版权声明: https://blog.csdn.net/dickdick111/article/details/89639264
信息检索系统——基于Lucene实现
题目要求
基于课程学习内容,实现简单的搜索引擎功能(界面可视化不做要求,可终端输出),要求实现以下基本功能:
- 拼写检查(参考最小编辑距离原理)
- 倒排索引
- 使用TF/IDF或者VSM进行文档排序
实现
这里使用的是lucene-8.0.0,由于版本不同,网上很多博客的教程已经失效,具体的api参数或者调用要参考官网最新的手册,这里需要一定的搜索与查阅文档的能力。
http://lucene.apache.org/core/8_0_0/core/
项目完整源码:Github传送门
下面只讲述部分关键的代码
1.构建倒排索引
-
这里利用IndexWriter类来构建索引,由于这里使用的是中文文档,故要使用分析中文的分析器
SmartChineseAnalyzer. -
根据建立索引的目录以及数据的目录来读取。
-
定义一个fieldType,并设置其属性,既保存在文件又用于索引建立
-
读取 file 转 string
-
用文件内容来建立倒排索引
-
用文件名来建立倒排索引
-
用文件路径来建立倒排索引
public class Indexer {
private IndexWriter writer;
public Indexer(String indexDirectoryPath) throws IOException{
// 获取目录directory
Directory indexDirectory = FSDirectory.open(FileSystems.getDefault().getPath(indexDirectoryPath));
// 中文分析器
Analyzer analyzer = new SmartChineseAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
writer = new IndexWriter(indexDirectory, config);
}
public void close() throws CorruptIndexException, IOException{
writer.close();
}
private Document getDocument(File file) throws IOException{
Document document = new Document();
// 定义一个fieldType,并设置其属性,既保存在文件又用于索引建立
FieldType fieldType = new FieldType();
fieldType.setStored(true);
fieldType.setIndexOptions(IndexOptions.DOCS_AND_FREQS_AND_POSITIONS);
// 读取 file 转 string
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
BufferedReader bf= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String s = null;
while((s = bf.readLine())!=null){//使用readLine方法,一次读一行
buffer.append(s.trim());
}
String xml = buffer.toString();
// 用文件内容来建立倒排索引
Field contentField = new Field(LuceneConstants.CONTENTS, xml,fieldType);
// 用文件名来建立倒排索引
Field fileNameField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_NAME,file.getName(),fieldType);
// 用文件路径来建立倒排索引
Field filePathField = new Field(LuceneConstants.FILE_PATH,file.getCanonicalPath(),fieldType);
// 添加到document
document.add(contentField);
document.add(fileNameField);
document.add(filePathField);
return document;
}
private void indexFile(File file) throws IOException{
System.out.println("Indexing "+file.getCanonicalPath());
Document document = getDocument(file);
writer.addDocument(document);
}
public int createIndex(String dataDirPath, FileFilter filter)
throws IOException{
//get all files in the data directory
File[] files = new File(dataDirPath).listFiles();
int count = 0;
for (File file : files) {
// System.out.println(file);
if(!file.isDirectory()
