第一种迭代删除方式:

第二种迭代删除方式:
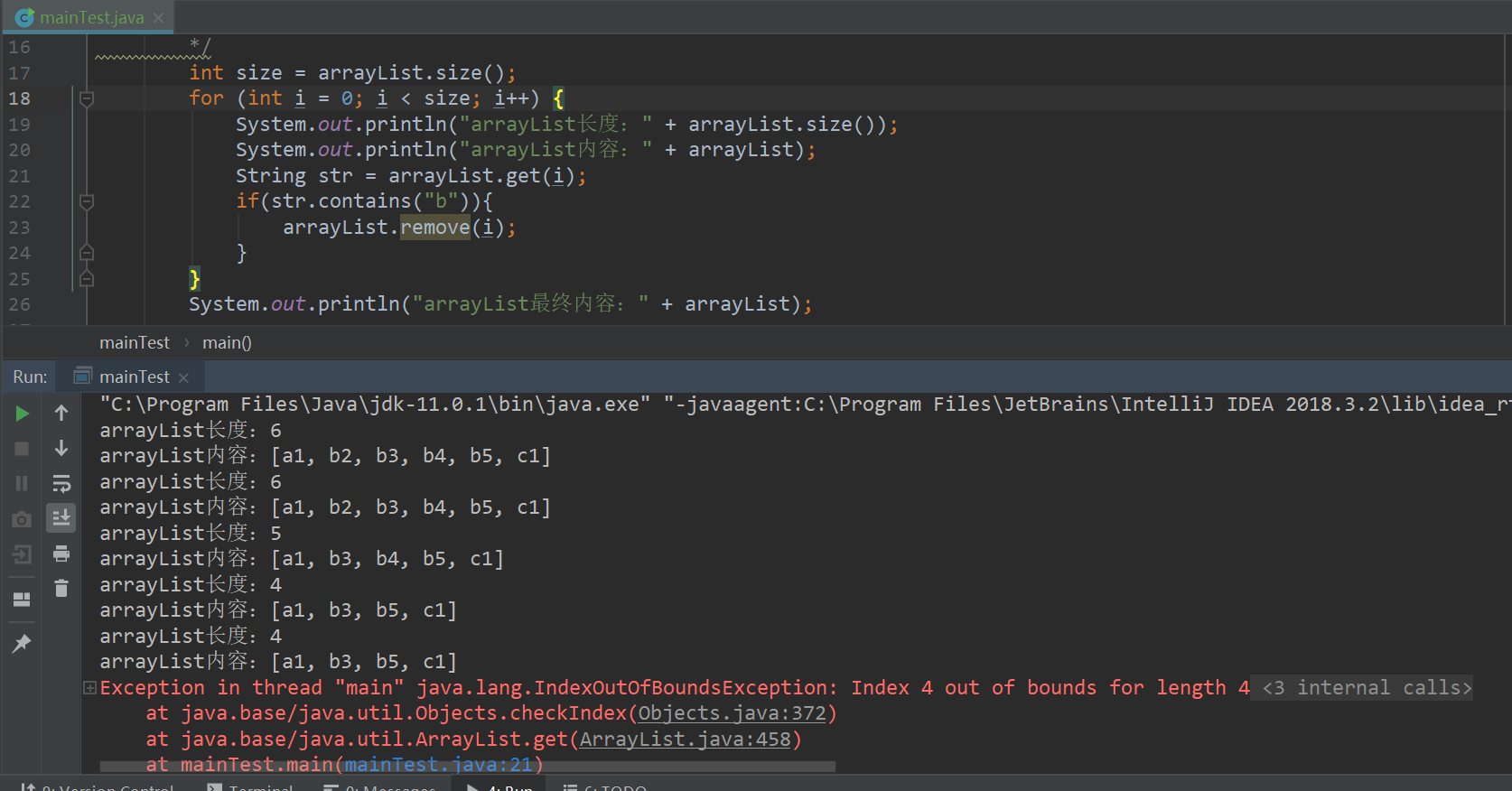
第三种迭代删除:
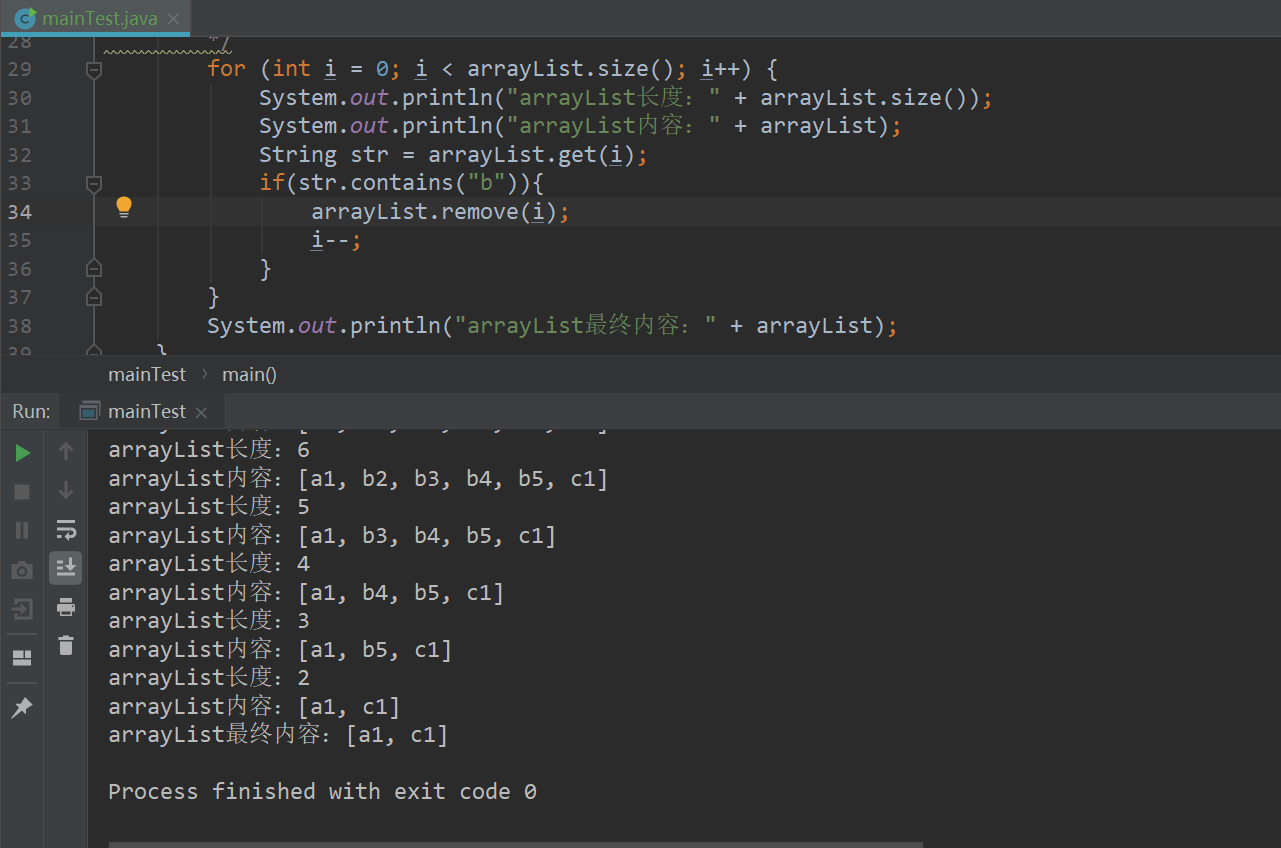
第四种迭代删除:

