The Domain Name System has become the largest distributed database in the world. Human usage of the internet would be difficult to imagine without something such as DNS to map IP addresses to human-readable names. We will examine the DNS structure and the query protocol. We will discuss many of the design decisions made when DNS was being conceived. We will then examine content distribution networks in the context of a creative and unforeseen use of DNS.
For another look at the idea of using DNS for CDNs (a not-very-happy look), check out Vixie2009.pdf in the Readings section.
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to:
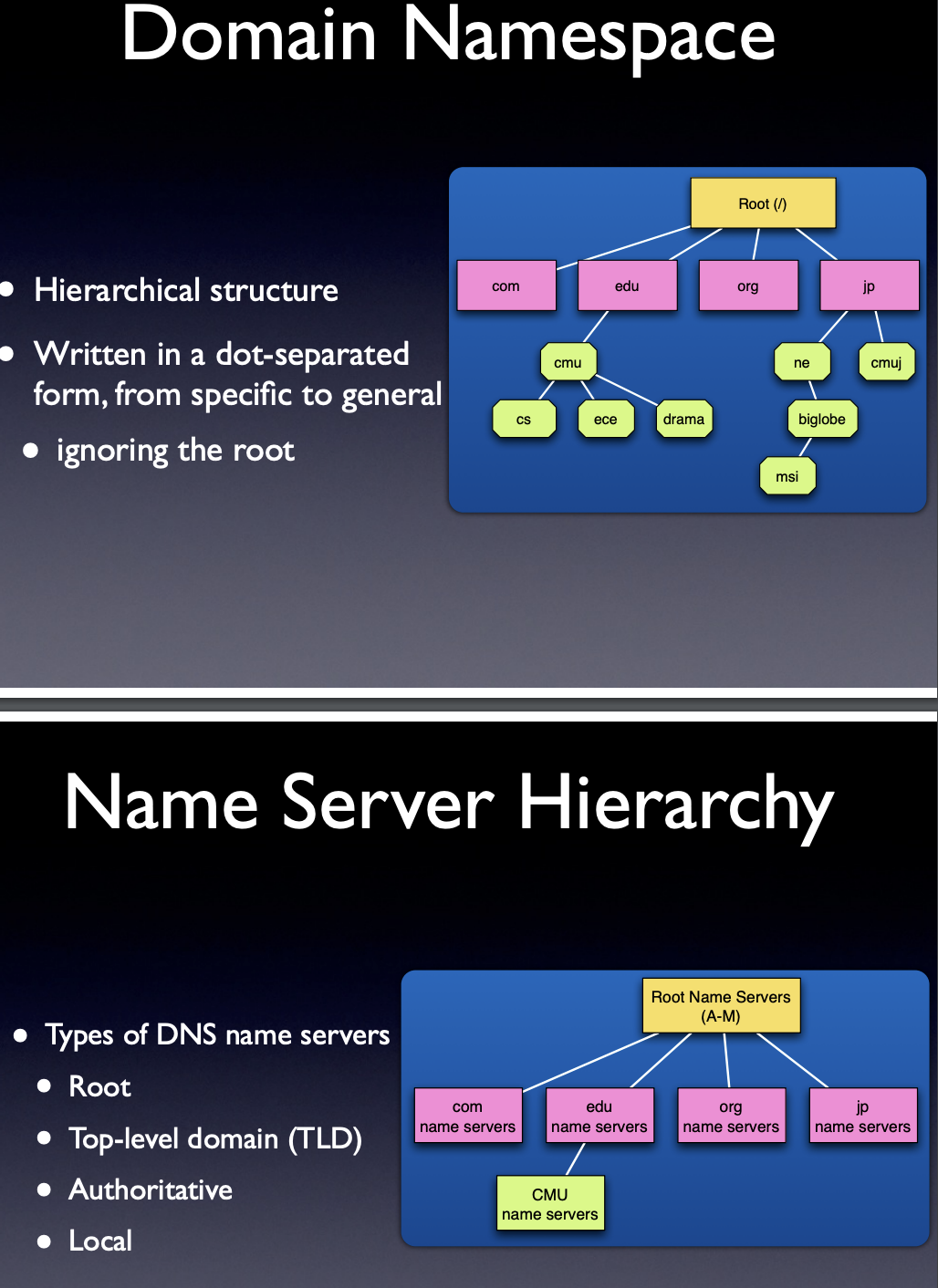
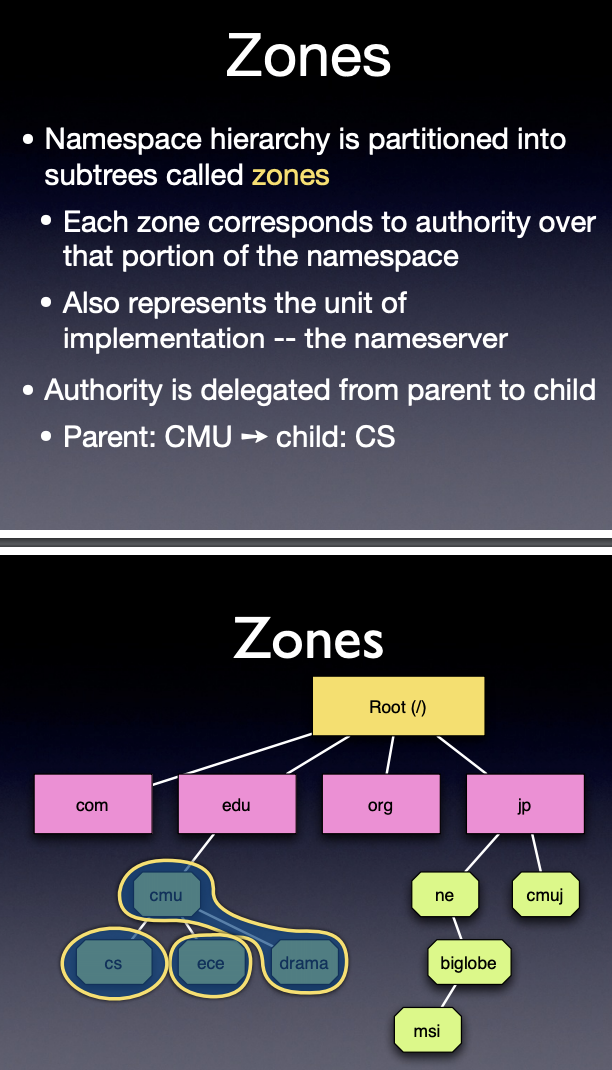
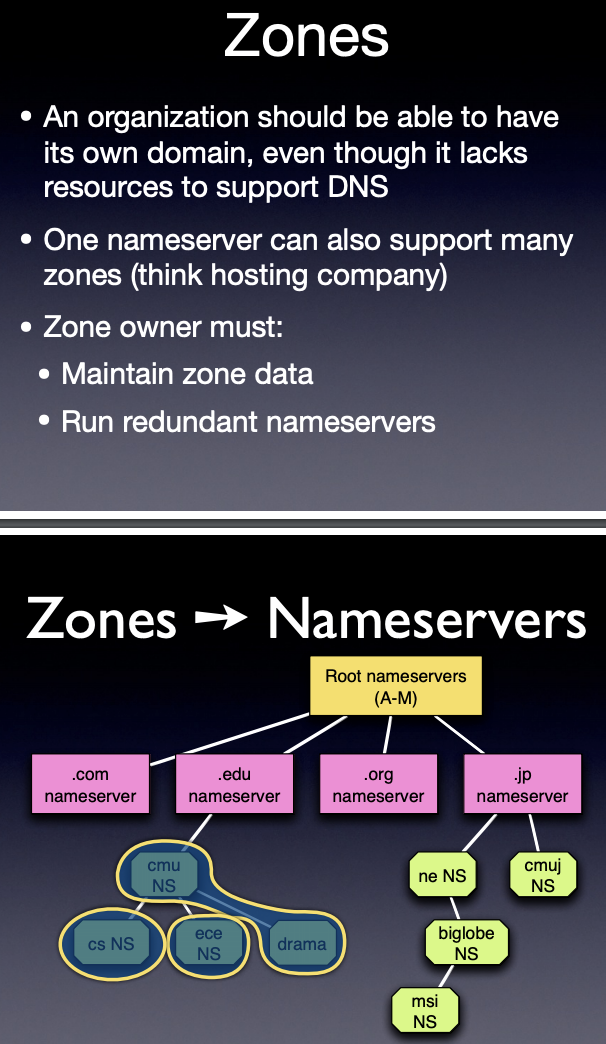
- describe the DNS service, including mission, interaction model, nameservers, domains, zones, load distribution, and domain name types.
- explain the DNS protocol, including message format, reliability, resource records, types, and caching mechanisms.