&& !file.isHidden()
&& file.exists()
&& file.canRead()
&& filter.accept(file)
){
indexFile(file);
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
测试函数:
public class LuceneTester {
String indexDir = "C:/Users/asus/Desktop/java/information-retrieval-system/index";
String dataDir = "C:/Users/asus/Desktop/java/information-retrieval-system/data";
Indexer indexer;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LuceneTester tester;
// File[] fs = new File("C:/Users/asus/Desktop/java/information-retrieval-system/data").listFiles();
// for (File f : fs){
// System.out.println(f);
// }
try {
tester = new LuceneTester();
tester.createIndex();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void createIndex() throws IOException{
indexer = new Indexer(indexDir);
int numIndexed;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
numIndexed = indexer.createIndex(dataDir, new TextFileFilter());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
indexer.close();
System.out.println(numIndexed+" File indexed, time taken: "
+(endTime-startTime)+" ms");
}
}
输出结果:这里我们就已经建立好索引,并在文件目录能找到索引文件
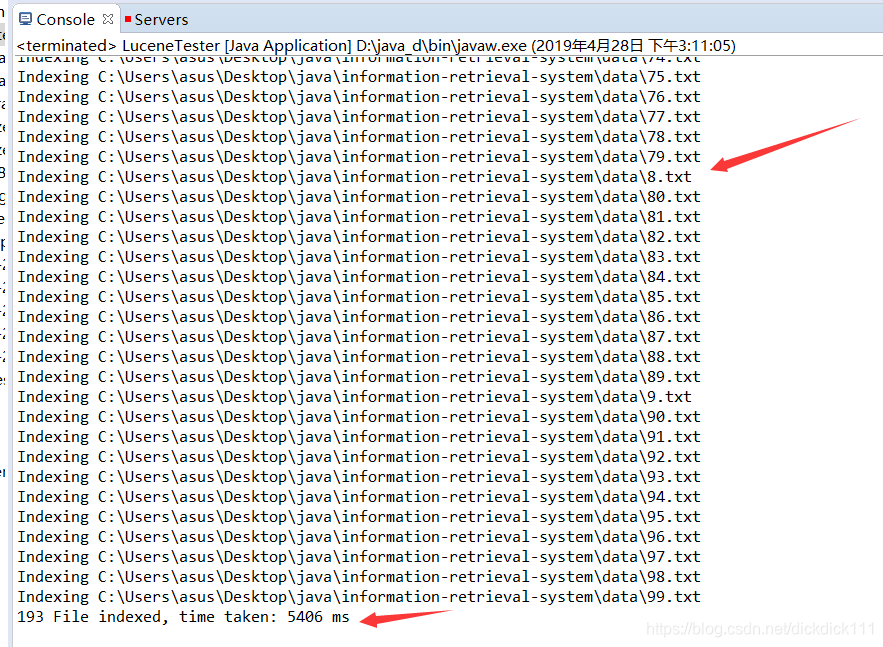
文件目录中的索引:
2. 使用TF/IDF进行文档排序,并使用关键词搜索文档
- 得到读取索引文件的路径
- 通过dir得到的路径下的所有的文件
- 设置为TF/IDF 排序
- 实例化分析器
- 建立查询解析器
- 根据传进来的q查找
- 开始查询
public class ReaderByIndexerTest {
public static void search(String indexDir,String q)throws Exception{
//得到读取索引文件的路径
Directory dir=FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir));
//通过dir得到的路径下的所有的文件
IndexReader reader=DirectoryReader.open(dir);
//建立索引查询器
IndexSearcher is=new IndexSearcher(reader);
// 设置为TF/IDF 排序
ClassicSimilarity sim = new ClassicSimilarity();
// Implemented as sqrt(freq).
// sim.tf(reader.getSumDocFreq(q));
// Implemented as log((docCount+1)/(docFreq+1)) + 1.
// sim.idf(reader.getSumDocFreq(q), reader.numDocs());
is.setSimilarity(sim);
// 实例化分析器
Analyzer analyzer=new SmartChineseAnalyzer();
// 建立查询解析器
/**
* 第一个参数是要查询的字段;
* 第二个参数是分析器Analyzer
* */
QueryParser parser=new QueryParser("contents", analyzer);
// 根据传进来的q查找
Query query=parser.parse(q);
// 计算索引开始时间
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
// 开始查询
/**
* 第一个参数是通过传过来的参数来查找得到的query;
* 第二个参数是要出查询的行数
* */
TopDocs hits=is.search(query, 10);
// 计算索引结束时间
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("匹配 "+q+" ,总共花费"+(end-start)+"毫秒"+"查询到"+hits.totalHits+"个记录");
//遍历hits.scoreDocs,得到scoreDoc
/**
* ScoreDoc:得分文档,即得到文档
