); char[] title = str.toCharArray(); Stack<Character> operator = new Stack<Character>(); //符号栈 operator.push('k'); //压入标志位'k' Stack<String> number = new Stack<String>(); //操作数栈 number.push("q"); //压入标志位"q" String molecule1, molecule2, denominator1, denominator2; String molecule, midel, denominator; char operating; String[] result; String[] finResult = new String[2]; int judgeXie, judgeFen, divisor; outer: for(int i = 0;i < title.length;i++){ judgeXie = 0; //初始化'/'标志 judgeFen = 0; //初始化'\''标志 if(title[i] == '(') //若从题目取出"(",则入运算符栈 operator.push(title[i]); else if(title[i] == ')'){ /*若从题目取出")",则从操作数栈取出两个操作数,并从运算符栈取出一个运算符,并进行运算 *运算完的结果重新压入操作数栈,重复以上过程,直到遇到第一个"(",最后将其出栈 * 计算时一次取两个数,即为操作数的分子和分母 */ while(!operator.peek().equals('(')){ denominator2 = number.pop(); //取第二个操作数分母 molecule2 = number.pop(); //取第二个操作数分子 denominator1 = number.pop(); //取第一个操作数分母 molecule1 = number.pop(); //取第一个操作数分母 operating = operator.pop(); //取操作符 result = CalcAndCheck(operating, molecule1, denominator1, molecule2, denominator2); //如果不符合规范(产生负数或除数为0),则返回null,重新生成一个新的算式 if(result == null) return null; else{ //将计算结果压栈 number.push(result[0]); number.push(result[1]); } } //将左括号出栈 operator.pop(); } else if(title[i] == '+' || title[i] == '-' || title[i] == '×' || title[i] == '÷'){ /*若从题目取出操作符,若栈顶操作符优先级高于该操作符,则从操作数栈取出两个操作数,并从运算符栈取出一个 *运算符,并进行运算,运算完的结果重新压入操作数栈,重复以上过程,直到操作符栈的栈顶元素优先级小于从题 *目取出的运算符的优先级(不含等于),则将该操作符压入栈,否则直接入栈 */ if(operator.peek()!='k' && number.peek()!="q"){ //判断栈是否为空 operating = operator.peek(); //取栈顶元素,但不出栈 while(operator.peek()!='k' && number.peek()!="q" && !JudgePriority(operating, title[i])){ //做上述操作直到栈空或者操作符优先级高于栈顶操作符 denominator2 = number.pop(); molecule2 = number.pop(); denominator1 = number.pop(); molecule1 = number.pop(); operating = operator.pop(); result = CalcAndCheck(operating, molecule1, denominator1, molecule2, denominator2); if(result == null) return null; else{ //将计算结果压栈 number.push(result[0]); number.push(result[1]); } operating = operator.peek(); } } //操作符压栈 operator.push(title[i]); } else if(title[i] >= '0' && title[i] <= '9'){ /*取出操作数,将操作数压栈 *这里的将自然数当作分数来算,分母为1,这样极大地减少了计算的复杂度 * 需要区分 * 若为真分数,则molecule代表分子部分,denominator代表分母部分 * 若为假分数,则molecule代表整数部分,midel代表分子部分,denominator代表分母部分 */ molecule = midel = denominator = String.valueOf(title[i]); //取第一个数 