在这篇文章里,我们从源代码的角度重点分析Session的创建、缓存、销毁、管理。
通常我们说的Session指的是在控制器中使用的Session字段,该字段的类型是HttpSessionState。可以获取SessionID,可以存储数据,可以增加删除数据等等。Session字段中使用的HttpSessionState对象,就是在下面介绍的模块中产生的。
在.Net Framework内部,来自浏览器的请求像工厂的流水线加工产品一样,在不同的部位进行不同的处理,最终被加工为一件成品。我们的请求也是如此,内部有许多的模块(实现了接口IHttpModule)对我们的请求进行处理,比如映射路由的模块(UrlRoutingModule),该模块的作用是从用户请求的url中获取信息,找到能处理这个IHttpHandler对象,用于后续处理处理请求。而我们这里讨论的则是关于会话Session的一个模块--SessionStateModule。
在这里模块里,有诸如这样的功能,生成SessionID、生成用于HttpSessionState内部存储数据的ISessionStateItemCollection对象。然后将这样的不同对象封装起来。
在IIS中,Session的存储生成有4中模式。
1-InProc进程内模式,将Session存储在web应用程序进程内部。这也是系统默认的模式。这种方式优点显而易见---存取速度很快,缺点也显而易见--一旦因为某种原因应用程序被关闭,不管是否重启应用程序,所有用户的Session全部都会丢失,这是不能接受的。
而且因为是进行内存储,当我们想做分布式的时候,Session无法共享。
2-StateServer状态服务器模式。在这种模式下,应用程序会启动一个会话状态服务器,专门用于存储Session。这种方式解决了重启web应用程序后session丢失的问题,但状态服务器本身会有问题,如:不支持故障转移等。
3-SQLServer数据库模式。在这种模式下,所有的会话数据都被存储在SQLServer数据库中,但是要求session中存储的时候是可以序列化的。在这种模式下,数据库强大的存储、搜索、故障转移群集等稳定功能,会给session带来强大的支持。
4-Custom自定义模式。在这种模式下,用户可以定义自己的session存储方式。
这些内容仅在这里做简单介绍,有兴趣的朋友可以查看微软官方的文档。https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ms178586(v=vs.100).aspx


1 void InitModuleFromConfig(HttpApplication app, SessionStateSection config) { 2 if (config.Mode == SessionStateMode.Off) { 3 return; 4 } 5 6 app.AddOnAcquireRequestStateAsync( 7 new BeginEventHandler(this.BeginAcquireState), 8 new EndEventHandler(this.EndAcquireState)); 9 10 app.ReleaseRequestState += new EventHandler(this.OnReleaseState); 11 app.EndRequest += new EventHandler(this.OnEndRequest); 12 13 _partitionResolver = InitPartitionResolver(config); 14 15 switch (config.Mode) { 16 case SessionStateMode.InProc: 17 if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { 18 s_canSkipEndRequestCall = true; 19 } 20 _store = new InProcSessionStateStore(); 21 _store.Initialize(null, null); 22 break; 23 24 case SessionStateMode.StateServer: 25 if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { 26 s_canSkipEndRequestCall = true; 27 } 28 _store = new OutOfProcSessionStateStore(); 29 ((OutOfProcSessionStateStore)_store).Initialize(null, null, _partitionResolver); 30 break; 31 32 case SessionStateMode.SQLServer: 33 _store = new SqlSessionStateStore(); 34 ((SqlSessionStateStore)_store).Initialize(null, null, _partitionResolver); 35 break; 36 37 case SessionStateMode.Custom: 38 _store = InitCustomStore(config); 39 break; 40 default: 41 break; 42 } 43 44 // 依赖SessionIDManager管理session id,所以在这里对管理器进行初始化 45 _idManager = InitSessionIDManager(config); 46 47 if ((config.Mode == SessionStateMode.InProc || config.Mode == SessionStateMode.StateServer) && 48 _usingAspnetSessionIdManager) { 49 //如果我们使用InProc模式或者StateServer模式,并且也使用我们自己的会话ID模块, 50 //我们知道我们不关心在所有会话状态存储读/写和会话ID读/写中的模拟。 51 _ignoreImpersonation = true; 52 } 53 }
模块进行初始化时,会进行许多设置,上面的方法时其中的设置之一。上面的方法中,如果会话状态的模式是关闭,则直接返回,不再进行任何操作。
然后向HttpApplication对象注册事件,当这个对象需要获取会话状态时,就调用这里注册的方法,进行会话状态的创建等共走。供后面的步骤使用。
然后根据会话状态模式加载不同的会话状态存储提供程序,默认的模式是SessionStateMode.InProc,则加载的提供程序是类是InProcSessionStateStore。
InProcSessionStateStore类内部实现的存储会话状态的方式是存储在运行时的缓存中。
从缓存中读取会话状态:
HttpRuntime.CacheInternal.Get(key)。
将回话状态写入缓存:
HttpRuntime.CacheInternal.UtcInsert(