- describe the navigation mechanisms of DNS nameservers.
- describe the roles of the different nameservers in the DNS.
- describe how a CDN operates, including goals, host-roles, URL rewriting and DNS redirection.
- contrast the advantages of CDNs and web proxies.
Outline
- Naming theory
- DNS: Domain Name System
- The Protocol
- Organization of domains, zones, nameservers
- Content Distribution Networks
Reading
- KR Ch 2.4
- KR Ch 2.6
- Classic DNS [Mockapetris88]
Slides
Due
- Paper Review: Mockapetris88
Video






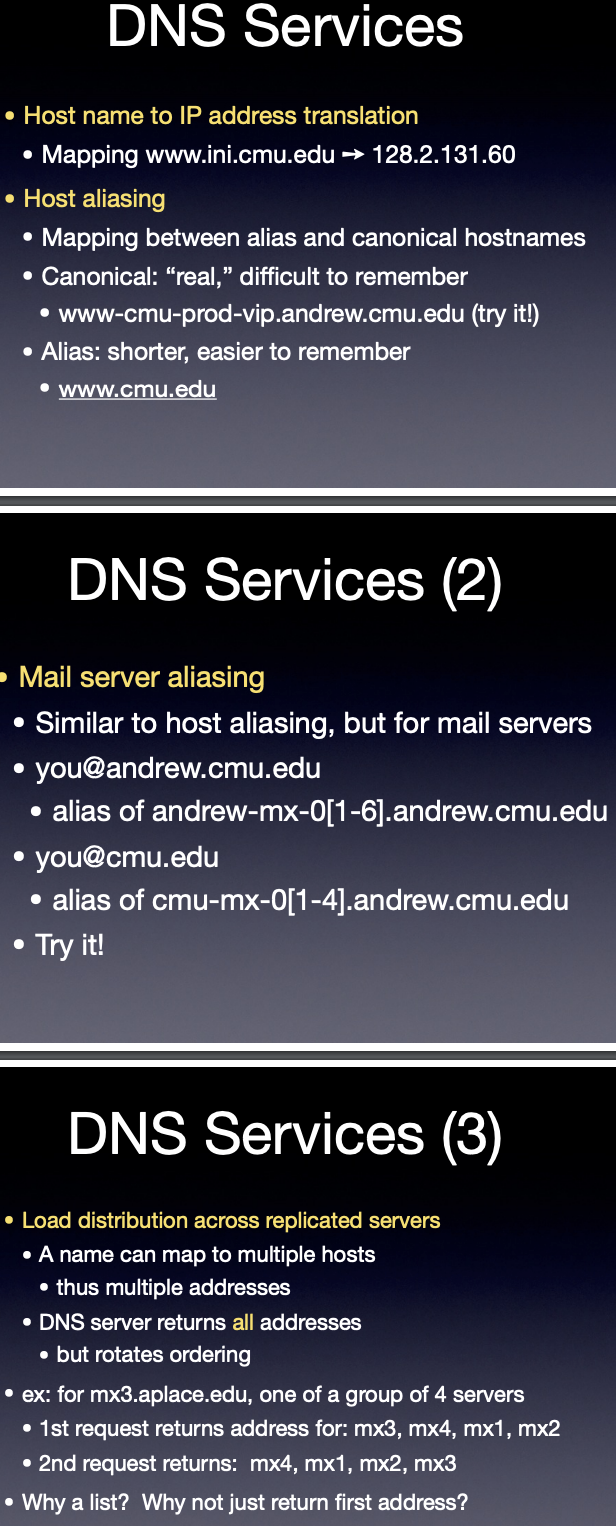
spread out the internet traffic
