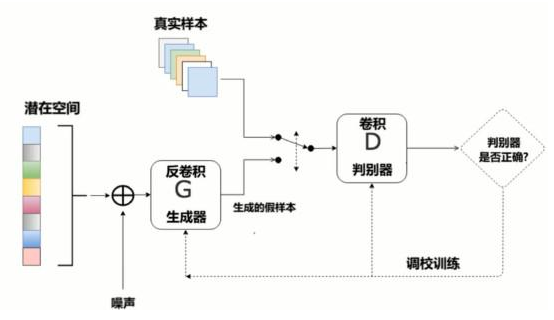
1、知识点
""" DCGAN:相比GAN而言,使用了卷积网络替代全连接 卷积:256*256*3 --- > 28*28*14 -->结果 ,即H,W变小,特征图变多 反卷积(就是把卷积的前向和反向传播完全颠倒了) :4*4*1024 ---> 28 * 28 *1 -->结果 即H,W变大,特征图变少 特点: 1、判别模型:使用带步长的卷积(strided convolutions)取代了的空间池化(spatial pooling),容许网络学习自己的空间下采样(spatial downsampling)。 2、生成模型:使用微步幅卷积(fractional strided),容许它学习自己的空间上采样(spatial upsampling)。 3、激活函数: LeakyReLU 4、Batch Normalization 批标准化:解决因糟糕的初始化引起的训练问题,使得梯度能传播更深层次。 Batch Normalization证明了生成模型初始化的重要性,避免生成模型崩溃:生成的所有样本都在一个点上(样本相同),这是训练GANs经常遇到的失败现象。
简而言之,DCGAN是利用数据生成图片的过程
"""
2、代码

# coding: utf-8 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import pickle import matplotlib.pyplot as plt get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline') from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('/MNIST_data/') # ## 获得数据 # In[4]: def get_inputs(noise_dim, image_height, image_width, image_depth): inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, image_height, image_width, image_depth], name='inputs_real') inputs_noise = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, noise_dim], name='inputs_noise') return inputs_real, inputs_noise # # 生成器 # In[5]: def get_generator(noise_img, output_dim, is_train=True, alpha=0.01): with tf.variable_scope("generator", reuse=(not is_train)): # 100 x 1 to 4 x 4 x 512 # 全连接层 layer1 = tf.layers.dense(noise_img, 4*4*512) layer1 = tf.reshape(layer1, [-1, 4, 4, 512]) # batch normalization layer1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer1, training=is_train) # Leaky ReLU layer1 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer1, layer1) # dropout layer1 = tf.nn.dropout(layer1, keep_prob=0.8) # 4 x 4 x 512 to 7 x 7 x 256 layer2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer1, 256, 4, strides=1, padding='valid') layer2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer2, training=is_train) layer2 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer2, layer2) layer2 = tf.nn.dropout(layer2, keep_prob=0.8) # 7 x 7 256 to 14 x 14 x 128 layer3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer2, 128, 3, strides=2, padding='same') layer3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer3, training=is_train) layer3 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer3, layer3) layer3 = tf.nn.dropout(layer3, keep_prob=0.8) # 14 x 14 x 128 to 28 x 28 x 1 logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer3, output_dim, 3, strides=2, padding='same') # MNIST原始数据集的像素范围在0-1,这里的生成图片范围为(-1,1) # 因此在训练时,记住要把MNIST像素范围进行resize outputs = tf.tanh(logits) return outputs # ## 判别器 # In[6]: def get_discriminator(inputs_img, reuse=False, alpha=0.01): with tf.variable_scope("discriminator", reuse=reuse): # 28 x 28 x 1 to 14 x 14 x 128 # 第一层不加入BN layer1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs_img, 128, 3, strides=2, padding='same') layer1 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer1, layer1) layer1 = tf.nn.dropout(layer1, keep_prob=0.8) # 14 x 14 x 128 to 7 x 7 x 256 layer2 = tf.layers.conv2d(layer1, 256, 3, strides=2, padding='same') layer2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer2, training=True) layer2 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer2, layer2) layer2 = tf.nn.dropout(layer2, keep_prob=0.8) # 7 x 7 x 256 to 4 x 4 x 512 layer3 = tf.layers.conv2d(layer2, 512, 3, strides=2, padding='same') layer3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer3, training=True) layer3 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer3, layer3) layer3 = tf.nn.dropout(layer3, keep_prob=0.8) # 4 x 4 x 512 to 4*4*512 x 1 flatten = tf.reshape(layer3, (-1, 4*4*512)) logits = tf.layers.dense(flatten, 1) outputs = tf.sigmoid(logits) return