78. 子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: nums = [1,2,3] 输出: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ]
python解答:
思路一:利用递归和回溯的思想。
import copy
def helper(nums, i, item, result):
if i > len(nums) - 1:
return
item.append(nums[i])
item_deep = copy.deepcopy(item)
result.append(item_deep)
helper(nums, i+1, item, result)
item.pop()
helper(nums, i+1, item, result)
item = []
result = []
i = 0
helper(nums, i, item, result)
result.append([])
return result思路二:直接利用循环
import copy
class Solution(object):
def subsets(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
'''
new_list = [[]]
lists = []
for i in range(len(nums)):
copy_list=copy.deepcopy(new_list)
for _list in copy_list:
_list.append(nums[i])
lists.append(_list)
for list1 in lists:
new_list.append(list1)
lists = []
return new_list90. 子集 II
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: [1,2,2] 输出: [ [2], [1], [1,2,2], [2,2], [1,2], [] ]
思路一:和第一道题类似,只不过后面加了一道排序的工序,将排序后是一样的
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
import copy
def get_sublist(nums, index, item, result):
if index > len(nums) - 1:
return
item.append(nums[index])
print(item)
item_deep = copy.deepcopy(item)
result.append(item_deep)
get_sublist(nums, index+1, item, result)
item.pop()
get_sublist(nums, index+1, item, result)
item = []
result = []
get_sublist(nums, 0, item, result)
lists = []
for _list in result:
_list.sort()
if _list not in lists:
lists.append(_list)
lists.append([])
return lists113. 路径总和 II
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和sum = 22,5 / \ 4 8 / / \ 11 13 4 / \ / \ 7 2 5 1返回:
[ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ]
思路: 利用递归和回溯的思想,找到满足条件的则返回
import copy
def helper(node, he, sum, item, result):
if node == None:
return
he += node.val
item.append(node.val)
if not node.left and not node.right:
if he == sum:
item_deep = copy.deepcopy(item)
result.append(item_deep)
helper(node.left, he, sum, item, result)
helper(node.right, he, sum, item, result)
he -= node.val
item.pop()
node = root
he = 0
item = []
result = []
helper(node, he, sum, item, result)
return result40. 组合总和 II
给定一个数组
candidates和一个目标数target,找出candidates中所有可以使数字和为target的组合。
candidates中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。说明:
- 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates =[10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target =8, 所求解集为: [ [1, 7], [1, 2, 5], [2, 6], [1, 1, 6] ]示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5, 所求解集为: [ [1,2,2], [5] ]
思路一: 回溯思想
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
def helper(nums, index, target, item, result, he):
if index > len(nums) - 1 or he > target:
return
he += nums[index]
item.append(nums[index])
if he == target:
item_deep = copy.deepcopy(item)
result.append(item_deep)
helper(nums, index+1, target, item, result, he)
he -= item[-1]
item.pop()
helper(nums, index+1, target, item, result, he)
nums = candidates
index = 0
item = []
result = []
he = 0
helper(nums, index, target, item, result, he)
final = []
for _list in result:
_list.sort()
if _list not in final:
final.append(_list)
return final
思路二:加上限制条件的递归,这个方法是从leetcode上面看到的
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
"""
:type candidates: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
if not candidates:
return res
candidates.sort()
def premutation(path, istart, target):
if target == 0:
res.append(path)
return
else:
index = istart
while index < len(candidates):
if candidates[index] > target:
break
else:
premutation(path + [candidates[index]], index + 1, target - candidates[index])
while index < len(candidates) - 1 and candidates[index] == candidates[index + 1]:
index += 1
if index == len(candidates) - 1:
break
index += 1
premutation([], 0, target)
return res236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
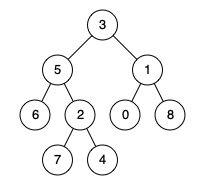
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出: 3 解释: 节点5和节点1的最近公共祖先是节点3。示例 2:
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出: 5 解释: 节点5和节点4的最近公共祖先是节点5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
思路:这个题按照递归的方法,只要找到节点就可以返回,每个节点调用一次函数,最后得到两个list,找出list中最靠后的那个节点就可以了,不过不知道怎么回事,我的解法卡在了第26个测试样例上,不是很理解, 如下图打印的节点明明是两个不相同的节点,但是退出函数之后再打印发现都是37 -48,不知道怎么回事,有兴趣的同学可以帮忙解答一下,谢谢。
37
-48
48
-54
-71
-71
*************
37
-48
48
48
*************
37
-48
************
37
-48
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def helper(curr, node, item):
if not curr:
return
item.append(curr)
if curr == node:
item.append(curr)
for i in item:
print(i.val)
print('*************')
return
helper(curr.left, node, item)
helper(curr.right, node, item)
item.pop()
curr = root
node1 = p
node2 = q
item1 = []
item2 = []
result = []
helper(curr, node1, item1)
curr = root
helper(curr, node2, item2)
for i in item1:
print(i.val)
print('************')
for i in item2:
print(i.val)
for i in item1:
if i in item2:
final = i
return final