前言:在【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(一)中已经分析了导入bean阶段,本篇接着分析bean解析阶段。
1.解析bean程序调用链
同样,先给出解析bean的程序调用链:

根据程序调用链,整理出在解析bean过程中主要涉及的类和相关方法。

2.解析bean源码分析
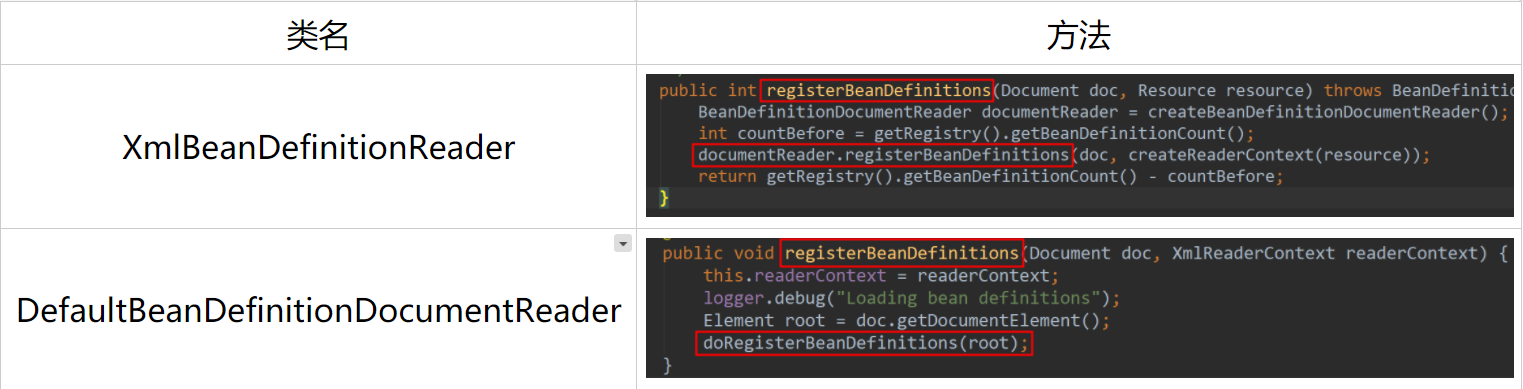
在导入bean阶段,已经分析到XmlBeanDefinitionReader#doLoadBeanDefinitions方法,在解析bean时,首先还是在XmlBeanDefinitionReader中,代码如下:
1 public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); 3 int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); 4 documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); 5 return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; 6 }
分析:
①第2行:首先创建一个BeanDefinitionDocumentReader。
②第3行:取出容器中之前实例化的bean的个数。
③第4行:进入具体解析阶段。转向DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法:
1 public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) { 2 this.readerContext = readerContext; 3 logger.debug("Loading bean definitions"); 4 Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); 5 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); 6 }
分析:
①第4行:从doc中取出根节点(前面已经将xml文件转换成了流,然后再转换成Document)。
②第5行:进入DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法:
1 protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) { 2 // Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In 3 // order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly, 4 // keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create 5 // the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes, 6 // then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference. 7 // this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one. 8 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate; 9 this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); 10 11 if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 12 String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); 13 if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { 14 String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( 15 profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); 16 if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { 17 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 18 logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + 19 "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); 20 } 21 return; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 26 preProcessXml(root); 27 System.out.println("DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#doRegisterBeanDefinitions函数中进行解析" + 28 "主要函数parseBeanDefinitions通过BeanDefinitionParserDelegate进行解析"); 29 parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); 30 postProcessXml(root); 31 32 this.delegate = parent; 33 }
分析:
①第8、9行:创建BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,通过委托去进行bean的解析。
②重点26-30行:preProcessXml和postProcessXml都是预留给用户自己实现,以便扩展。我们着重关注parseBeanDefinitions(DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader)函数:
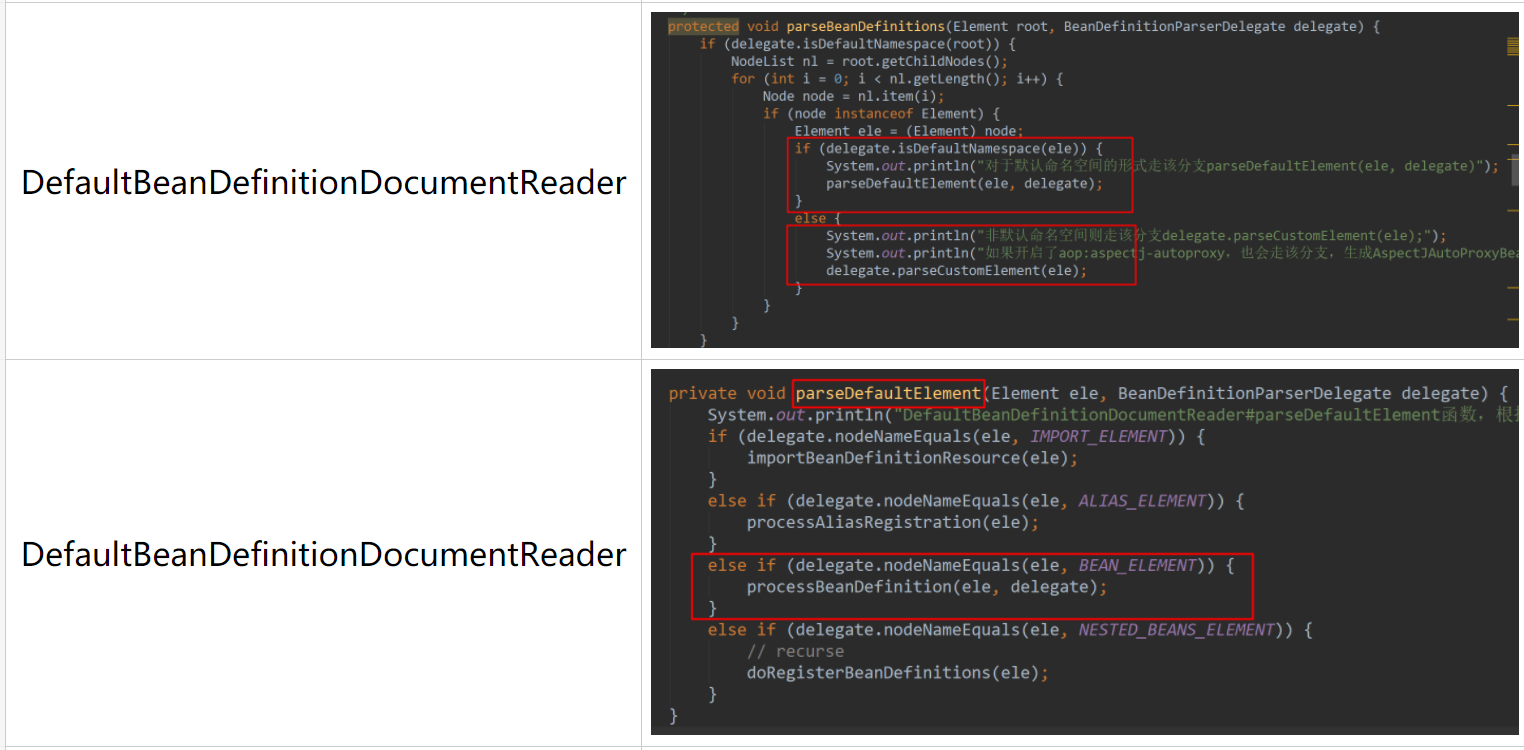
1 protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 2 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { 3 NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); 4 for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { 5 Node node = nl.item(i); 6 if (node instanceof Element) { 7 Element ele = (Element) node; 8 if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { 9 System.out.println("对于默认命名空间的形式走该分支parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)"); 10 parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); 11 } 12 else { 13 System.out.println("非默认命名空间则走该分支delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);"); 14 System.out.println("如果开启了aop:aspectj-autoproxy,也会走该分支,生成AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser解析器"); 15 delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 else { 21 delegate.parseCustomElement(root); 22 } 23 }
