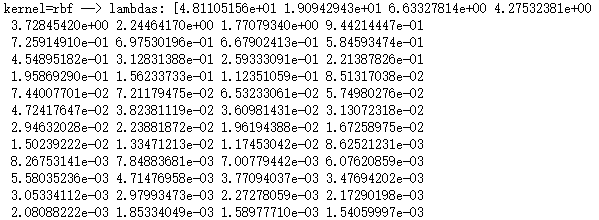
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,decomposition def load_data(): ''' 加载用于降维的数据 ''' # 使用 scikit-learn 自带的 iris 数据集 iris=datasets.load_iris() return iris.data,iris.target #核化PCAKernelPCA模型 def test_KPCA(*data): X,y=data kernels=['linear','poly','rbf','sigmoid'] # 依次测试四种核函数 for kernel in kernels: kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=None,kernel=kernel) kpca.fit(X) print('kernel=%s --> lambdas: %s'% (kernel,kpca.lambdas_)) # 产生用于降维的数据集 X,y=load_data() # 调用 test_KPCA test_KPCA(X,y)

...................

....................
def plot_KPCA(*data): ''' 绘制经过 KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点 ''' X,y=data kernels=['linear','poly','rbf','sigmoid'] fig=plt.figure() # 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) for i,kernel in enumerate(kernels): kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel=kernel) kpca.fit(X) # 原始数据集转换到二维 X_r=kpca.transform(X) ## 两行两列,每个单元显示一种核函数的 KernelPCA 的效果图 ax=fig.add_subplot(2,2,i+1) for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors): position=y==label ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label, color=color) ax.set_xlabel("X[0]") ax.set_ylabel("X[1]") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title("kernel=%s"%kernel) plt.suptitle("KPCA") plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA plot_KPCA(X,y)

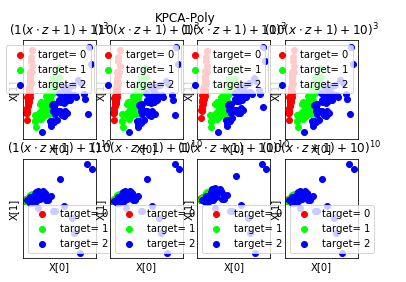
def plot_KPCA_poly(*data): ''' 绘制经过 使用 poly 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点 ''' X,y=data fig=plt.figure() # 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) # poly 核的参数组成的列表。 # 每个元素是个元组,代表一组参数(依次为:p 值, gamma 值, r 值) # p 取值为:3,10 # gamma 取值为 :1,10 # r 取值为:1,10 # 排列组合一共 8 种组合 Params=[(3,1,1),(3,10,1),(3,1,10),(3,10,10),(10,1,1),(10,10,1),(10,1,10),(10,10,10)] for i,(p,gamma,r) in enumerate(Params): # poly 核,目标为2维 kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='poly',gamma=gamma,degree=p,coef0=r) kpca.fit(X) # 原始数据集转换到二维 X_r=kpca.transform(X) ## 两行四列,每个单元显示核函数为 poly 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图 ax=fig.add_subplot(2,4,i+1) for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors): position=y==label ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label, color=color) ax.set_xlabel("X[0]") # 隐藏 x 轴刻度 ax.set_xticks([]) # 隐藏 y 轴刻度 ax.set_yticks([]) ax.set_ylabel("X[1]") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title(r"$ (%s (x \cdot z+1)+%s)^{%s}$"%(gamma,r,p)) plt.suptitle("KPCA-Poly") plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_poly plot_KPCA_poly(X,y)
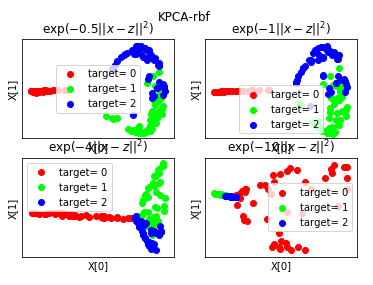
def plot_KPCA_rbf(*data): ''' 绘制经过 使用 rbf 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点 ''' X,y=data fig=plt.figure() # 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) # rbf 核的参数组成的列表。每个参数就是 gamma值 Gammas=[0.5,1,4,10] for i,gamma in enumerate(Gammas): kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='rbf',gamma=gamma) kpca.fit(X) # 原始数据集转换到二维 X_r=kpca.transform(X) ## 两行两列,每个单元显示核函数为 rbf 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图 ax=fig.add_subplot(2,2,i+1) for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors): position=y==label ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label, color=color) ax.set_xlabel("X[0]") # 隐藏 x 轴刻度 ax.set_xticks([]) # 隐藏 y 轴刻度 ax.set_yticks([]) ax.set_ylabel("X[1]") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title(r"$\exp(-%s||x-z||^2)$"%gamma) plt.suptitle("KPCA-rbf") plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_rbf plot_KPCA_rbf(X,y)
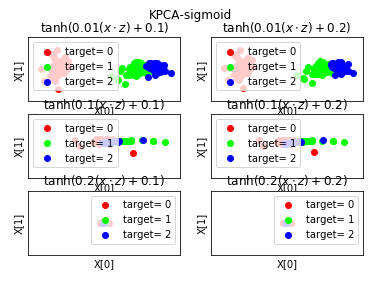
def plot_KPCA_sigmoid(*data): ''' 绘制经过 使用 sigmoid 核的KernelPCA 降维到二维之后的样本点 ''' X,y=data fig=plt.figure() # 颜色集合,不同标记的样本染不同的颜色 colors=((1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1),(0.5,0.5,0),(0,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0,0.5),(0.4,0.6,0),(0.6,0.4,0),(0,0.6,0.4),(0.5,0.3,0.2)) # sigmoid 核的参数组成的列表。 Params=[(0.01,0.1),(0.01,0.2),(0.1,0.1),(0.1,0.2),(0.2,0.1),(0.2,0.2)] # 每个元素就是一种参数组合(依次为 gamma,coef0) # gamma 取值为: 0.01,0.1,0.2 # coef0 取值为: 0.1,0.2 # 排列组合一共有 6 种组合 for i,(gamma,r) in enumerate(Params): kpca=decomposition.KernelPCA(n_components=2,kernel='sigmoid',gamma=gamma,coef0=r) kpca.fit(X) # 原始数据集转换到二维 X_r=kpca.transform(X) ## 三行两列,每个单元显示核函数为 sigmoid 的 KernelPCA 一组参数的效果图 ax=fig.add_subplot(3,2,i+1) for label ,color in zip( np.unique(y),colors): position=y==label ax.scatter(X_r[position,0],X_r[position,1],label="target= %d"%label, color=color) ax.set_xlabel("X[0]") # 隐藏 x 轴刻度 ax.set_xticks([]) # 隐藏 y 轴刻度 ax.set_yticks([]) ax.set_ylabel("X[1]") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title(r"$\tanh(%s(x\cdot z)+%s)$"%(gamma,r)) plt.suptitle("KPCA-sigmoid") plt.show() # 调用 plot_KPCA_sigmoid plot_KPCA_sigmoid(X,y)