key,/*缓存的key,此处缓存会话,所以是在sessionid的基础上进行了其他操作组合而成。*/
state,/*这就是我们的会话状态*/
null,/*依赖属性,这里不需要,所以传空值*/
Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration,/*绝对过期时间。在这里我们不希望有绝对过期时间,所以传递了Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration,该字段的值是 DateTime.MaxValue;*/
new TimeSpan(0, state._timeout, 0),/*滑动到期时间,传递的是会话状态的过期值。*/
CacheItemPriority.NotRemovable,/*缓存优先级,告诉运行时缓存,在进行内存优化时,不能删除这个缓存值*/
_callback /*缓存项被移除的回调方法。正是因为InProcSessionStateStore类内部使用运行时缓存且运行时缓存带有缓存项移除回调方法,所以在SessionStateMode.InProc模式下,会话状态过期时,会调用在Global.asax中注册的Session_End方法*/
);
继续看代码。
紧接着,会根据配置文件对SessionIDManager进行初始化,默认情况下会初始化一个SessionIDManager的对象。我们使用这个会话管理器进行sessionid的管理。创建sessionid,验证sessionid的合法性等功能。
模块的初始化工作已经介绍完毕,这里介绍的只是最基础的一部分,其他还涉及的会话状态的锁定、优化等扩展开来则过于复杂。
下面我们按一个请求的处理过程为顺序,介绍会话状态的相关处理。从获得会话状态开始。上代码。

1 IAsyncResult BeginAcquireState(Object source, EventArgs e, AsyncCallback cb, Object extraData) { 2 bool requiresState; 3 bool isCompleted = true; 4 bool skipReadingId = false; 5 6 _acquireCalled = true; 7 _releaseCalled = false; 8 ResetPerRequestFields(); 9 10 _rqContext = ((HttpApplication)source).Context; 11 _rqAr = new HttpAsyncResult(cb, extraData); 12 13 ChangeImpersonation(_rqContext, false); 14 15 try { 16 17 /* Notify the store we are beginning to get process request */ 18 _store.InitializeRequest(_rqContext); 19 20 /* determine if the request requires state at all */ 21 requiresState = _rqContext.RequiresSessionState; 22 23 // SessionIDManager may need to do a redirect if cookieless setting is AutoDetect 24 if (_idManager.InitializeRequest(_rqContext, false, out _rqSupportSessionIdReissue)) { 25 _rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); 26 return _rqAr; 27 } 28 29 // See if we can skip reading the session id. See inline doc of s_allowInProcOptimization 30 // for details. 31 if (s_allowInProcOptimization && 32 !s_sessionEverSet && 33 (!requiresState || // Case 1 34 !((SessionIDManager)_idManager).UseCookieless(_rqContext)) ) { // Case 2 35 36 skipReadingId = true; 37 } 38 else { 39 /* Get sessionid */ 40 _rqId = _idManager.GetSessionID(_rqContext); 41 } 42 43 if (!requiresState) { 44 if (_rqId == null) { 45 } 46 else { 47 // Still need to update the sliding timeout to keep session alive. 48 // There is a plan to skip this for perf reason. But it was postponed to 49 // after Whidbey. 50 _store.ResetItemTimeout(_rqContext, _rqId); 51 } 52 _rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); 53 return _rqAr; 54 } 55 56 _rqExecutionTimeout = _rqContext.Timeout; 57 58 if (_rqExecutionTimeout == DEFAULT_DBG_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT) { 59 _rqExecutionTimeout = s_configExecutionTimeout; 60 } 61 62 /* determine if we need just read-only access */ 63 _rqReadonly = _rqContext.ReadOnlySessionState; 64 65 if (_rqId != null) { 66 /* get the session state corresponding to this session id */ 67 isCompleted = GetSessionStateItem(); 68 } 69 else if (!skipReadingId) { 70 /* if there's no id yet, create it */ 71 bool redirected = CreateSessionId(); 72 73 _rqIdNew = true; 74 75 if (redirected) { 76 if (s_configRegenerateExpiredSessionId) { 77 // See inline comments in CreateUninitializedSessionState() 78 CreateUninitializedSessionState(); 79 } 80 _rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); 81 return _rqAr; 82 } 83 } 84 85 if (isCompleted) { 86 CompleteAcquireState(); 87 _rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); 88 } 89 90 return _rqAr; 91 } 92 finally { 93 RestoreImpersonation(); 94 } 95 }