why a list? =>
(1) more information, so from a reliability and redundancy perspective, if mx1 happens to be down/ doesnt work, we still have backup;
(2) fill cache with more than one answers, we have more than 1 answer
https://www.wikiwand.com/en/SIMPLE_(instant_messaging_protocol)
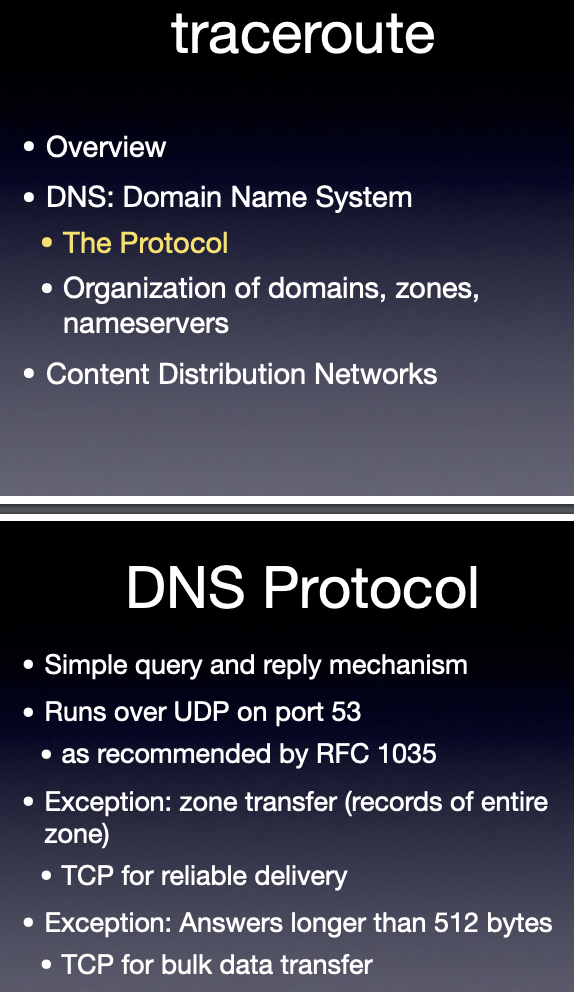

tcp => large file, reliable
udp => small file, unreliable => in the DNS context, if fail, just try other DNS servers. => now reliable


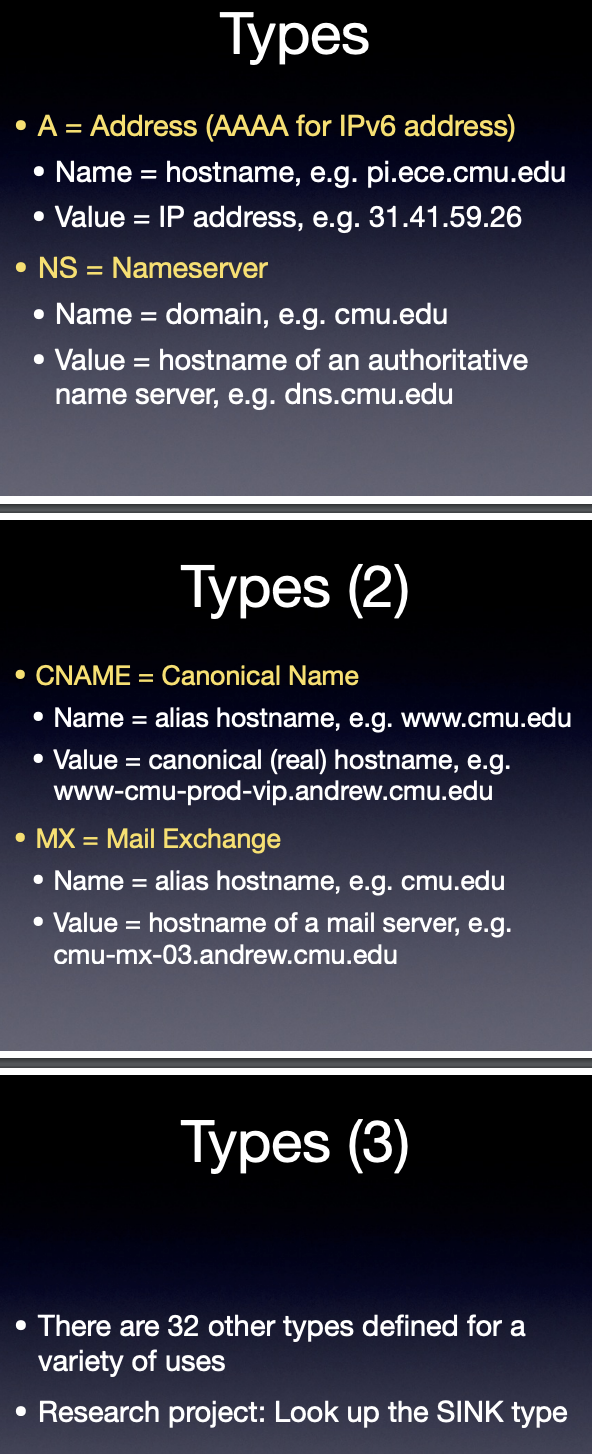
name, value => information we need
type => record of alias or canonical name
