一、flume架构概述
1、flume简介
Flume是一种分布式,可靠且可用的服务,用于有效地收集,聚合和移动大量日志数据。它具有基于流数据流的简单灵活的架构。它具有可靠的可靠性机制和许多故障转移和恢复机制,具有强大的容错性。它使用简单的可扩展数据模型,允许在线分析应用程序。
flume 作为 cloudera 开发的实时日志收集系统,受到了业界的认可与广泛应用。
Flume参考资料:
官方网站: http://flume.apache.org/
用户文档: http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html
开发文档: http://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html
2、flume的特点
##flume的特点:
Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(比如文本、HDFS、Hbase等)的能力 。
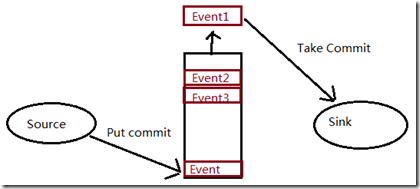
flume的数据流由事件(Event)贯穿始终。事件是Flume的基本数据单位,它携带日志数据(字节数组形式)并且携带有头信息,这些Event由Agent外部的Source生成,Event是Flume数据传输的基本单元;
当Source捕获事件后会进行特定的格式化,然后Source会把事件推入(单个或多个)Channel中。你可以把Channel看作是一个缓冲区,它将保存事件直到Sink处理完该事件。
Sink负责持久化日志或者把事件推向另一个Source。
flume的可靠性:
当节点出现故障时,日志能够被传送到其他节点上而不会丢失。Flume提供了三种级别的可靠性保障,从强到弱依次分别为:
end-to-end(收到数据agent首先将event写到磁盘上,当数据传送成功后,再删除;如果数据发送失败,可以重新发送。)
Store on failure(这也是scribe采用的策略,当数据接收方crash时,将数据写到本地,待恢复后,继续发送)
Besteffort(数据发送到接收方后,不会进行确认)。
flume的可恢复性:
还是靠Channel。推荐使用FileChannel,事件持久化在本地文件系统里(性能较差)。
3、flume的一些核心概念
Client:Client生产数据,运行在一个独立的线程。
Event: 一个数据单元,消息头和消息体组成。(Events可以是日志记录、 avro 对象等。)
Flow: Event从源点到达目的点的迁移的抽象。
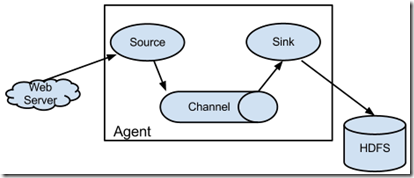
Agent: 一个独立的Flume进程,包含组件Source、 Channel、 Sink。(Agent使用JVM 运行Flume。每台机器运行一个agent,但是可以在一个agent中包含多个sources和sinks。)
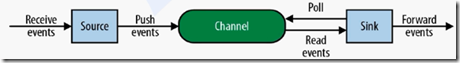
Source: 数据收集组件。(source从Client收集数据,传递给Channel)
Channel: 中转Event的一个临时存储,保存由Source组件传递过来的Event。(Channel连接 sources 和 sinks ,这个有点像一个队列,起到一个缓冲的作用。)
Sink: 从Channel中读取并移除Event, 将Event传递到FlowPipeline中的下一个Agent(如果有的话)(Sink从Channel收集数据,运行在一个独立线程。)
##agent
Flume 运行的核心是 Agent。Flume以agent为最小的独立运行单位。一个agent就是一个JVM。
它是一个完整的数据收集工具,含有三个核心组件,分别是:
source、 channel、 sink。通过这些组件, Event 可以从一个地方流向另一个地方,如下图所示。
Channel/Event/Sink
A Flume agent with one flow;
二、安装使用flume
1、安装
##解压包
[root@hadoop-senior flume]# tar zxf flume-ng-1.5.0-cdh5.3.6.tar.gz -C /opt/cdh-5.3.6/
[root@hadoop-senior cdh-5.3.6]# mv apache-flume-1.5.0-cdh5.3.6-bin/ ./flume-1.5.0-cdh5.3.6
2、配置
flume-env.sh文件 //先重命名
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/modules/jdk1.7.0_80
复制jar包
##flume的lib目录中没有与hdfs基础的jar包,这里手动放进去
[root@hadoop-senior flume]# ls flume-hdfs-jars/
commons-configuration-1.6.jar core-site.xml hadoop-auth-2.5.0-cdh5.3.6.jar hadoop-common-2.5.0-cdh5.3.6.jar hadoop-hdfs-2.5.0-cdh5.3.6.jar hdfs-site.xml
[root@hadoop-senior flume]# cd flume-hdfs-jars/
[root@hadoop-senior flume-hdfs-jars]# cp ./*.jar /opt/cdh-5.3.6/flume-1.5.0-cdh5.3.6/lib/
3、常用命令
##常用命令、参数 commands: agent run a Flume agent global options: --conf,-c <conf> use configs in <conf> directory -Dproperty=value sets a Java system property value agent options: --name,-n <name> the name of this agent (required) --conf-file,-f <file> specify a config file (required if -z missing)
三、编写一个agent
1、agent配置文件
##准备配置文件
[root@hadoop-senior conf]# cp flume-conf.properties.template a1.conf
#####vim a1.conf####内容如下:
# The configuration file needs to define the sources,
# the channels and the sinks.
####define agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
###define sources
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop-senior.ibeifeng.com
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
###define channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
###define sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.sinks.k1.maxBytesToLog = 2014
###bind the soures and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
对上面配置文件的解释:
参考手册:http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.9.0/FlumeUserGuide.html
define agent字段:
定义了agent的名字a1,sources 、channels、sinks的名字;
define sources字段:
定义了source的类型、绑定的主机、端口
define channel字段:
定义了channel的存储类型,memory指数据存在内存中,
a1.channels.c1.capacity :设置channel的容量,
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity:每次最大可以从source中拿到或者送到sink中的event数量;
define sink字段:
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger:记录INFO级别的日志;
a1.sinks.k1.maxBytesToLog:要记录的事件主体的最大字节数
bind the soures and sink to the channel字段:
将source与channel,sink与channel绑定;
2、Source 、channel、sink了解
参考手册:http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.9.0/FlumeUserGuide.html
##Source
Flume支持多种类型的Source,包括Avro、Thrift、Exec、JMS、Spooling Directory、Taildir、Kafka、NetCat、Sequence Generator、Syslog Sources、HTTP、Stress、Custom、Scribe。
安装后测试时,可以使用NetCat Source监听一个端口,然后Telnet登录该端口输入字符串即可。
程序接入最便捷的方式是让Flume读取现有的日志文件,可以使用如下Source:
Taildir Source:观察指定的文件,并在检测到添加到每个文件的新行后几乎实时地尾随它们。
Spooling Directory Source:监测配置的目录下新增的文件,并将文件中的数据读取出来。需要注意两点:拷贝到 spool 目录下的文件不可以再打开编辑;spool 目录下不可包含相应的子目录。
Exec Source:以运行Linux命令的方式,持续的输出最新的数据,如tail -F文件名指令。
##Channel
Flume支持多种类型的Channel,包括Memory、JDBC、Kafka、File、Spillable Memory、Custom、Pseudo Transaction。其中,Memory Channel 可以实现高速的吞吐,但是无法保证数据的完整性;File Channel 是一个持久化的隧道(channel),它持久化所有的事件,并将其存储到磁盘中。
##Sink
Flume支持多种类型的Sink,包括HDFS、Hive、Logger、Avro、Thrift、IRC、File Roll、Null、HBase、MorphlineSolr、Elastic Search、Kite Dataset、Kafka、Custom。Sink在设置存储数据时,可以向文件系统、数据库、Hadoop存数据,在日志数据较少时,可以将数据存储在文件系中,并且设定一定的时间间隔保存数据。在日志数据较多时,可以将相应的日志数据存储到Hadoop中,便于日后进行相应的数据分析。
3、运行flume agent
##先安装Telnet
[root@hadoop-senior telnet-rpms]# ls
netcat-1.10-891.2.x86_64.rpm telnet-0.17-47.el6_3.1.x86_64.rpm telnet-server-0.17-47.el6_3.1.x86_64.rpm xinetd-2.3.14-38.el6.x86_64.rpm
[root@hadoop-senior telnet-rpms]# rpm -ivh xinetd-2.3.14-38.el6.x86_64.rpm
[root@hadoop-senior telnet-rpms]# rpm -ivh telnet-server-0.17-47.el6_3.1.x86_64.rpm
[root@hadoop-senior telnet-rpms]# rpm -ivh telnet-0.17-47.el6_3.1.x86_64.rpm
[root@hadoop-senior telnet-rpms]# /etc/init.d/xinetd start
##运行flume agent
bin/flume-ng agent \
-c conf \
-n a1 \
-f conf/a1.conf \
-Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
##参数解释
-c参数,是配置文件的目录
-n参数,agent名称
-f参数,具体的配置文件
-D参数,将日志显示在控制台
##检查
[root@hadoop-senior ~]# netstat -ntlp |grep 44444
tcp 0 0 ::ffff:192.168.1.129:44444 :::* LISTEN 29636/java
4、测试
##Telnet连接主机的44444端口,并发送一条信息“hello flume!”
[root@hadoop-senior ~]# telnet hadoop-senior.ibeifeng.com 44444
Trying 192.168.1.129...
Connected to hadoop-senior.ibeifeng.com.
Escape character is '^]'.
hello flume!
OK
##此时flume端就已经监听到了
2019-05-08 08:56:49,384 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:70)] Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 6C 75 6D 65 21 21 21 0D hello flume!. }