这是获取Session的入口,每当有请求到达时,这是必须要有的步骤,经过这个方法处理后,请求上下文会拥有一个与当前请求匹配的Session。
下面我们具体分析方法中的一些代码。
requiresState = _rqContext.RequiresSessionState;
上面这行代码判断请求是否需要会话状态。主要取决于两方面,一方面是我们的控制器是否需要会话状态.控制器本身是否设置了SessionStateAttribute特性或者用于处理请求的实现了IHttpHandler接口的类是否标记了IRequiresSessionState这个接口。
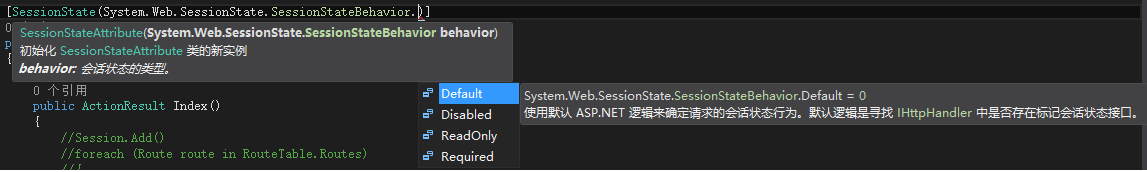
当我们没有给控制器标记SessionStateAttribute特性时,会默认使用SessionStateBehavior.Default这个选项。这个选项的意思参考第一个截图。
我把这个属性的内部代码贴出来,有兴趣的可以看看。

internal bool RequiresSessionState { get { switch (SessionStateBehavior) { case SessionStateBehavior.Required: case SessionStateBehavior.ReadOnly: return true; case SessionStateBehavior.Disabled: return false; case SessionStateBehavior.Default: default: return _requiresSessionStateFromHandler; } } } //从上面的代码中可以看出,当设置SessionStateBehavior.Default时, //会返回_requiresSessionStateFromHandler这个变量的值。 //我们再看看这个值是如何被设置的. public IHttpHandler Handler { get { return _handler;} set { _handler = value; _requiresSessionStateFromHandler = false; _readOnlySessionStateFromHandler = false; InAspCompatMode = false; if (_handler != null) { if (_handler is IRequiresSessionState) { _requiresSessionStateFromHandler = true; } if (_handler is IReadOnlySessionState) { _readOnlySessionStateFromHandler = true; } Page page = _handler as Page; if (page != null && page.IsInAspCompatMode) { InAspCompatMode = true; } } } } //从上面代码中的可以看出, // if (_handler is IRequiresSessionState) { // _requiresSessionStateFromHandler = true; // } //而我们的MvcHandler是扩展了IRequiresSessionState这个接口的,所以_requiresSessionStateFromHandler是true;
BeginAcquireState方法中的代码主要是用来判断是否满足优化的目的。比如是否要延迟获取一个session id,是否要加载session等。
我们假设是第一次请求,走一次完整的流程。那么,我们的代码就要进入CompleteAcquireState这个方法中了。
在介绍这个方法前,首先介绍一个点。
在控制器中访问的Session共分两个部分,一个是用来存储数据的部分,例如这样的形式--Session["key1"] = 123;
一个是Session的id---Session.SessionID
他们虽然都归属在Session下面,但是它们的生成、存储、删除等机制完全不同。

1 // Called when AcquireState is done. This function will add the returned 2 // SessionStateStore item to the request context. 3 void CompleteAcquireState() { 4 bool delayInitStateStoreItem = false; 5 try { 6 //_rqItem就是session中用来存储数据的 7 //当第一次访问时,这个值肯定是空值,所以会走else的分支 8 if (_rqItem != null) { 9 _rqSessionStateNotFound = false; 10 11 if ((_rqActionFlags & SessionStateActions.InitializeItem) != 0) { 12 _rqIsNewSession = true; 13 } 14
该函数将把返回的SessionStateStore项添加到请求上下文中。
这个方法的主要作用是向请求上下文中(HttpContext)添加一个会话状态存储,Session中存储数据的功能就是靠这个对象实现的。
这个方法中,添加会话状态存储的功能是靠InitStateStoreItem这个方法来实现的。我们也看看这个方法的内部。

