1.ipv4和ipv6的报文结构
2.交换机中的ram和rom
3.路由器的启动过程
1) Performing POST and Load Bootstrap Program (Figure 2)
During the Power-On Self-Test (POST), the router executes diagnostics from ROM on several hardware components, including the CPU, RAM, and NVRAM. After the POST, the bootstrap program is copied from ROM into RAM. The main task of the bootstrap program is to locate the Cisco IOS and load it into RAM.
Note: At this point, if you have a console connection to the router, you begin to see the output on the screen.
2) Locating and Loading Cisco IOS (Figure 3)
The IOS is typically stored in flash memory and is copied into RAM for execution by the CPU. If the IOS image is not located in flash, then the router may look for it using a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. If a full IOS image cannot be located, a limited IOS is copied into RAM, which can be used to diagnose problems and transfer a full IOS into Flash memory.
3)Locating and Loading the Configuration File (Figure 4)
The bootstrap program then copies the startup configuration file from NVRAM into RAM. This becomes the running configuration. If the startup configuration file does not exist in NVRAM, the router may be configured to search for a TFTP server. If a TFTP server is not found, then the router displays the setup mode prompt.
4.SLAAC uses ICMPv6 messages when dynamically assigning an IPv6 address to a host. DHCPv6 is an alternate method of assigning an IPv6 addresses to a host. ARPv6 does not exist. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) provides the functionality of ARP for IPv6 networks. UDP is the transport layer protocol used by DHCPv6.
5.ipv6的全球单播地址:
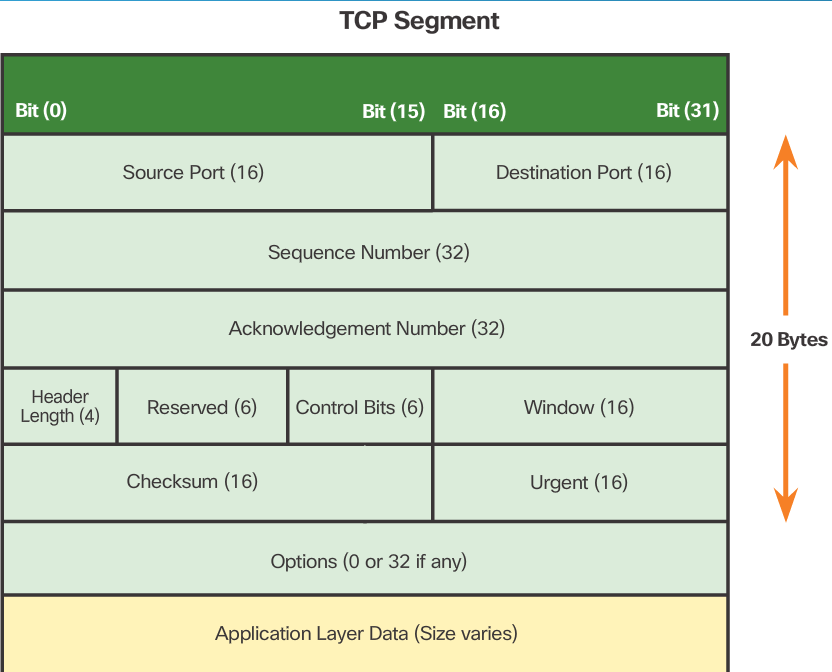
6.tcp的报文结构
As shown in the figure, each TCP segment has 20 bytes of overhead in the header encapsulating the application layer data:
- Source Port (16 bits) and Destination Port (16 bits) - Used to identify the application.
- Sequence number (32 bits) - Used for data reassembly purposes.
- Acknowledgment number (32 bits) - Indicates the data that has been received.
- Header length (4 bits) - Known as ʺdata offsetʺ. Indicates the length of the TCP segment header.
- Reserved (6 bits) - This field is reserved for the future.
- Control bits (6 bits) - Includes bit codes, or flags, which indicate the purpose and function of the TCP segment.
