import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression(): ''' 加载用于回归问题的数据集 ''' diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes() #使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集 # 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4 return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #支持向量机线性回归SVR模型 def test_LinearSVR(*data): X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data regr=svm.LinearSVR() regr.fit(X_train,y_train) print('Coefficients:%s, intercept %s'%(regr.coef_,regr.intercept_)) print('Score: %.2f' % regr.score(X_test, y_test)) # 生成用于回归问题的数据集 X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression() # 调用 test_LinearSVR test_LinearSVR(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_LinearSVR_loss(*data): ''' 测试 LinearSVR 的预测性能随不同损失函数的影响 ''' X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data losses=['epsilon_insensitive','squared_epsilon_insensitive'] for loss in losses: regr=svm.LinearSVR(loss=loss) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) print("loss:%s"%loss) print('Coefficients:%s, intercept %s'%(regr.coef_,regr.intercept_)) print('Score: %.2f' % regr.score(X_test, y_test)) # 调用 test_LinearSVR_loss test_LinearSVR_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_LinearSVR_epsilon(*data): ''' 测试 LinearSVR 的预测性能随 epsilon 参数的影响 ''' X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data epsilons=np.logspace(-2,2) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for epsilon in epsilons: regr=svm.LinearSVR(epsilon=epsilon,loss='squared_epsilon_insensitive') regr.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(regr.score(X_train, y_train)) test_scores.append(regr.score(X_test, y_test)) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) ax.plot(epsilons,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' ) ax.plot(epsilons,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' ) ax.set_title( "LinearSVR_epsilon ") ax.set_xscale("log") ax.set_xlabel(r"$\epsilon$") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) plt.show() # 调用 test_LinearSVR_epsilon test_LinearSVR_epsilon(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

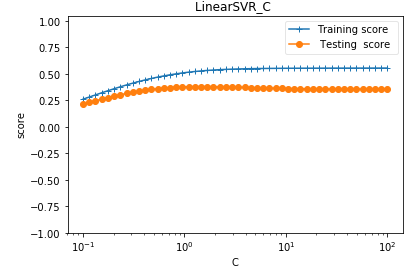
def test_LinearSVR_C(*data): ''' 测试 LinearSVR 的预测性能随 C 参数的影响 ''' X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data Cs=np.logspace(-1,2) train_scores=[] test_scores=[] for C in Cs: regr=svm.LinearSVR(epsilon=0.1,loss='squared_epsilon_insensitive',C=C) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) train_scores.append(regr.score(X_train, y_train)) test_scores.append(regr.score(X_test, y_test)) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) ax.plot(Cs,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' ) ax.plot(Cs,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' ) ax.set_title( "LinearSVR_C ") ax.set_xscale("log") ax.set_xlabel(r"C") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05) ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) plt.show() # 调用 test_LinearSVR_C test_LinearSVR_C(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)