i++; if(i == title.length){ //如果到达算式末尾,则直接压入栈 number.push(molecule); number.push("1"); //这种情况只能为整数,所以分母压入1 continue; } //取完整的操作数 while(i < title.length && title[i] != ' ' && title[i] != ')'){ if(title[i] == '/') { //遇到'/',则为分母,取分母部分 judgeXie = 1; i++; denominator = String.valueOf(title[i]); //取分母的第一位 if(i == title.length - 1){ //到达算式末尾 i--; if(judgeFen == 1){ //判断是否为真分数,如果是,则将需要将带分数转化为假分数,再压栈 number.push(String.valueOf(Integer.valueOf(molecule) * Integer.valueOf(denominator) + Integer.valueOf(midel))); } else number.push(molecule); number.push(denominator); break outer; //下一个循环 } i++; continue; } if(title[i] == '\''){ //遇到'\'',即为带分数,则取分子部分 judgeFen = 1; judgeXie = 2; i++; midel = String.valueOf(title[i]); i++; continue; } if(judgeXie == 0) molecule = molecule + String.valueOf(title[i]); else if(judgeXie == 1) denominator = denominator + String.valueOf(title[i]); else if(judgeFen == 1) midel = midel + String.valueOf(title[i]); i++; } if(judgeXie == 1){ i--; if(judgeFen == 1) { number.push(String.valueOf(Integer.valueOf(molecule) * Integer.valueOf(denominator) + Integer.valueOf(midel))); } else number.push(molecule); number.push(denominator); } else{ i--; number.push(molecule); number.push("1"); } } } //计算最终结果 while(operator.peek()!='k'){ denominator2 = number.pop(); molecule2 = number.pop(); denominator1 = number.pop(); molecule1 = number.pop(); operating = operator.pop(); result = CalcAndCheck(operating, molecule1, denominator1, molecule2, denominator2); if(result == null) //不符合规范,返回null重新生成新的算式 return null; else{ //将计算结果压栈 number.push(result[0]); number.push(result[1]); } } finResult[1] = number.pop(); //取最终结果分母 finResult[0] = number.pop(); //取最终结果分子 if(finResult[1].equals("1")) //若分母为1,则为整数 return finResult[0]; else if(finResult[0].equals("0")) //若分子为0,则答案为0 return "0"; else{ divisor = gen.CommonDivisor(Integer.valueOf(finResult[0]), Integer.valueOf(finResult[1])); //计算最大公约数 //将结果化简和化成分数,并返回 return gen.ChangePorper(Integer.valueOf(finResult[0]), Integer.valueOf(finResult[1]), divisor); } } /** * 判断符号优先级,只有 * @param befor 符号栈顶的符号 * @param after 算式的符号 * @return */ public boolean JudgePriority(char befor, char after){ if((befor == '+' || befor == '-') && (after == '×' || after == '÷')) return true; else if(befor == '(') { //'('标志着边界,不能再往左计算 return true; } else { return false; } } /** * 对操作数进行运算,具体就是简单的两个分数相运算 * @param operator 操作符 * @param mole1 操作数1分子 * @param demo1 操作数1分母 * @param mole2 操作数2分子 * @param demo2 操作数2分母 * @return */ public String[] CalcAndCheck(char operator, String mole1, String demo1, String mole2, String demo2){ String[] result = new String[2]; int m1, m2, d1, d2; m1 = Integer.valueOf(mole1); m2 = Integer.valueOf(mole2); d1 = Integer.valueOf(demo1); d2 = Integer.valueOf(demo2); if(operator == '+'){ result[0] = String.valueOf(m1 * d2 + m2 * d1); result[1] = String.valueOf(d1 * d2); } else if(operator == '-'){ if((m1 * d2 - m2 * d1) < 0) //判断在计算过程中是否会产生负数 return null; result[0] = String.valueOf(m1 * d2 - m2 * d1); result[1] = String.valueOf(d1 * d2); } else if(operator == '×'){ result[0] = String.valueOf(m1 * m2); result[1] = String.valueOf(d1 * d2); } else{ if(m2 == 0 || d2 == 0) //除数是否为0 return null; result[0] = String.valueOf(m1 * d2); result[1] = String.valueOf(d1 * m2); } return result; }
3、FileOperation类
这个类就是基本的IO操作,最主要但也相当简单的是对答案的方法,直接调用CheckResult类的计算方法,然后用equals方法来检测答案是否相同就行了。
/** * 写入文件方法,将生成的题目和答案写入文本文件 * @param title 题目数组 * @param answer 答案数组 */ public void FWriter(String[] title,String[] answer){ String titleFile = "src\\Exercises.txt"; String answerFile = "src\\Answers.txt"; int length = title.length; int i = 0; try{ //打开文件输出流 BufferedWriter tFile = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File(titleFile))); BufferedWriter aFile = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File(answerFile))); while(i < length){ //用字符流输出 tFile.write(title[i]); aFile.write(answer[i]); tFile.newLine(); aFile.newLine(); i++; } tFile.close(); aFile.close(); }catch(Exception ex){ ex.getMessage(); } } /** * 读取文件方法,读取用户输入的题目和答案文件并进行校对,将成绩输入到Grade文件 * @param titlePath 题目路径 * @param answerPath 答案路径 * @return */ public int FReader(String titlePath, String answerPath){ String title = null; String answer = null; String correct = "Correct:("; String wrong = "Wrong:("; String[] str = new String[2]; int i = 1,correctNum = 0; try{ //读取文件内容 BufferedReader titleReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(titlePath))); BufferedReader answerReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(answerPath))); while((title = titleReader.readLine()) != null){ //每读取一行,就进行判断,并进行统计对错数量 answer = answerReader.readLine(); if(CheckAnswer(title, answer)){ correctNum++; if(correct.equals("Correct:(")) correct = correct + Integer.toString(i); else correct = correct + ", " + Integer.toString(i); } else if(wrong.equals("Wrong:(")) wrong = wrong + Integer.toString(i); else wrong = wrong + ", " + Integer.toString(i); i++; } titleReader.close(); answerReader.close(); str = correct.split(":"); correct = str[0] + ":" + Integer.toString(correctNum) + str[1] + ")"; str = wrong.split(":"); wrong = str[0] + ":" + Integer.toString(i - correctNum - 1) + str[1] + ")"; //将成绩写入Grade文档 BufferedWriter gradeFile = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("src\\Grade.txt"))); gradeFile.write(correct); gradeFile.newLine(); gradeFile.write(wrong); gradeFile.close(); return 1; }catch(Exception ex){ ex.getMessage(); System.out.println("文件路径不正确"); return 2; } } /** * 对答案方法,将计算题目答案并和用户答案对比 * @param title 题目 * @param answer 答案 * @return */ public boolean CheckAnswer(String title, String answer){ CheckResult check = new CheckResult(); String[] str; str = title.split("\\. ",2); title = str[str.length-1]; str = answer.split("\\. ",2); answer = str[str.length-1]; if(check.Calc(title).equals(answer)) return true; else return false; }
4、Main类
检测输入,防止程序在某些地方死掉
public static void main(String[] args) { GenerateTitle generateTitle = new GenerateTitle(); CheckResult checkResult = new CheckResult(); FileOperation fileOperation = new FileOperation(); String fileHandle; String[] fileSpit; System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println("小学生四则运算生成器"); System.out.println("请按格式输入来选择以下功能:"); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -n x -r y x为生成题目个数,y为题目中自然数,真分数,真分数分母的范围(x和y大于0)"); System.out.println("题目和答案分别在Exercises.txt和Answers.txt中生成"); System.out.println(" "); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt"); System.out.println("以上两个txt文件分别为想要判定对错的题目和答案"); System.out.println(" "); System.out.println("-q 退出生成器"); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------"); final String FILEMATCHONE = "(Myapp.exe|myapp.exe)(\\s+(-n))(\\s+\\d+)(\\s+(-r))(\\s+\\d+)"; final String FILEMATCHTWO = "(Myapp.exe|myapp.exe)(\\s+(-e))(\\s+\\S+)(\\s+(-a))(\\s+\\S+)"; int