一、前言
二、框架结构及实现流程
三、总结
一、前言
当我们了解了Web应用和Web框架,以及HTTP协议的原理之后,我们可以自己动手DIY一个最简单的WEB框架,以加深对Web框架的理解,并为即将学习的Django探探路。
二、框架结构及实现流程
1.框架结构的内容如下图所示
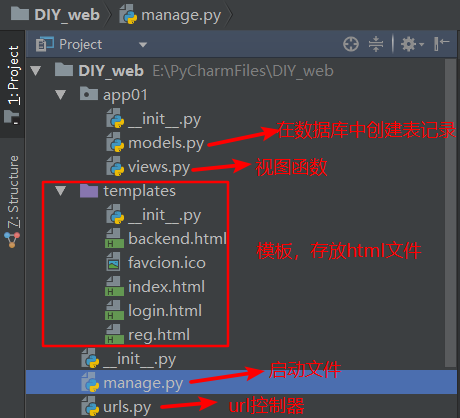
我们DIY的这个Web框架按照启动的先后顺序,大致分为这样几个部分,分别是models.py、manage.py、urls.py、views.py、templates(html文件)五个部分,下面我们分别对这五个部分进行实现,最后,进行运行测试,验证框架的的可用性。
2.实现流程
(1) models.py -- 与数据库相关的,在我们的项目启动前,利用models.py在数据库中创建表结构,注意,仅运行一次。
#!/usr/bin/env python3 #!-*- coding:utf-8-*- # write by cc import pymysql # 1.建立连接 conn = pymysql.connect( host = 'localhost', port = 3306, user = 'cc1', password = 'cc111', db = 'db1', charset = 'utf8' ) # 2.获取游标 cursor = conn.cursor() # cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursor.DictCursor) # 设游标类型为字典类型 # 3.执行sql语句 sql = "create table users(id int,user char(12),pwd char(12))" rows = cursor.execute(sql) print(rows) # 打印受影响的记录条数 # 4.提交(必须提交,才能实现操作) conn.commit() # 5.关闭游标和连接 cursor.close() conn.close()
(2) manage.py -- 项目的启动文件
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server from urls import url_list def application(environ,start_response): path = environ.get("PATH_INFO") print(path) start_response("200 OK",[('Content-Type','text/html')]) func = None for item in url_list: if path == item[0]: func = item[1] break if func: return [func(environ)] else: return [b'404 Not found'] if __name__ == '__main__': httpd = make_server("",8080,application) # 指定端口 print('Serving HTTP on port 8080...') httpd.serve_forever() # 开启监听
(3) urls.py -- url控制器,反映路径与视图函数的映射关系
from app01.views import * url_list = [ ('/favcion.ico',fav), ('/index',index), ('/login',login), ('/reg',reg), ('/timer',timer), ('/auth',auth) ]
(4) views.py -- 视图函数,固定接收一个形式参数:environ
from urllib.parse import parse_qs def fav(environ): with open('templates/favcion.ico','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def index(environ): with open('templates/index.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def login(environ): with open('templates/login.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def reg(environ): with open('templates/reg.html','rb') as f: data = f.read() return data def timer(environ): import datetime now = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%y-%m-%d %X") return now.encode('utf-8') def auth(environ): try: request_body_size = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH',0)) except(ValueError): request_body_size = 0 request_body = environ['wsgi.input'].read(request_body_size) data = parse_qs(request_body) # 解析出用户输入的用户名和密码 user = data.get(b'user')[0].decode('utf8') pwd = data.get(b'pwd')[0].decode('utf8') # 连接数据库 import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='cc1',password='cc111',db='db1',charset='utf8') # 创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 执行数据查询、插入等操作 sql = 'select * from users where user=%s and pwd=%s' cursor.execute(sql,(user,pwd)) # 验证是否能取出相关记录 if cursor.fetchone(): print(cursor.fetchone()) f = open('templates/backend.html','rb') data = f.read() data = data.decode('utf8') return data else: return b'user or password is wrong'
(5) templates -- 储存 html 文件,当用户输入的路径正确存在与url控制器中时,为用户展示指定的页面。
favcion.ico 是一个缩略图,可自由指定。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello world!</h1> <h2>Boys and girls!</h2> <h3><a href="https://www.cnblogs.com/schut"/>This is my web</a></h3> <img src="https://pic.cnblogs.com/avatar/1209144/20170813234607.png"> </body> </html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello world!</h1> <h2>Boys and girls!</h2> <form action="http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth" method="post"> 姓名<input type="text" name="user"> 密码<input type="password" name="pwd"> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
reg.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>注册页面</title> </head> <body> <h3>欢迎来到注册页面</h3> <form action="" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="pwd"><br/> 再次输入密码:<input type="password" name="pwd2"><br/> <input type="submit"> <input type="reset"> </form> </body> </html>
backend.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h2>欢迎登录</h2> </body> </html>
三、总结
以上DIY的简易框架,大致可以分为五个部分,各自承担不同的作用,缺一不可。
manage.py -- 启动文件,封装socket
1 urls.py -- 路径与视图函数的映射关系 ------------- url控制器
2 views.py -- 视图函数,固定接收一个形式参数:environ ------- 视图函数
3 templates文件夹 -- html文件 -------模板
4 models --在项目启动前,在数据库中创建表结构 ----- 与数据库相关