分析:
①第2行:判断是否属于默认空间,如果不是则走自定义元素解析分支。
②第10行:如果为元素为默认空间,则转向DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的parseDefaultElement方法:
1 private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 2 System.out.println("DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseDefaultElement函数,根据标签类型进行元素的解析"); 3 if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { 4 importBeanDefinitionResource(ele); 5 } 6 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { 7 processAliasRegistration(ele); 8 } 9 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { 10 processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate); 11 } 12 else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { 13 // recurse 14 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele); 15 } 16 }
分析:
从该函数中可以非常清晰的看到,走了几个分支:import、alias、bean和beans。对于不同的分支会进行不同的解析,但大致流程一样。这里我们走bean分支,第10行:转向DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition函数:
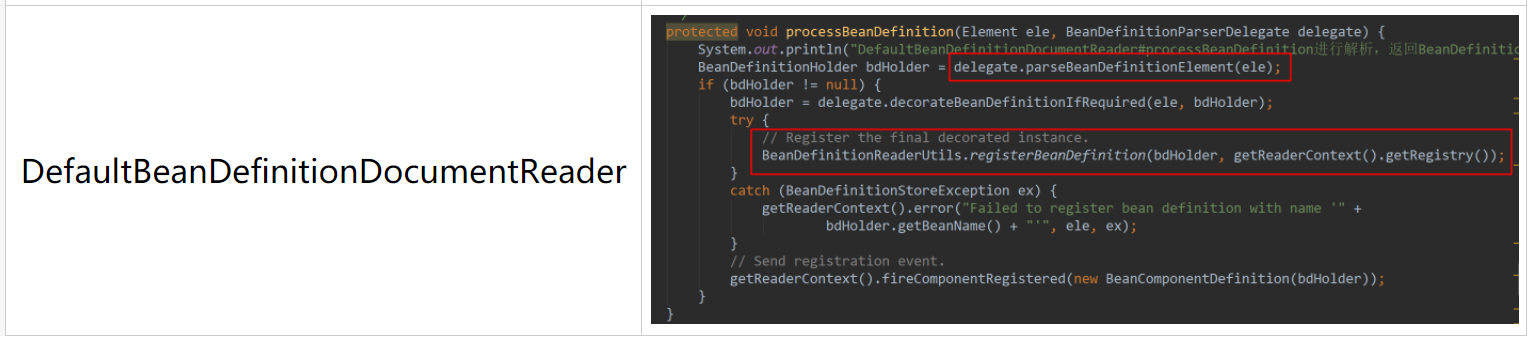
1 protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { 2 System.out.println("DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#processBeanDefinition进行解析,返回BeanDefinitionHolder"); 3 BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele); 4 if (bdHolder != null) { 5 bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); 6 try { 7 // Register the final decorated instance. 8 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); 9 } 10 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { 11 getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + 12 bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); 13 } 14 // Send registration event. 15 getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); 16 } 17 }
分析:
对bean的解析过程在第3行中,通过委托这里会转向BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法(A段代码):
1 public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) { 2 System.out.println("取出xml的id和name属性,用于生成beanDefinition"); 3 String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); 4 String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); 5 6 List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>(); 7 if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) { 8 String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); 9 aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); 10 } 11 12 String beanName = id; 13 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) { 14 beanName = aliases.remove(0); 15 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 16 logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName + 17 "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); 18 } 19 } 20 21 if (containingBean == null) { 22 checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); 23 } 24 25 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); 26 if (beanDefinition != null) { 27 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { 28 try { 29 if (containingBean != null) { 30 beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( 31 beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); 32 } 33 else { 34 beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); 35 // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, 36 // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. 37 // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. 