* scoreDocs:代表的是topDocs这个文档数组
* @throws Exception
* */
for(ScoreDoc scoreDoc:hits.scoreDocs){
Document doc=is.doc(scoreDoc.doc);
System.out.println(doc.get(LuceneConstants.FILE_PATH));
}
//关闭reader
reader.close();
}
3. 拼写检查
- 建立目录
- 创建初始化索引
- 根据创建好的索引来检查k个建议的关键词
- 返回正确的关键词
public static String[] checkWord(String queryWord){
//新索引目录
String spellIndexPath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\java\\information-retrieval-system\\newPath";
//已有索引目录
String oriIndexPath = "C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\java\\information-retrieval-system\\index";
//拼写检查
try {
//目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open((new File(spellIndexPath)).toPath());
SpellChecker spellChecker = new SpellChecker(directory);
// 以下几步用来初始化索引
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(FSDirectory.open((new File(oriIndexPath)).toPath()));
// 利用已有索引
Dictionary dictionary = new LuceneDictionary(reader, LuceneConstants.CONTENTS);
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(new SmartChineseAnalyzer());
spellChecker.indexDictionary(dictionary, config, true);
int numSug = 5;
String[] suggestions =
spellChecker.suggestSimilar(queryWord, numSug);
reader.close();
spellChecker.close();
directory.close();
return suggestions;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
4. 综合测试
这里调用之前实现好的基类和工具类,并制作简陋的命令行界面来进行信息检索
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String indexDir="C:\\Users\\asus\\Desktop\\java\\information-retrieval-system\\index";
// 处理输入
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = null;
System.out.println("请输入你要搜索的关键词:");
try {
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
// 拼写检查
String temp = str;
String[] suggestions = checkWord(str);
if (suggestions != null && suggestions.length != 0){
System.out.println("你可能想输入的是:");
for(int i = 0; i < suggestions.length; i++){
System.out.println((i+1) + " : " + suggestions[i]);
}
System.out.println("请选择上面的一个正确的关键词(输入 1 ~ 5),或继续原词(输入0)进行搜索:");
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println();
if (str != "0"){
str = suggestions[str.charAt(0) - '1'];
}
else{
str = temp;
}
}
try {
search(indexDir,str);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
测试结果:
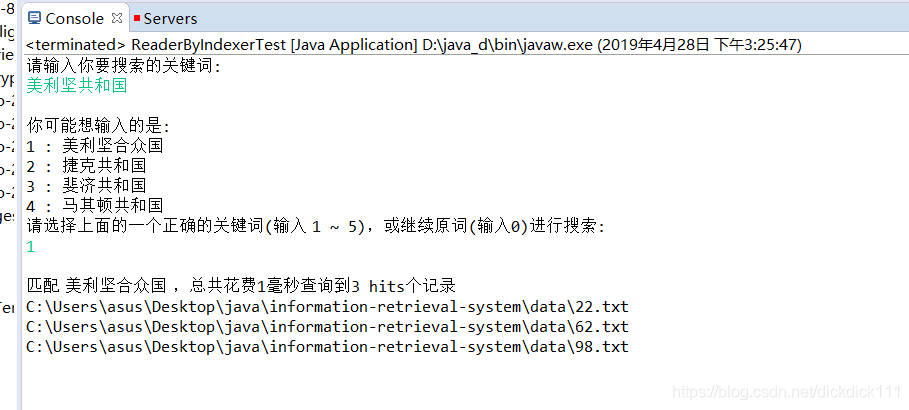
测试用例1解析:
这里我输入一个错误的关键词美利坚共和国,试图进行搜索,然后系统马上就会告诉我拼写检查的结果让我重新选择。
重新选择后会输出美利坚合众国的正确查询结果
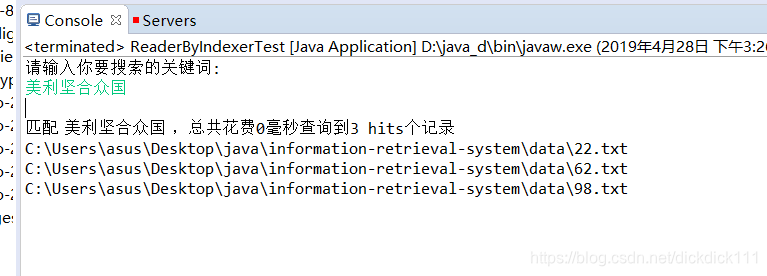
测试用例2解析:
这里直接输入一个正确的存在的关键词,就会直接输出美利坚合众国的正确查询结果,不会出现拼写检查的提醒