1 internal void InitStateStoreItem(bool addToContext) { 2 try { 3 4 if (_rqItem == null) { 5 _rqItem = _store.CreateNewStoreData(_rqContext, s_timeout); 6 } 7 8 _rqSessionItems = _rqItem.Items; 9 if (_rqSessionItems == null) { 10 throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Null_value_for_SessionStateItemCollection)); 11 } 12 13 // No check for null because we allow our custom provider to return a null StaticObjects. 14 _rqStaticObjects = _rqItem.StaticObjects; 15 16 _rqSessionItems.Dirty = false; 17 18 _rqSessionState = new HttpSessionStateContainer( 19 this, 20 _rqId, // could be null if we're using InProc optimization 21 _rqSessionItems, 22 _rqStaticObjects, 23 _rqItem.Timeout, 24 _rqIsNewSession, 25 s_configCookieless, 26 s_configMode, 27 _rqReadonly); 28 29 if (addToContext) { 30 SessionStateUtility.AddHttpSessionStateToContext(_rqContext, _rqSessionState); 31 } 32 } 33 finally { 34 RestoreImpersonation(); 35 } 36 } 37 public static class SessionStateUtility { 38 // Called by custom session state module 39 static public void AddHttpSessionStateToContext(HttpContext context, IHttpSessionState container) { 40 HttpSessionState sessionState = new HttpSessionState(container); 41 42 //在这个方法中,将用于存取数据的数据结构存储在了context.Items中。 43 //存储的key是变量SESSION_KEY 44 try { 45 context.Items.Add(SESSION_KEY, sessionState); 46 } 47 catch (ArgumentException) { 48 throw new HttpException(SR.GetString(SR.Cant_have_multiple_session_module)); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 53 54 //这是HttpContext中Session的内部代码 55 public HttpSessionState Session { 56 get { 57 if (HasWebSocketRequestTransitionCompleted) { 58 // Session is unavailable at this point 59 return null; 60 } 61 //省略了部分代码 62 63 //访问session时,从context.Items中取出这一数据结构 64 //存储的key是变量SESSION_KEY 65 return(HttpSessionState)Items[SessionStateUtility.SESSION_KEY]; 66 } 67 }
经过这个方法后,我们的请求上下文真正有了用了可以让我们用于访问,用于存取数据的对象。
经过上面的两个大方法,我们的请求上下文终于获得了session,然后代码进入了我们的控制器,我们在控制器中会具体的处理的代码,与session相关的可能就是从session中读取数据,但是这个数据只是存储在这个用来存储数据的对象中了,并没有存储在缓存中。当我们再次请求时,数据从哪里来呢?下面介绍的方法就是负责session相关的收尾工作---OnReleaseState。
当控制器中的代码处理完毕后。应用程序就会进行其他的一些收尾步骤,比如将session中的数据存储起来,再次查询时使用。
在下面的代码中,对部分关键代码做了相应的注释。
这个方法的主要作用就是判断是否要把会话存储放进系统缓存中,是否把session id继续保存在cookie中

1 void OnReleaseState(Object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { 2 HttpApplication app; 3 HttpContext context; 4 bool setItemCalled = false; 5 6 _releaseCalled = true; 7 8 app = (HttpApplication)source; 9 context = app.Context; 10 11 ChangeImpersonation(context, false); 12 13 try { 14 if (_rqSessionState != null) { 15 bool delayedSessionState = (_rqSessionState == s_delayedSessionState); 16 SessionStateUtility.RemoveHttpSessionStateFromContext(_rqContext, delayedSessionState); 17 18 if ( 19 //如果会话状态是新的,并且没有被访问过, 20 //那么这样的会话状态存储不用保存到系统的缓存中,保存了没有意义。 21 //所以不做任何处理(不保存在系统缓存中) 22 _rqSessionStateNotFound 23 && _sessionStartEventHandler == null 24 // Nothing has been stored in session state 25 && (delayedSessionState || !_rqSessionItems.Dirty) 26 && (delayedSessionState || _rqStaticObjects == null || _rqStaticObjects.NeverAccessed) 27 ) { 28 } 29 //如果会话被丢弃了,即我们在控制器中调用了Session.Abandon(),常用于注销操作。 30 else if (_rqSessionState.IsAbandoned) { 31 if (_rqSessionStateNotFound) { 32 // The store provider doesn't have it, and so we don't need to remove it from the store. 