前言:在【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(八)中多次提到了前置处理与后置处理,本篇文章针对此问题进行分析。Spring对前置处理或后置处理主要通过BeanPostProcessor进行实现。
BeanPostProcessor的作用:在Bean实例化前后,如果需要对Bean进行一些配置、增加一些自己的处理逻辑,则使用BeanPostProcessor。
BeanPostProcessor示例
定义一个类实现BeanPostProcessor接口:
1 public class UserDefinedBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { 2 3 @Override 4 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 5 System.out.println("BeanName=" + beanName + " 初始化之前进入"); 6 if ("beanPostProcessorBase".equals(beanName)) { 7 BeanPostProcessorBase processorBase = (BeanPostProcessorBase) bean; 8 processorBase.setMsg("Hello BeanPostProcessor!!!!!!!"); 9 } 10 return bean; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 15 System.out.println("BeanName=" + beanName + " 初始化之后进入"); 16 return bean; 17 } 18 19 public void showMsg() { 20 System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor Test!!!!!!"); 21 } 22 }
再定义一个基础测试类:
1 public class BeanPostProcessorBase { 2 3 private String msg; 4 5 public String getMsg() { 6 return msg; 7 } 8 9 public void setMsg(String msg) { 10 this.msg = msg; 11 } 12 }
测试方法:
1 @Test 2 public void beanPostProcessorTest() { 3 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/dev/config/beanpostprocessor/beanpostprocessor.xml"); 4 BeanPostProcessorBase postProcessor = context.getBean(BeanPostProcessorBase.class); 5 System.out.println(postProcessor.getMsg()); 6 }
运行结果:
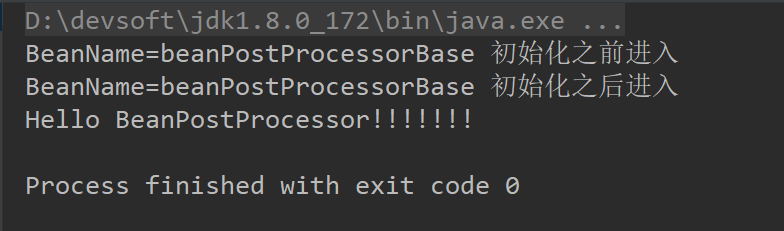
分析:
首先必须明确BeanPostProcessor的执行时机:AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean方法
1 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 2 // 安全模式 3 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 4 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { 5 // 激活Aware方法,对特殊bean处理:Aware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware 6 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 7 return null; 8 }, getAccessControlContext()); 9 } else { 10 // 非安全模式下激活Aware方法,对特殊bean处理:Aware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware 11 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 12 } 13 14 // 后置处理器 before 15 Object wrappedBean = bean; 16 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 17 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 18 } 19 20 // 处理初始化方法 21 try { 22 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 23 } catch (Throwable ex) { 24 throw new BeanCreationException( 25 (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), 26 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); 27 } 28 // 后置处理器 after 29 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 30 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 31 } 32 33 return wrappedBean; 34 }
分析:
- 从该函数逻辑可以看出,BeanPostProcessor的执行时机是在bean初始化前后,其实这里也可以看出bean的生命周期,这里后面再分析。
- 还有为什么要创建一个基础测试类来进行演示,如果直接使用UserDefinedBeanPostProcessor类进行演示是得不到我们所需要的效果的,因为ApplicationContext对象会自动注册BeanPostProcessor,并且在注册会实例化BeanPostProcessor,然后在第二次调用的时候就会从单例缓存中取值,因此得不到想要的效果。自动注册并实例化BeanPostProcessor参看PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors函数,细读该函数就会豁然开朗。
BeanPostProcessor总结
BeanPostProcessor可以理解为是Spring的一个工厂钩子(其实Spring提供一系列的钩子,如Aware 、InitializingBean、DisposableBean),它是Spring提供的对象实例化阶段强有力的扩展点,允许Spring在实例化bean阶段对其进行定制化修改,比较常见的使用场景是处理标记接口实现类或者为当前对象提供代理实现(例如 AOP)。
BeanPostProcessor的执行时机如下:
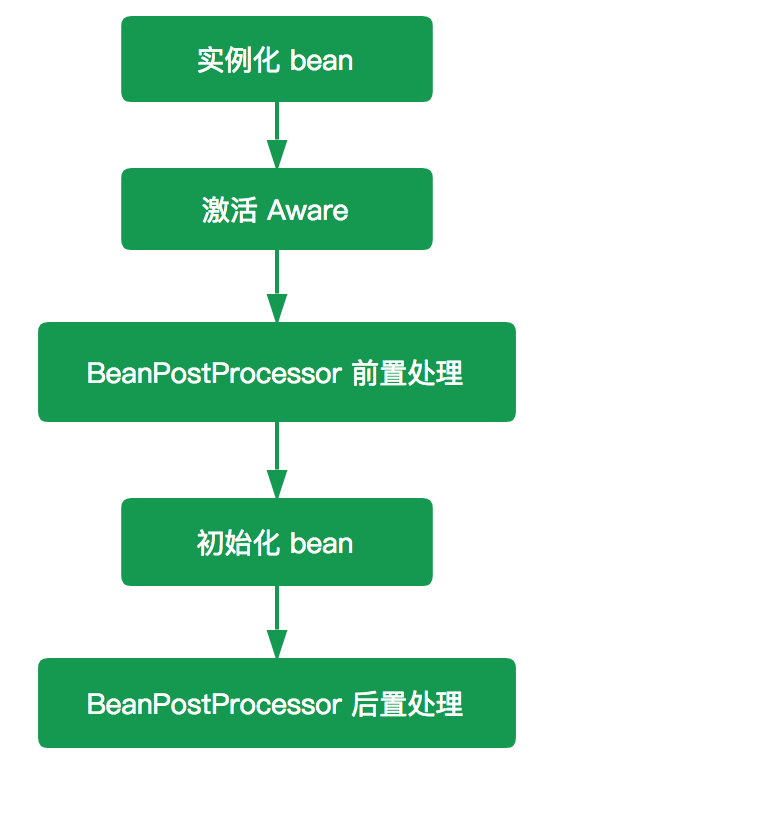
注意:一般的BeanFactory是不支持自动注册BeanPostProcessor,需手动调用addBeanPostProcessor进行注册,但是ApplicationContext支持自动注册,但是在其注册过程中就会对BeanPostProcessor进行初始化并进缓存,因此在示例代码中利用了基础测试类来进行演示。
BeanPostProcessor的作用域是容器级别的,它只和所在的容器相关,当BeanPostProcessor完成注册后,它会应用于所有跟它在同一容器内的bean。
by Shawn Chen,2019.05.05,上午。