在软件开发中,会遇到有些问题多次重复出现,而且有一定的相似性和规律性。如果将它们归纳成一种简单的语言,那么这些问题实例将是该语言的一些句子,这样就可以用“编译原理”中的解释器模式来实现了。
解释器(Interpreter)模式的定义:给分析对象定义一个语言,并定义该语言的文法表示,再设计一个解析器来解释语言中的句子。也就是说,用编译语言的方式来分析应用中的实例。这种模式实现了文法表达式处理的接口,该接口解释一个特定的上下文。
解释器模式是一种类行为型模式,其主要优点如下。
- 扩展性好。由于在解释器模式中使用类来表示语言的文法规则,因此可以通过继承等机制来改变或扩展文法。
- 容易实现。在语法树中的每个表达式节点类都是相似的,所以实现其文法较为容易。
解释器模式的主要缺点如下。
- 执行效率较低。解释器模式中通常使用大量的循环和递归调用,当要解释的句子较复杂时,其运行速度很慢,且代码的调试过程也比较麻烦。
- 会引起类膨胀。解释器模式中的每条规则至少需要定义一个类,当包含的文法规则很多时,类的个数将急剧增加,导致系统难以管理与维护。
- 可应用的场景比较少。在软件开发中,需要定义语言文法的应用实例非常少,所以这种模式很少被使用到。
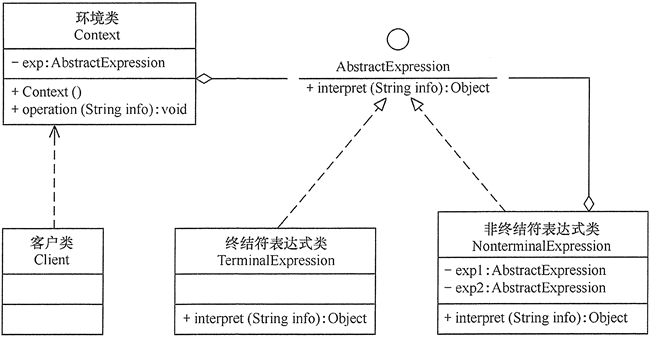
举例说明:
创建出一种机器人编程语言,给予一定的语法规则可以控制机器人的移动,转向和平台升降,规则如下:
Robot Move [distance] distance为机器人移动的距离
Robot Turn [Right/Left] Right/Left可以控制机器人向左转还是向右转
Robot Platform [Up/Down] Up/Down控制机器人平台升降
C++ 实现:
1 #include <stdlib.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 enum Orientation{ 7 x_increase = 1, 8 y_increase = 2, 9 x_decrease = 3, 10 y_decrease = 4 11 }; 12 13 class Robot{ 14 private: 15 string name; 16 int x; 17 int y; 18 Orientation orientation; 19 public: 20 Robot(string _name) { 21 name = _name; 22 x = 0; 23 y = 0; 24 orientation = x_increase; 25 } 26 27 string getName(){ 28 return name; 29 } 30 31 void turn(string direction){ 32 if (direction == "Left"){ 33 switch (orientation){ 34 case x_increase:{ 35 orientation = y_increase; 36 break; 37 } 38 case y_increase:{ 39 orientation = x_decrease; 40 break; 41 } 42 case x_decrease:{ 43 orientation = y_decrease; 44 break; 45 } 46 case y_decrease:{ 47 orientation = x_increase; 48 } 49 } 50 } else if (direction == "Right"){ 51 switch (orientation) { 52 case x_increase:{ 53 orientation = y_decrease; 54 break; 55 } 56 case y_increase:{ 57 orientation = x_increase; 58 break; 59 } 60 case x_decrease:{ 61 orientation = y_increase; 62 break; 63 } 64 case y_decrease:{ 65 orientation = x_decrease; 66 break; 67 } 68 } 69 } else { 70 cout << "Wrong input !!" << endl; 71 } 72 } 73 74 void move(int distance){ 75 switch(orientation) { 76 case x_increase:{ 77 x += distance; 78 break; 79 } case y_increase:{ 80 y += distance; 81 break; 82 } case x_decrease:{ 83 x -= distance; 84 break; 85 } case y_decrease:{ 86 y -= distance; 87 break; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 92 void platform(string platformStatus){ 93 cout << name << " platform " << platformStatus << endl; 94 } 95 96 void getPosition(){ 97 cout << name << "position is (" << x << "," << y << ")" << endl; 98 } 99 }; 100 101 102 class Expression{ 103 public: 104 virtual void interpret(string parameter)=0; 105 }; 106 107 class RobotExpression:public Expression{ 108 protected: 109 Robot* robot; 110 public: 111 virtual void interpret(string parameter) = 0; 112 RobotExpression(Robot *_robot){ 113 robot = _robot; 114 } 115 }; 116 117 class MoveExpression:public RobotExpression { 118 public: 119 using RobotExpression::RobotExpression; 120 virtual void interpret(string parameter){ 121 int pace = atoi(parameter.c_str()); 122 robot->move(pace); 123 } 124 }; 125 126 class TurnExpression:public RobotExpression{ 127 using RobotExpression::RobotExpression; 