logits, outputs # ## 目标函数 # In[7]: def get_loss(inputs_real, inputs_noise, image_depth, smooth=0.1): g_outputs = get_generator(inputs_noise, image_depth, is_train=True) d_logits_real, d_outputs_real = get_discriminator(inputs_real) d_logits_fake, d_outputs_fake = get_discriminator(g_outputs, reuse=True) # 计算Loss g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake, labels=tf.ones_like(d_outputs_fake)*(1-smooth))) d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_real, labels=tf.ones_like(d_outputs_real)*(1-smooth))) d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake, labels=tf.zeros_like(d_outputs_fake))) d_loss = tf.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake) return g_loss, d_loss # ## 优化器 # In[8]: def get_optimizer(g_loss, d_loss, beta1=0.4, learning_rate=0.001): train_vars = tf.trainable_variables() g_vars = [var for var in train_vars if var.name.startswith("generator")] d_vars = [var for var in train_vars if var.name.startswith("discriminator")] # Optimizer with tf.control_dependencies(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)): g_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(g_loss, var_list=g_vars) d_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(d_loss, var_list=d_vars) return g_opt, d_opt # In[9]: def plot_images(samples): fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=25, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(50,2)) for img, ax in zip(samples, axes): ax.imshow(img.reshape((28, 28)), cmap='Greys_r') ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) fig.tight_layout(pad=0) # In[10]: def show_generator_output(sess, n_images, inputs_noise, output_dim): cmap = 'Greys_r' noise_shape = inputs_noise.get_shape().as_list()[-1] # 生成噪声图片 examples_noise = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=[n_images, noise_shape]) samples = sess.run(get_generator(inputs_noise, output_dim, False), feed_dict={inputs_noise: examples_noise}) result = np.squeeze(samples, -1) return result # ## 训练网络 # In[11]: # 定义参数 batch_size = 64 noise_size = 100 epochs = 5 n_samples = 25 learning_rate = 0.001 # In[12]: def train(noise_size, data_shape, batch_size, n_samples): # 存储loss losses = [] steps = 0 inputs_real, inputs_noise = get_inputs(noise_size, data_shape[1], data_shape[2], data_shape[3]) g_loss, d_loss = get_loss(inputs_real, inputs_noise, data_shape[-1]) g_train_opt, d_train_opt = get_optimizer(g_loss, d_loss, beta1, learning_rate) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 迭代epoch for e in range(epochs): for batch_i in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size): steps += 1 batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) batch_images = batch[0].reshape((batch_size, data_shape[1], data_shape[2], data_shape[3])) # scale to -1, 1 batch_images = batch_images * 2 - 1 # noise batch_noise = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=(batch_size, noise_size)) # run optimizer _ = sess.run(g_train_opt, feed_dict={inputs_real: batch_images, inputs_noise: batch_noise}) _ = sess.run(d_train_opt, feed_dict={inputs_real: batch_images, inputs_noise: batch_noise}) if steps % 101 == 0: train_loss_d = d_loss.eval({inputs_real: batch_images, inputs_noise: batch_noise}) train_loss_g = g_loss.eval({inputs_real: batch_images, inputs_noise: batch_noise}) losses.append((train_loss_d, train_loss_g)) # 显示图片 samples = show_generator_output(sess, n_samples, inputs_noise, data_shape[-1]) plot_images(samples) print("Epoch {}/{}....".format(e+1, epochs), "Discriminator Loss: {:.4f}....".format(train_loss_d), "Generator Loss: {:.4f}....". format(train_loss_g)) # In[13]: with tf.Graph().as_default(): train(noise_size, [-1, 28, 28, 1], batch_size, n_samples)
3、结构图