38 String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); 39 if (beanClassName != null && 40 beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && 41 !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { 42 aliases.add(beanClassName); 43 } 44 } 45 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 46 logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + 47 "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); 48 } 49 } 50 catch (Exception ex) { 51 error(ex.getMessage(), ele); 52 return null; 53 } 54 } 55 String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); 56 return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); 57 } 58 59 return null; 60 }
分析:
①第3、4行:取出配置文件bean标签的id和name属性,id属性必须有,name可有可无。
②第22行:检查类名的唯一性。
③第25行:进行元素的解析,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法(B段代码):
1 public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement( 2 Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) { 3 4 this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName)); 5 6 String className = null; 7 if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) { 8 className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim(); 9 } 10 String parent = null; 11 if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) { 12 parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE); 13 } 14 15 try { 16 AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent); 17 18 parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); 19 bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)); 20 21 System.out.println("BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseBeanDefinitionElement中会对xml中的相关标签进行解析" + 22 "meta标签、lookup方法、replaceMethod、构造函数等"); 23 parseMetaElements(ele, bd); 24 parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); 25 parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); 26 27 parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); 28 parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); 29 parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); 30 31 bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource()); 32 bd.setSource(extractSource(ele)); 33 34 return bd; 35 } 36 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 37 error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex); 38 } 39 catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) { 40 error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err); 41 } 42 catch (Throwable ex) { 43 error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex); 44 } 45 finally { 46 this.parseState.pop(); 47 } 48 49 return null; 50 }
分析:
①第8行:取出bean标签中的class属性,用作反射生成实例对象。
②着重第16行:创建Beandefinition,最终会转向BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的createBeanDefinition方法:
1 public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition( 2 @Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException { 3 4 GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition(); 5 bd.setParentName(parentName); 6 if (className != null) { 7 if (classLoader != null) { 8 bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader)); 9 } 10 else { 11 bd.setBeanClassName(className); 12 } 13 } 14 return bd; 15 }
分析:
查看该方法的源码通过注释可知:该方法会创建一个GenericBeanDefinition,并且如果classLoder已指定,它会立即通过反射实例化对象,如果classLoader未指定,则设置bean的类名(注:这里的类名为类的全路径名)。
GenericBeanDefinition创建后转向B段代码的18行(解析bean的默认属性值):