- Window size (16 bits) - Indicates the number of bytes that can be accepted at one time.
- Checksum (16 bits) - Used for error checking of the segment header and data.
- Urgent (16 bits) - Indicates if data is urgent
7.udp的报文结构
- Well-known Ports (Numbers 0 to 1023) - These numbers are reserved for services and applications. They are commonly used for applications such as web browsers, email clients, and remote access clients. By defining these well-known ports for server applications, client applications can be programmed to request a connection to that specific port and its associated service.
- Registered Ports (Numbers 1024 to 49151) - These port numbers are assigned by IANA to a requesting entity to use with specific processes or applications. These processes are primarily individual applications that a user has chosen to install, rather than common applications that would receive a well-known port number. For example, Cisco has registered port 1985 for its Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP) process.
- Dynamic or Private Ports (Numbers 49152 to 65535) - Also known as ephemeral ports, these are usually assigned dynamically by the client’s OS when a connection to a service is initiated. The dynamic port is then used to identify the client application during communication.
8.DNS系统
9.DHCP
Assuming that the IPv4 address requested by the client, or offered by the server, is still available, the server returns a DHCP acknowledgment (DHCPACK) message that acknowledges to the client that the lease has been finalized. If the offer is no longer valid, then the selected server responds with a DHCP negative acknowledgment (DHCPNAK) message. If a DHCPNAK message is returned, then the selection process must begin again with a new DHCPDISCOVER message being transmitted. After the client has the lease, it must be renewed prior to the lease expiration through another DHCPREQUEST message.
The DHCP server ensures that all IP addresses are unique (the same IP address cannot be assigned to two different network devices simultaneously). Most Internet providers use DHCP to allocate addresses to their customers.
DHCPv6 has similar set of messages to those shown in the figure for DHCP for IPv4. The DHCPv6 messages are SOLICIT, ADVERTISE, INFORMATION REQUEST, and REPLY
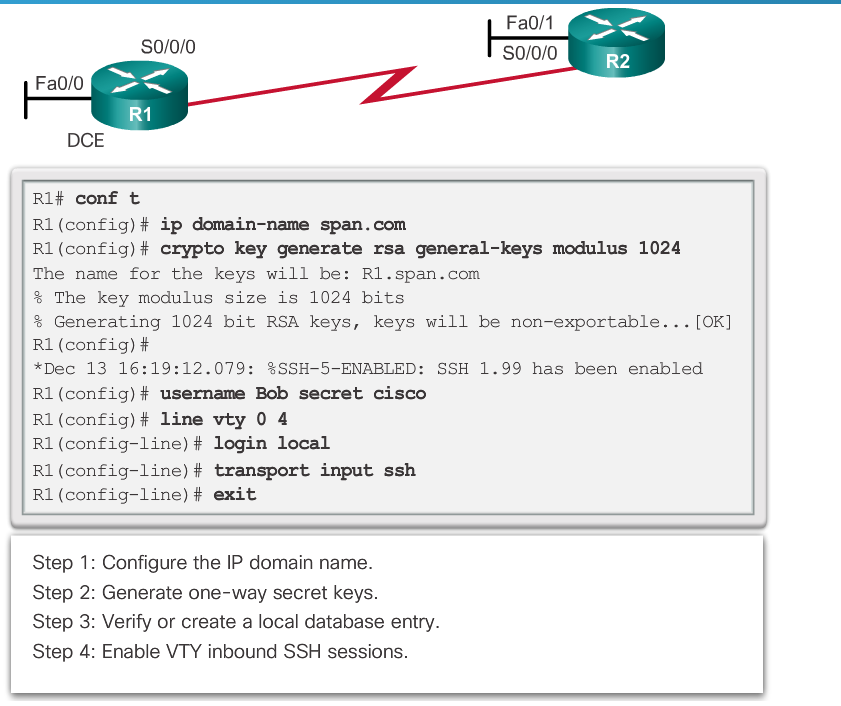
10.SSH的配置