class => almost useless


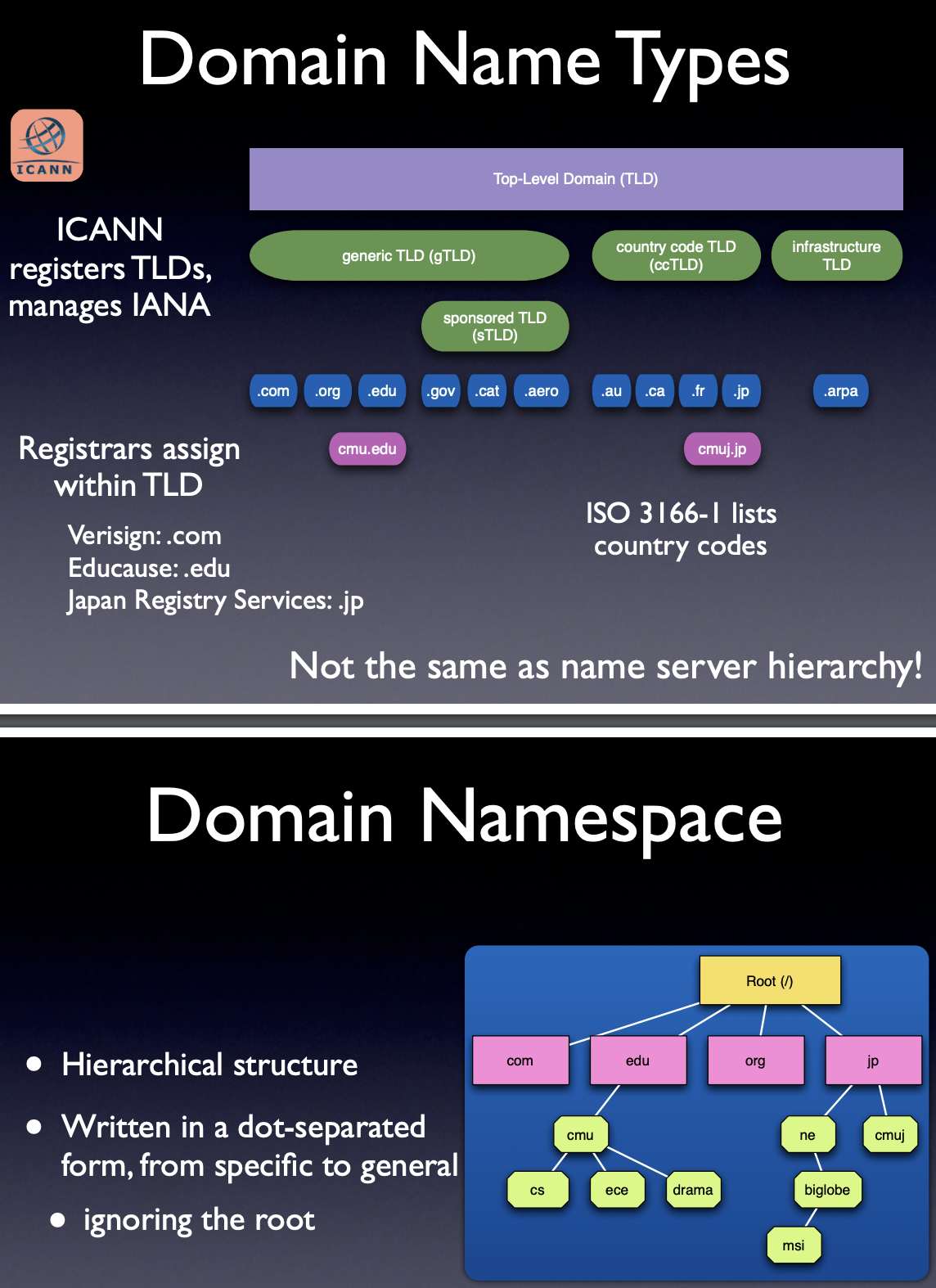
could be a mixture of different navigation forms










↓


ISP => internet service provider
CDN => provide DNS parsing, and return a CDN's cache location according to the client's IP
CDN => content distribution server => cache content for a region <= CNN or other media pays and controls what's cached (proactively)
Proxy caching => local caching in an institution <= local instituion pays and CNN or other media has no control of what's cached
DNS => provided by CDN, ISP, large IT companies, ... <= chosen by local computer