128 virtual void interpret(string parameter){ 129 robot->turn(parameter); 130 } 131 }; 132 133 class PlatformExpression:public RobotExpression{ 134 using RobotExpression::RobotExpression; 135 virtual void interpret(string parameter){ 136 robot->platform(parameter); 137 } 138 }; 139 140 class Context{ 141 private: 142 RobotExpression *expression; 143 Robot* robot; 144 public: 145 Context(Robot *_robot){ 146 robot = _robot; 147 } 148 void executeSentence(string sentence){ 149 int firstBlankIndex = sentence.find_first_of(" "); 150 int lastBlankIndex = sentence.find_last_of(" "); 151 int sentenceLen = sentence.length(); 152 string robotName = sentence.substr(0, firstBlankIndex); 153 string command = sentence.substr(firstBlankIndex + 1, lastBlankIndex - firstBlankIndex - 1); 154 string parameter = sentence.substr(lastBlankIndex + 1); 155 if (robotName == robot->getName()){ 156 if (command == "move"){ 157 expression = new MoveExpression(robot); 158 } else if (command == "turn"){ 159 expression = new TurnExpression(robot); 160 } else if (command == "platform"){ 161 expression = new PlatformExpression(robot); 162 } else { 163 cout << "Wrong input command" << endl; 164 return; 165 } 166 expression->interpret(parameter); 167 delete expression; 168 } 169 } 170 }; 171 172 173 174 int main() 175 { 176 Robot *robot = new Robot("Turtlebot"); 177 Context *context = new Context(robot); 178 context->executeSentence("Turtlebot move 3"); 179 context->executeSentence("Turtlebot move 2"); 180 context->executeSentence("Turtlebot turn Left"); 181 context->executeSentence("Turtlebot move 10"); 182 context->executeSentence("Turtlebot platform down"); 183 robot->getPosition(); 184 return 0; 185 }
Java:
1 public class Robot { 2 3 private String name; 4 private int x; 5 private int y; 6 private Orientation orientation; 7 8 public Robot(String name){ 9 this.name = name; 10 this.x = 0; 11 this.y = 0; 12 this.orientation = Orientation.x_increase; 13 } 14 15 public String getName() { 16 return name; 17 } 18 19 public void turn(String direction){ 20 if ("Left".equals(direction)){ 21 switch (orientation){ 22 case x_increase:{ 23 orientation = Orientation.y_increase; 24 break; 25 } 26 case y_increase:{ 27 orientation = Orientation.x_decrease; 28 break; 29 } 30 case x_decrease:{ 31 orientation = Orientation.y_decrease; 32 break; 33 } 34 case y_decrease:{ 35 orientation = Orientation.x_increase; 36 break; 37 } 38 } 39 } else if ("Right".equals(direction)){ 40 switch (orientation){ 41 case x_increase:{ 42 orientation = Orientation.y_decrease; 43 break; 44 } 45 case y_increase:{ 46 orientation = Orientation.x_increase; 47 break; 48 } 49 case x_decrease:{ 50 orientation = Orientation.y_increase; 51 break; 52 } 53 case y_decrease:{ 54 orientation = Orientation.x_decrease; 55 break; 56 } 57 } 58 } else { 59 System.out.println("Wrong input direction"); 60 } 61 } 62 63 public void move(int pace){ 64 switch (orientation){ 65 case x_increase:{ 66 x += pace; 67 break; 68 } 69 case x_decrease:{ 70 x -= pace; 71 break; 72 } 73 case