judge = 0; while(true){ judge = 0; Scanner instruct = new Scanner(System.in); fileHandle = instruct.nextLine(); fileSpit = fileHandle.split("\\s+"); if(fileHandle.equals("-q")){ System.out.println("谢谢使用"); break; } else if(Pattern.matches(FILEMATCHONE, fileHandle)){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取开始时间 judge = generateTitle.creatTitle(Integer.valueOf(fileSpit[2]), Integer.valueOf(fileSpit[4])); if(judge == 0) System.out.println("题目答案生成成功"); else if(judge == 1) { System.out.println("参数错误,n需要大于0"); System.out.println("请重新输入,格式为:"); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -n x -r y x为生成题目个数,y为题目中自然数,真分数,真分数分母的范围(x和y大于0)"); } else { System.out.println("参数错误,r需要大于0"); System.out.println("请重新输入,格式为:"); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -n x -r y x为生成题目个数,y为题目中自然数,真分数,真分数分母的范围(x和y大于0)"); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取结束时间 System.out.println("程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); //输出程序运行时间 } else if(Pattern.matches(FILEMATCHTWO, fileHandle)){ judge = fileOperation.FReader(fileSpit[2], fileSpit[4]); if(judge == 1) System.out.println("答案校对完毕,成绩已在Grade.txt出生成"); else{ System.out.println("请重新输入正确的文件路径"); } } else { System.out.println("参数输入错误,请按照格式输入"); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println("请按格式输入来选择以下功能:"); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -n x -r y x为生成题目个数,y为题目中自然数,真分数,真分数分母的范围(x和y大于0)"); System.out.println("题目和答案分别在Exercises.txt和Answers.txt中生成"); System.out.println(" "); System.out.println("Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt"); System.out.println("以上两个txt文件分别为想要判定对错的题目和答案"); System.out.println(" "); System.out.println("-q 退出生成器"); } System.out.println("-------------------------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println("请输入命令:"); } }
六、测试运行
测试题目
Myapp.exe -n 10000 -r 40
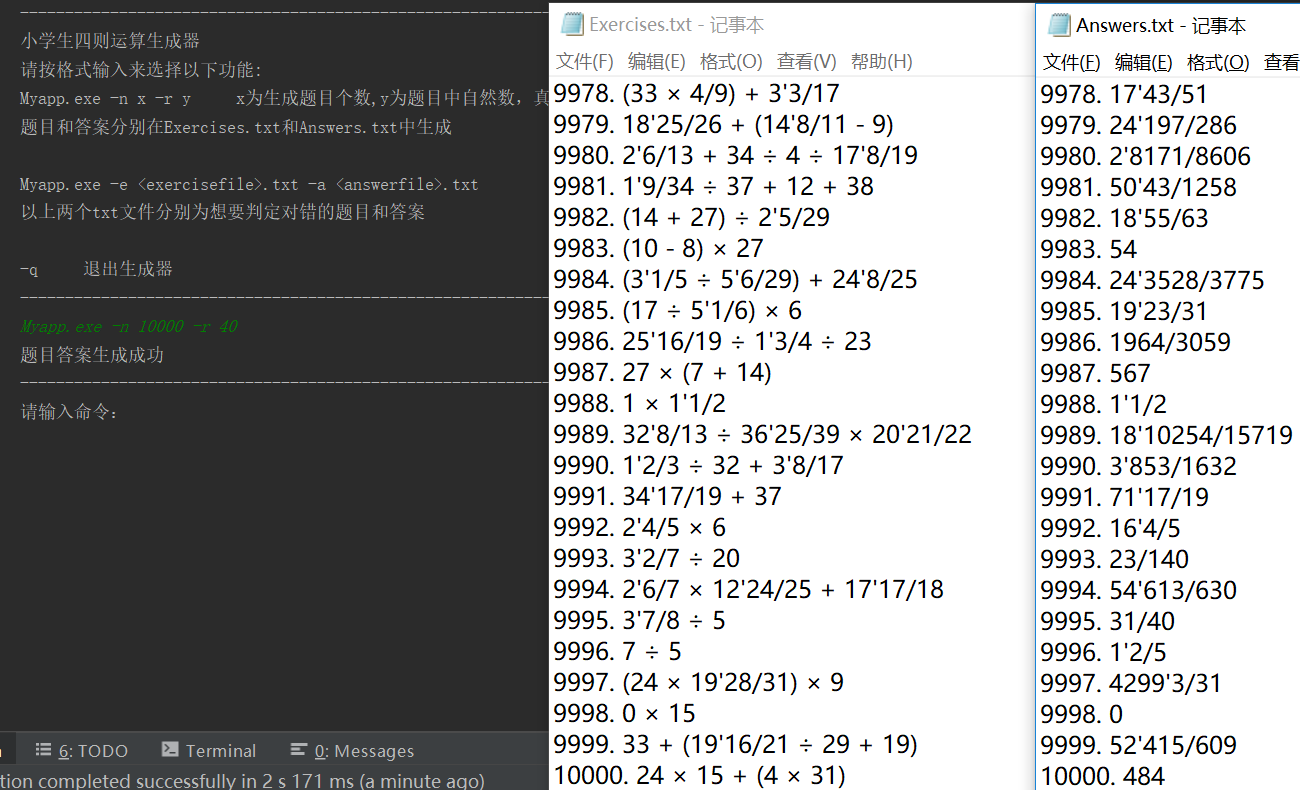
更改(9982,9983,9990,9992,9996,9998,10000)的值,然后检验答案

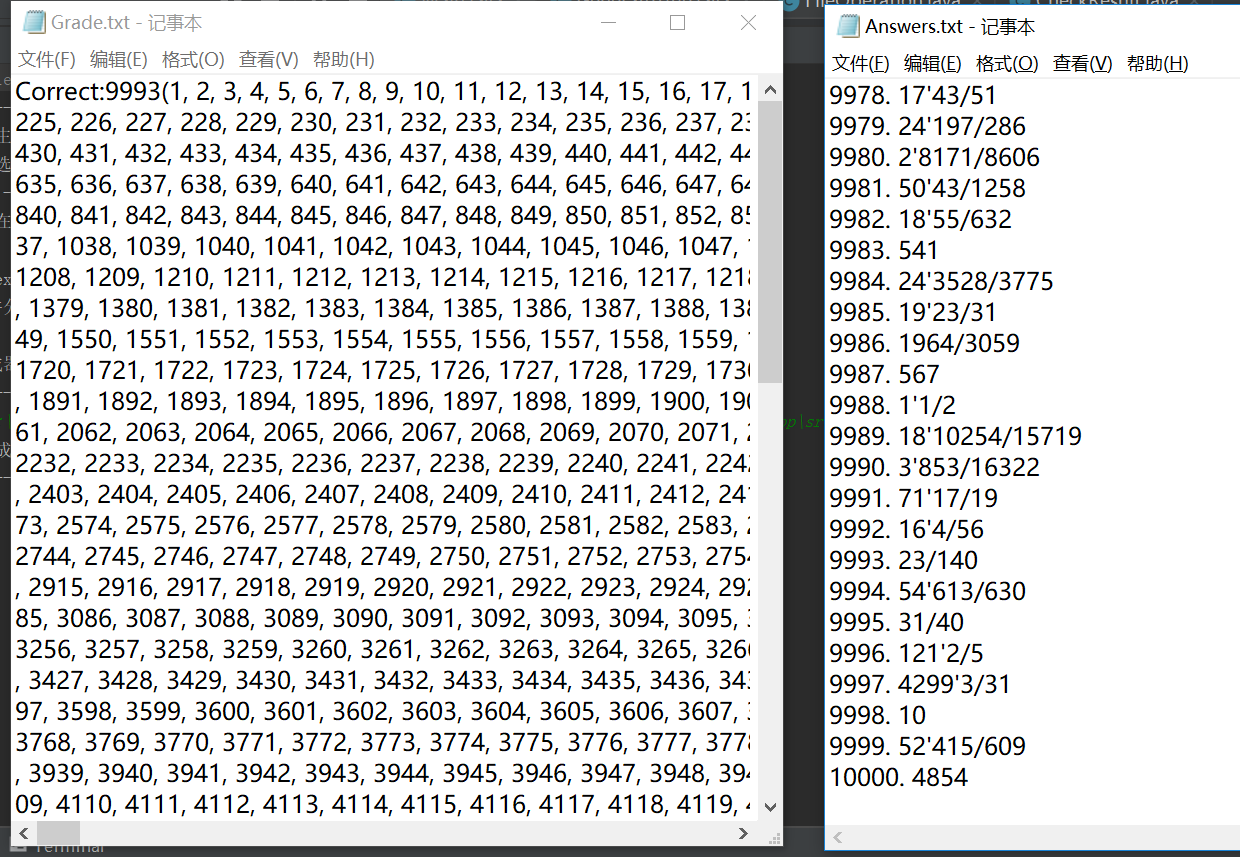
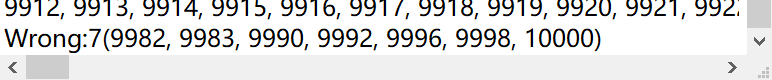
由此可见,能够检测到错误的答案并进行统计。
七、项目小结
这次结对项目是我们之间第一次合作,因为彼此能力间的有所差距,所以开发的时间比较长,有一部分时间是在指导对方,虽然不能说编程的能力有明显的增长,但是双方在不断交流中也学到了许多东西,也能够把之前对方的建议用在后面的编程中。结对编程对于扩宽编程思路还是有很大帮助的,在自己想不到或者想到的思路不是很好的时候,对方能够提出一些自己没有想到的思路,或者指出自己存在的问题,这样把思路扩宽了,编程也更有效率,准确率也大大提高了。