1 public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName, 2 @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) { 3 4 System.out.println("BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseBeanDefinitionAttributes对默认属性进行解析"); 5 if (ele.hasAttribute(SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE)) { 6 error("Old 1.x 'singleton' attribute in use - upgrade to 'scope' declaration", ele); 7 } 8 else if (ele.hasAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)) { 9 bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)); 10 } 11 else if (containingBean != null) { 12 // Take default from containing bean in case of an inner bean definition. 13 bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope()); 14 } 15 16 if (ele.hasAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)) { 17 bd.setAbstract(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE))); 18 } 19 20 String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute(LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE); 21 if (DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(lazyInit)) { 22 lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit(); 23 } 24 bd.setLazyInit(TRUE_VALUE.equals(lazyInit)); 25 26 String autowire = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE); 27 bd.setAutowireMode(getAutowireMode(autowire)); 28 29 if (ele.hasAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE)) { 30 String dependsOn = ele.getAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE); 31 bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(dependsOn, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS)); 32 } 33 34 String autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE); 35 if ("".equals(autowireCandidate) || DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate)) { 36 String candidatePattern = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates(); 37 if (candidatePattern != null) { 38 String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidatePattern); 39 bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName)); 40 } 41 } 42 else { 43 bd.setAutowireCandidate(TRUE_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate)); 44 } 45 46 if (ele.hasAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)) { 47 bd.setPrimary(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE))); 48 } 49 50 if (ele.hasAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) { 51 String initMethodName = ele.getAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE); 52 bd.setInitMethodName(initMethodName); 53 } 54 else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) { 55 bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod()); 56 bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false); 57 } 58 59 if (ele.hasAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) { 60 String destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE); 61 bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName); 62 } 63 else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) { 64 bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod()); 65 bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false); 66 } 67 68 if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) { 69 bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)); 70 } 71 if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)) { 72 bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)); 73 } 74 75 return bd; 76 }
分析:
上面代码主要对bean标签的默认属性进行解析,主要包括:
1 public static final String ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE = "abstract"; 2 3 public static final String SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE = "scope"; 4 5 private static final String SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE = "singleton"; 6 7 public static final String LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE = "lazy-init"; //懒加载 8 9 public static final String AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire"; 10 11 public static final String AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE = "autowire-candidate"; 12 13 public static final String PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE = "primary"; 14 15 public static final String DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE = "depends-on"; 16 17 public static final String INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "init-method"; //初始化方法 18 19 public static final String DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "destroy-method"; //bean销毁时调用方法 20 21 public static final String FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-method"; 22 23 public static final String FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE = "factory-bean";
继续看B段代码的23~32行,分别解析:meta标签、lookup方法、replaceMethod方法、构造函数等,为实例化对象做准备。在对bean标签的相关属性解析完成后,返回到A段代码的25行:
1 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); 2 if (beanDefinition != null) { 3 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { 4 try { 5 if (containingBean != null) { 6 beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( 7 beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); 8 } 9 else { 10 beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); 11 // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, 12 // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. 13 // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. 14 String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); 15 if (beanClassName != null && 16 beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && 17 !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { 18 aliases.add(beanClassName); 19 } 20 } 21 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 22 logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + 23 "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); 24 } 25 } 26 catch (Exception ex) { 27 error(ex.getMessage(), ele); 28 return null; 29 } 30 } 31 String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); 32 return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); 33 } 34 35 return null; 36 }
分析:
这里会判断beanName是否为空,如果为空则会通过beanDefinition来生成beanName,如果不为空,则直接转向32行,生成BeanDefinitionHolder。在生成BeanDefinitionHolder后会返回到DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition函数:
1 if (bdHolder != null) { 2 bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder); 3 try { 4 // Register the final decorated instance. 5 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); 6 } 7 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { 8 getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + 9 bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); 10 } 11 // Send registration event. 12 getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); 13 }
分析:
①第2行:对bean的自定义属性值赋值,这里会转向BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired方法:
