以前学习Spring时,使用IOC,需要利用到xml配置文件进行组建的注册和设定等等。同样也可以使用注解的方式进行操作,下面是个人在学习注解开发过程中做的一些总结;
1、@Configuration:告诉Spring,当前class类是一个配置类,等同于以前的xml文件;在@Configuration里面,其实也是一个@Component;要想被@Configuration注解,当前类不可以是final类型,不可以是匿名类;
2、@Bean:注册一个组件;相当于以前在xml文件中的<bean/>标签;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Bean {可以看到@Bean可以再METHOD(方法),ANNOCITION_TYPE上进行注解,@Bean有如下几个属性可以进行设置:
| 参数 | 默认值 | 概念 |
| value |
默认为方法名 | bean别名,和name相互依赖关联的,value,name如果都使用的话值必须要一致 |
| name | 默认方法名 | 相当于xml配置中<bean/>标签的id |
| autowire |
Autowire.NO,默认不开启自动装配 | |
| initMethod |
-- | 初始化方法 |
| destroyMethod |
-- | 注销方法 |
3、@ComponentScan:指定包扫描策略,相当于xml配置文件中的<context:component-scan/>标签,其中可以进行一些属性设定,常用的属性有以下几种:
| 参数 | 默认值或者类型 | 概念 |
| value |
string | 指定需要扫描的包路径 |
| excludeFilters | Filter [] | 按照一定策略,排除需要扫描的包 |
| includeFilters |
Filter [] | 按照一定策略,只需要扫描指定的包,需要和useDefaultFilters=false搭配使用,要不然没效果 |
| useDefaultFilters |
true | 默认宝扫描策略 |
其中excludeFilter和includeFilter在使用是,需要使用到@Filter注解来指定策略,如下例子:
1、指定只扫描包含@Controller注解的bean
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false
2、指定只扫描不包含@Controller注解的bean
excludeFilters= {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
}
上面Filter的type可以有以下集中扫描策略:
| FilterType.ANNOTATION | 按照注解规则,过滤被指定注解标记的类 |
| FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE | 按照给定的类型 |
| FilterType.ASPECTJ | ASPECTJ表达式 |
| FilterType.REGEX | 正则表达式 |
| FilterType.CUSTOM | 自定义规则 |
当然,@ComponentScan可以写多个,同样也可是使用@ComponentScans包含多个@ComponentScan;
@ComponentScans(value = {
@ComponentScan(value = "com.snail.tool.annocation",
excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
}
),
@ComponentScan(value = "com.snail.tool.annocation",
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
}
,useDefaultFilters = false
)
})做个测试,首先测试一下@Configuration和@Bean;定义一个bean类Student,在定义一个MyConfig的配置类,往容器中注入一个名为stu的Student类型的bean,编写测试类,看是否可以拿到;
1、student类
@Data
@ToString
public class Student {
private int age;
private String name;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
2、Myconfig配置类
/**
* @Configuration 作用是:告诉spring,当前class文件为一个配置类文件
*/
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
/**
* @Bean 作用是:向容器中注册一个bean对象,改对象的类型为返回值类型,id为方法名。
* 相当于配置文件中的bean标签
*/
@Bean()
public Student student(){
return new Student(20,"idea");
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------------
3、测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootAnnocationApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
ApplicationContext alicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
Object student = alicationContext.getBean("stu");
System.out.println(student);
}
}
结果:
Student(age=20, name=idea)测试二,测试excludeFilter:新建controller,service,dao,分别使用@Controller,@service,@Repository注解,首先扫描不包括controller的所有bean;
1、Myconfig类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.snail.tool.annocation",
excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
}
)
public class MyConfig {
}
------------------------------------------------------
2、测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootAnnocationApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
}
}
结果:

可以看到,没有controllrt。但是为什么会有myconfig?因为@Configuration底层是使用@Component注解的;
测试三,测试includeFilter:扫描只包括controller的所有bean;
1、Myconfig类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.snail.tool.annocation",
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false
)
public class MyConfig {
}
------------------------------------------------------
2、测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootAnnocationApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
}
}
结果:
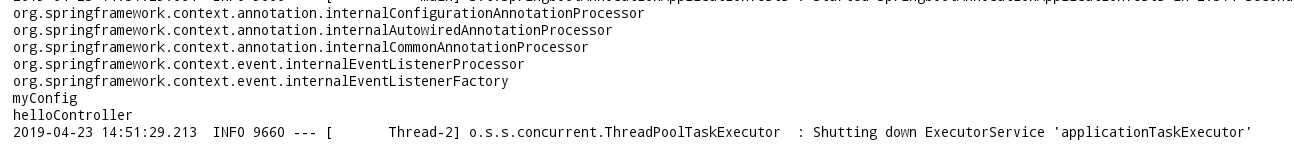
上面便是自己总结的一部分只是内容,当初学的时候也是整个人都傻傻的,学就完事了。如有不对,还请指出,谢谢;