y_increase:{ 74 y += pace; 75 break; 76 } 77 case y_decrease:{ 78 y -= pace; 79 break; 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 84 public void platform(String platform){ 85 System.out.println(name + " platform" + platform); 86 } 87 88 public void getPosition(){ 89 System.out.println(name + " position:{" + x + "," + y + ")"); 90 } 91 } 92 93 public interface Expression { 94 void interpret(String parameter); 95 } 96 97 public abstract class RobotExpression implements Expression { 98 99 protected Robot robot; 100 101 public RobotExpression(Robot robot) {this.robot = robot;} 102 } 103 104 public class MoveExpression extends RobotExpression { 105 106 public MoveExpression(Robot robot){ 107 super(robot); 108 } 109 110 public void interpret(String parameter) { 111 int pace = Integer.parseInt(parameter); 112 robot.move(pace); 113 } 114 } 115 116 public class TurnExpression extends RobotExpression { 117 public TurnExpression(Robot robot){ 118 super(robot); 119 } 120 121 public void interpret(String parameter) { 122 robot.turn(parameter); 123 } 124 } 125 126 public class PlatformExpression extends RobotExpression { 127 PlatformExpression(Robot robot){ 128 super(robot); 129 } 130 131 public void interpret(String parameter) { 132 robot.platform(parameter); 133 } 134 } 135 136 public class Context { 137 138 private Expression expression; 139 private Robot robot; 140 141 public Context(Robot robot){ 142 this.robot = robot; 143 } 144 145 public void execute(String sentence){ 146 String[] means = sentence.split(" "); 147 String name = means[0]; 148 String command = means[1]; 149 String parameter = means[2]; 150 if (name.equals(robot.getName())){ 151 if (command.equals("move")){ 152 this.expression = new MoveExpression(robot); 153 } else if (command.equals("turn")){ 154 this.expression = new TurnExpression(robot); 155 } else if (command.equals("platform")){ 156 this.expression = new PlatformExpression(robot); 157 } else { 158 System.out.println("Wrong input command"); 159 return; 160 } 161 expression.interpret(parameter); 162 } 163 } 164 } 165 166 public class Main { 167 168 public static void main(String[] args) { 169 Robot robot = new Robot("Turtlebot"); 170 Context context = new Context(robot); 171 context.execute("Turtlebot move 3"); 172 context.execute("Turtlebot move 2"); 173 context.execute("Turtlebot turn Left"); 174 context.execute("Turtlebot move 10"); 175 context.execute("Turtlebot platform Down"); 176 robot.getPosition(); 177 } 178 179 }
Java的拓展:
在项目开发中,如果要对数据表达式进行分析与计算,无须再用解释器模式进行设计了,Java 提供了以下强大的数学公式解析器:Expression4J、MESP(Math Expression String Parser) 和 Jep 等,它们可以解释一些复杂的文法,功能强大,使用简单。
示例:
1 import com.singularsys.jep.*; 2 public class JepDemo 3 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws JepException 5 { 6 Jep jep=new Jep(); 7 //定义要计算的数据表达式 8 String 存款利息="本金*利率*时间"; 9 //给相关变量赋值 10 jep.addVariable("本金",10000); 11 jep.addVariable("利率",0.038); 12 jep.addVariable("时间",2); 13 jep.parse(存款利息); //解析表达式 14 Object accrual=jep.evaluate(); //计算 15 System.out.println("存款利息:"+accrual); 16 } 17 }