33 34 // However, if the store provider supports session expiry, and we have a Session_End in global.asax, 35 // we need to explicitly call Session_End. 36 if (_supportSessionExpiry) { 37 if (delayedSessionState) { 38 InitStateStoreItem(false /*addToContext*/); 39 } 40 _onEndTarget.RaiseSessionOnEnd(ReleaseStateGetSessionID(), _rqItem); 41 } 42 } 43 else { 44 // Remove it from the store because the session is abandoned. 45 _store.RemoveItem(_rqContext, ReleaseStateGetSessionID(), _rqLockId, _rqItem); 46 } 47 } 48 else if (!_rqReadonly || 49 (_rqReadonly && 50 _rqIsNewSession && 51 _sessionStartEventHandler != null && 52 !SessionIDManagerUseCookieless)) { 53 54 // We save it only if there is no error, and if something has changed (unless it's a new session) 55 if ( context.Error == null // no error 56 && ( _rqSessionStateNotFound 57 || _rqSessionItems.Dirty // SessionItems has changed. 58 || (_rqStaticObjects != null && !_rqStaticObjects.NeverAccessed) // Static objects have been accessed 59 || _rqItem.Timeout != _rqSessionState.Timeout // Timeout value has changed 60 ) 61 ) { 62 63 if (delayedSessionState) { 64 InitStateStoreItem(false /*addToContext*/); 65 } 66 if (_rqItem.Timeout != _rqSessionState.Timeout) { 67 _rqItem.Timeout = _rqSessionState.Timeout; 68 } 69 //该标识设置为true,说明该模块设置过session,该标识用于一些优化 70 s_sessionEverSet = true; 71 //为true说明我们已经把当前的session保存进系统缓存中了 72 setItemCalled = true; 73 //将这个会话状态存储放入系统缓存中,在这个代码中,我们看到使用了ReleaseStateGetSessionID()这个方法去获取session id 74 //有这样的意思。如果已经有session id了,则直接使用,如果没有则会创建一个session id,且写入cookie ,则浏览器端就有了这个id 75 //如果这是一个全新的请求,而且也没有在控制器中也没有Session.SessionID这样的访问,那么到了此处,session id就是空值 76 _store.SetAndReleaseItemExclusive(_rqContext, ReleaseStateGetSessionID(), _rqItem, _rqLockId, _rqSessionStateNotFound); 77 } 78 else { 79 // Can't save it because of various reason. Just release our exclusive lock on it. 80 if (!_rqSessionStateNotFound) { 81 _store.ReleaseItemExclusive(_rqContext, ReleaseStateGetSessionID(), _rqLockId); 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 //上面是决定是否保存会话状态存储的代码,下面是决定是否将session id保存在cookie中的代码 87 //有这样一种情况,在一次全新的请求中,如果我们在控制器中有了Session.SessionID这样的访问 88 //那么,此时会创建一个SessionID且写入cookie中,但是如果我们没有向Session中存储数据 89 //那么这样的SessionID继续保存在cookie中,就是没有意义的,所以就从cookie中删除这个id 90 if (_rqAddedCookie && !setItemCalled && context.Response.IsBuffered()) { 91 _idManager.RemoveSessionID(_rqContext); 92 } 93 } 94 finally { 95 RestoreImpersonation(); 96 } 97 98 bool implementsIRequiresSessionState = context.RequiresSessionState; 99 if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline 100 && (context.NotificationContext.CurrentNotification == RequestNotification.ReleaseRequestState) 101 && (s_canSkipEndRequestCall || !implementsIRequiresSessionState)) { 102 context.DisableNotifications(RequestNotification.EndRequest, 0 /*postNotifications*/); 103 _acquireCalled = false; 104 _releaseCalled = false; 105 ResetPerRequestFields(); 106 } 107 }
上面对于初次的访问关于session的获取等已经介绍完毕,而对于非初次访问(已经想session中存储过数据),则简单很多。
因为已经存储过数据,所以cookie中有session id,系统缓存中数据。
则先从cookie中读取session id,然后根据此id去缓存中读取数据,然后返回。
结束语:SessionStateModule模块已经介绍完毕,这个模块的主要作用,就是在正式处理请求前,为我们生成存储数据用的session内部对象,请求处理完毕后,将
存储数据的对象保存在系统缓存中。这些功能也是这个模块的部分功能,还有其他很重要的功能。比如用于同步的锁机制,比如生成sessionid的类等。这些内容 就放在其他文章里再做介绍。