1 public BeanDefinitionHolder decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired( 2 Element ele, BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) { 3 4 System.out.println("BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired对自定义属性进行解析"); 5 BeanDefinitionHolder finalDefinition = definitionHolder; 6 7 // Decorate based on custom attributes first. 8 NamedNodeMap attributes = ele.getAttributes(); 9 for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) { 10 Node node = attributes.item(i); 11 finalDefinition = decorateIfRequired(node, finalDefinition, containingBd); 12 } 13 14 // Decorate based on custom nested elements. 15 NodeList children = ele.getChildNodes(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) { 17 Node node = children.item(i); 18 if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { 19 finalDefinition = decorateIfRequired(node, finalDefinition, containingBd); 20 } 21 } 22 return finalDefinition; 23 }
分析:
①第11行:为bean的自定义属性赋值,转向BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的decorateIfRequired方法:
1 public BeanDefinitionHolder decorateIfRequired( 2 Node node, BeanDefinitionHolder originalDef, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) { 3 4 String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(node); 5 if (namespaceUri != null && !isDefaultNamespace(namespaceUri)) { 6 NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri); 7 if (handler != null) { 8 BeanDefinitionHolder decorated = 9 handler.decorate(node, originalDef, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd)); 10 if (decorated != null) { 11 return decorated; 12 } 13 } 14 else if (namespaceUri.startsWith("http://www.springframework.org/")) { 15 error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", node); 16 } 17 else { 18 // A custom namespace, not to be handled by Spring - maybe "xml:...". 19 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 20 logger.debug("No Spring NamespaceHandler found for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]"); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 return originalDef; 25 }
分析:
①第6行:取出bean空间的解析器。
②第9行:进行bean自定义属性赋值,转向SimplePropertyNamespaceHandler的decorate方法:
1 public BeanDefinitionHolder decorate(Node node, BeanDefinitionHolder definition, ParserContext parserContext) { 2 if (node instanceof Attr) { 3 Attr attr = (Attr) node; 4 String propertyName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(attr); 5 String propertyValue = attr.getValue(); 6 MutablePropertyValues pvs = definition.getBeanDefinition().getPropertyValues(); 7 if (pvs.contains(propertyName)) { 8 parserContext.getReaderContext().error("Property '" + propertyName + "' is already defined using " + 9 "both <property> and inline syntax. Only one approach may be used per property.", attr); 10 } 11 if (propertyName.endsWith(REF_SUFFIX)) { 12 propertyName = propertyName.substring(0, propertyName.length() - REF_SUFFIX.length()); 13 pvs.add(Conventions.attributeNameToPropertyName(propertyName), new RuntimeBeanReference(propertyValue)); 14 } 15 else { 16 pvs.add(Conventions.attributeNameToPropertyName(propertyName), propertyValue); 17 } 18 } 19 return definition; 20 }
分析:
该函数功能比较简单,从代码中可直接知晓:从节点中取出属性的名称和值,然后封装到MutablePropertyValues中,MutablePropertyValues是BeanDefinitionHolder的一个属性,这样就将属性值带出去了。
在将bean的自定义属性封装后,将返回到DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition函数中:
1 try { 2 // Register the final decorated instance. 3 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry()); 4 } 5 catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { 6 getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" + 7 bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex); 8 } 9 // Send registration event. 10 getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder)); 11 }
至此,整个bean解析阶段已走完,大致过程就是将xml文件流根据不同配置进行各种解析,最终得到BeanDefinitionHolder,接下来进入bean注册阶段。
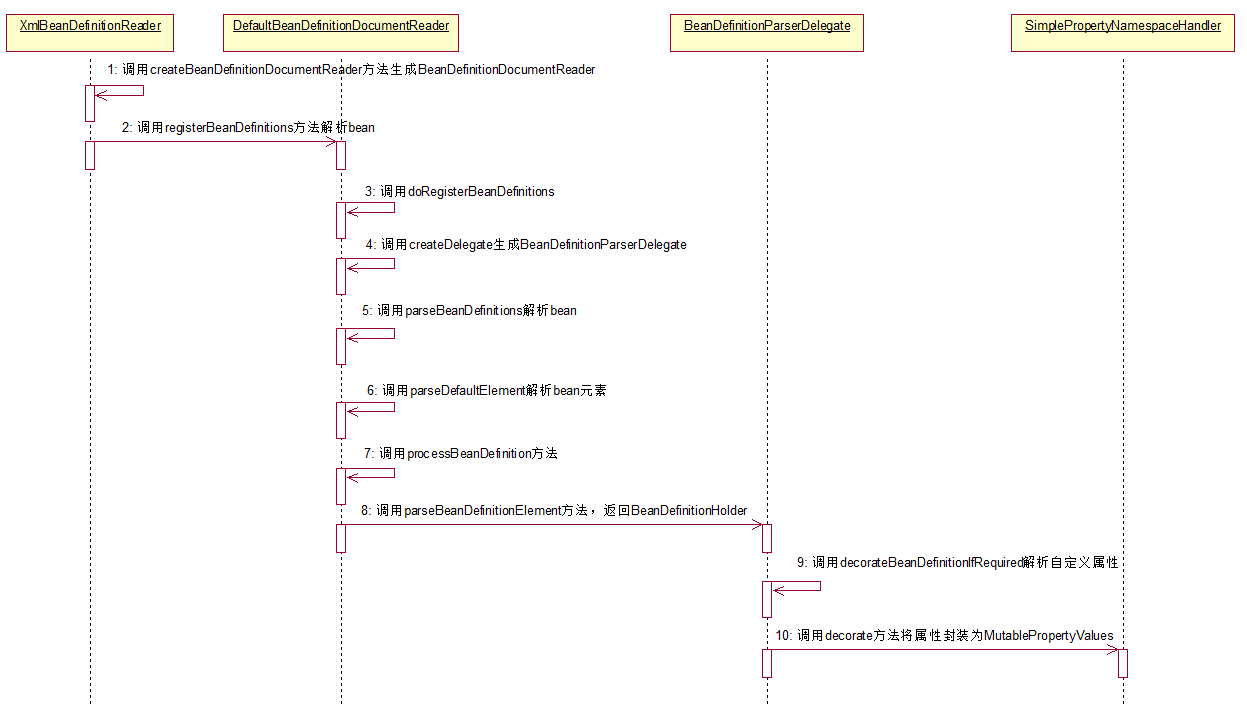
下面给出解析bean阶段的大致时序图:
by Shawn Chen,2018.12.5日,下午。