前言:你说栈和队列全部都用数组实现多好 非得找麻烦 到头来底层还是数组
上课弄了两节课 终于弄懂了这个栈和队列的相互实现
烦死了 还不如给学妹做图标开心
19.04.17更新:自闭ing…开心有个什么用?图标被直接弃用!!!连个修改的机会都没有!!!简直要比阿里的主管面给我的打击还要大!疯狂自闭中!!!气炸了气炸了,以后再也不做图标了!这将是我的封笔之作
栈和队列
用栈实现队列
两个栈实现
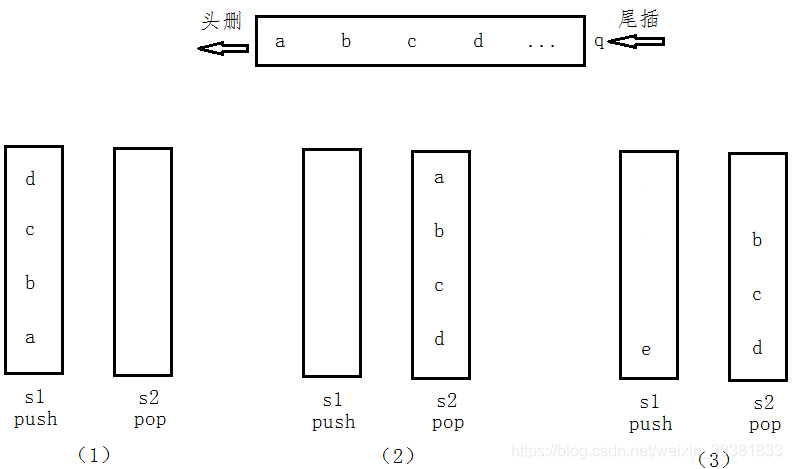
图(1):元素“abcd”压入stack1中,stack2为空;
图(2):stack1中的元素pop进stack2中,pop一下stack2中的元素,和队列一样了
图(3):可能有些人很疑惑,就像图3,当stack2只pop了一个元素a时,satck1中可能还会插入元素e,这时如果将stack1中的元素e插入stack2中,在a之后出栈的元素就是e了,显然,这样想是不对的,我们必须规定当stack2中的元素pop完之后,也就是satck2为空时,再插入stack1中的元素
Java实现
class MyQueue {
Stack <Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack <Integer> stackTemp = new Stack<Integer>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
stackTemp.push(stack.pop());
}
int temp = stackTemp.pop();
while(!stackTemp.isEmpty()){
stack.push(stackTemp.pop());
}
return temp;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
stackTemp.push(stack.pop());
}
int temp = stackTemp.peek();
while(!stackTemp.isEmpty()){
stack.push(stackTemp.pop());
}
return temp;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
用队列实现栈
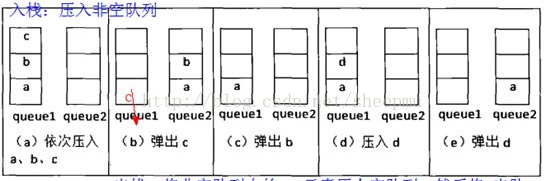
所有元素进入q1,因为我们的目的是栈,也就是最先出c,而队是从队头开始出,所有先把ab出q1并入q2,此时目标c跑到了队头,出q1。此时q1已经为空,下一个要出的是b,把a从q2出队并进q1,此时目标b在q2队头,出队
public class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;
private Queue<Integer> queue2;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/**
* Push element x onto stack.
*/
public void push(int x) {
if (queue1.peek() != null){
while (queue1.peek() != null) {
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
queue1.offer(x);
while (queue2.peek() != null) {
queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
}
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
/**
* Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element.
*/
public int pop() {
if (queue1.peek() == null){
return 0;
}
return queue1.poll();
}
/**
* Get the top element.
*/
public int top() {
if (queue1.peek() == null){
return 0;
}
return queue1.peek();
}
/**
* Returns whether the stack is empty.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.peek() == null ? true : false;
}
}
以上记录的是用两个栈实现队列和用两个队列实现栈,看到还有分别用一个实现的高级解法,日后遇到在更新
或许以后就会知道为什么不直接用数组实现的原因了吧