一、std::async和std::future的用法
std::async是一个函数模板,std::future是一个类模板
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 #include <Windows.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int mythread() 9 { 10 cout << "my thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 11 int temp = 0; 12 temp++; 13 Sleep(5000); 14 cout << "my thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 15 return temp; 16 } 17 int main() 18 { 19 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 20 std::future<int> result = std::async(std::launch::async, mythread); 21 //std::async(mythread);相当于std::async(std::launch::async, mythread); 22 //自动创建一个线程开始执行线程入口函数,并返回一个std::future对象给result 23 24 cout << result.get() << endl; //等待入口函数执行,直到拿到返回值,即temp 25 //result.wait(); //只等待入口函数执行完,但不返回结果 26 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 27 system("pause"); 28 return 0; 29 }
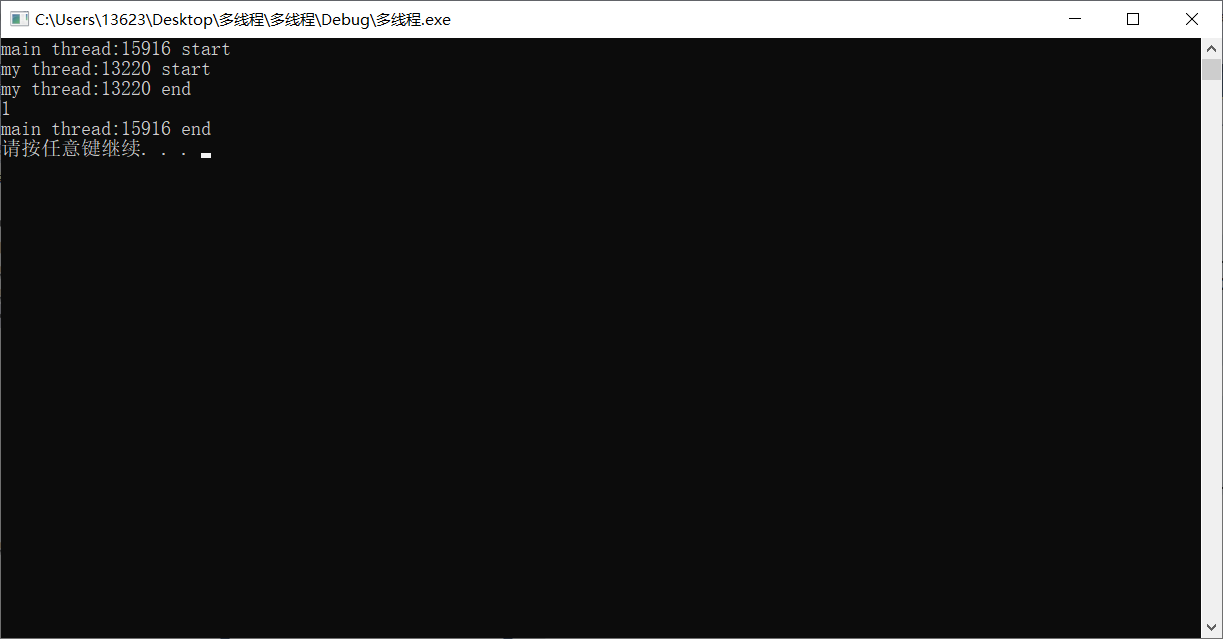
std::async(std::launch::async, mythread);如果std::async()的第一个参数改成std::lauch::deferred,那么线程不会被马上执行,而是延迟到std::future的wait()或者get()函数调用时才执行线程的入口函数。实际上,并没有创建
子线程,而只是在主函数中调用了入口函数。
二、std::packaged_task的用法
std::packaged_task是一个类模板,模板参数各种可调用对象,通过它把各种可调用对象包装起来,方便作为线程入口函数来调用
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 #include <Windows.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int fun(int val) 9 { 10 cout << "my thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 11 val++; 12 cout << "my thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 13 return val; 14 } 15 int main() 16 { 17 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 18 std::packaged_task<int(int)> pack(fun); 19 thread t1(std::ref(pack), 0); 20 t1.join(); 21 std::future<int> result = pack.get_future(); 22 cout << result.get() << endl; 23 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 24 system("pause"); 25 return 0; 26 }
三、std::promise的用法
std::promise是一个类模板,能够在某个线程中给它赋值,然后可以在其他线程中,在将来的某个时刻,可以把这个值取出来。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <thread> 3 #include <future> 4 #include <Windows.h> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void mythread1(std::promise<int> &pro, int val) 9 { 10 cout << "my thread1:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 11 val++; 12 val--; 13 Sleep(500); //假设运算了500毫秒 14 int result = val; 15 pro.set_value(val);//保存结果 16 cout << "my thread1:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 17 } 18 19 20 void mythread2(std::future<int> &getful) 21 { 22 cout << "my thread2:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 23 auto getval = getful.get(); 24 cout << getval << endl; 25 cout << "my thread2:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 26 } 27 int main() 28 { 29 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " start" << endl; 30 std::promise<int> prom; //声明一个promise对象,保存类型为int 31 thread t1(mythread1, std::ref(prom), 10); 32 t1.join(); 33 34 std::future<int> ful = prom.get_future(); //promise和future绑定,用于返回保存的结果 35 36 //在主线程获取结果 37 //auto result = ful.get(); //get()只能使用一次,如果主线程中使用了,t2就不能使用了 38 //cout << result << endl; 39 40 //在线程t2中获取结果 41 thread t2(mythread2, std::ref(ful)); 42 t2.join(); 43 44 cout << "main thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << " end" << endl; 45 system("pause"); 46 return 0; 47 }
std::ref 用于包装按引用传递的值。