第五种迭代删除:

扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
5991052 查看本文章


第六种:

ArrayList中remove()方法的机制,首先看源码:
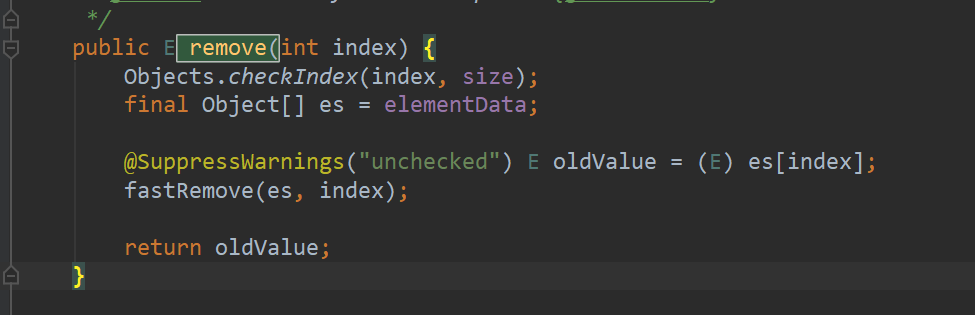

真正的删除操作在fastRemove(),首先定义一个新列表的长度newSize,其值为原列表长度减一 (newS-ze = size-1),然后将 索引 i 之后的数组元素全部向前进一位(System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i)),接着最后一个原数组的最后一个元素置为null(es[size = newSize] = null;)。
所以使用for循环遍历删除的时候,每次循环时都要重新获取ArrayList的长度,并在删除元素之后将索引减1(i--)。
或者倒序删除。
迭代器删除:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return // 最后一个返回的元素的索引位置 int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; // prevent creating a synthetic constructor Itr() {} // 当前迭代指示器是否指向列表末尾 public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; // 迭代指示器指向下一个元素 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } /** * 删除 */ public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { // 调用fastRemove删除元素 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); // 迭代指示器指向被删除元素所在的索引位置 cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } @Override public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); final int size = ArrayList.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i < size) { final Object[] es = elementData; if (i >= es.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++) action.accept(elementAt(es, i)); // update once at end to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
黄色部分是关键,删除元素后迭代指示器重新指向 “新” 元素,确保每一个元素都能被迭代指示器 “指” 过。