8.4.1 Spring的事务机制
所有的数据访问技术都有事务处理机制,这些技术提供了API用来开启事务、提交事务来完成数据操作,或者在发生错误的时候回滚数据。
而Spring的事务机制是用统一的机制来处理不同数据访问技术的事务处理。Spring的事务机制提供了一个PlatformTransactionManager接口,不同的数据访问技术的事务使用不同的接口实现,如表
| 数据访问技术 | 实现 |
|---|---|
| JDBC | DataSourceTransactionManager |
| JPA | JpaTransactionManager |
| Hibernate | HibernateTransactionManager |
| JDO | JdoTransactionManager |
| 分布式事务 | JtaTrasactionManager |
在程序中定义事务管理器的代码如下:
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource());
return transactionManager;
}
8.4.2声名式事务
spring支持声名式事务,即使用注解来选择需要使用事务的方法,它使用@Transactional注解在方法上表明该方法需要事务支持。这是一个基于AOP的实现操作,读者可以重温1.3.3节中使用注解式的拦截方式来理解Spring的声明式事务。被注解的方法在被调用时,Spring开启一个新的事务,当方法无异常运行结束后,Spring会提交这个事务。
@Transactional
public void saveSomething(Long id,Sring name){
//数据库操作
}
在此处需要特别注意的是,此注解来自org.springframework.transaction.annotation包,而不是javax.transaction。
Spring提供了一个@EnableTransactionManagement注解在配置类上来开启声名式事务的支持。使用了@EnableTrasactionManagement后,Spring容器会自动扫描注解@Transactional的方法和类。
@EnableTransactionManagement的使用方式如下:
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class Appconfig{
}
8.4.3 注解事务行为
@Transactional有如下所示的属性来定制事务行为。
例:@Transactional (propagation= Propagation.REQUIRED)
REQUIRED(默认值):在有transaction状态下执行;如当前没有transaction,则创建新的transaction;
SUPPORTS:如当前有transaction,则在transaction状态下执行;如果当前没有transaction,在无transaction状态下执行;
MANDATORY:必须在有transaction状态下执行,如果当前没有transaction,则抛出异常IllegalTransactionStateException;
REQUIRES_NEW:创建新的transaction并执行;如果当前已有transaction,则将当前transaction挂起;
NOT_SUPPORTED:在无transaction状态下执行;如果当前已有transaction,则将当前transaction挂起;
NEVER:在无transaction状态下执行;如果当前已有transaction,则抛出异常IllegalTransactionStateException。
8.4.4 类级别使用@Transactional
@Transactional不仅可以注解在方法上,也可以注解在类上。当注解在类上的时候意味着此类的所有public方法都是开启事务的。如果类级别和方法级别同时使用@Transactional注解,则使用方法级别注解覆盖类级别注解。
8.4.5 Spring Data JPA的事务支持
Spring Data JPA 对所有的默认方法都开启了事务支持,且查询类事务默认启用readOnly = true属性。
这些我们在SimpleJpaRepository的源码中可以看到,下面就来看看缩减的SimpleJpaRepository的源码:
@Repository
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class SimpleJpaRepository<T, ID> implements JpaRepositoryImplementation<T, ID> {
private static final String ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL = "The given id must not be null!";
private final JpaEntityInformation<T, ?> entityInformation;
private final EntityManager em;
private final PersistenceProvider provider;
private @Nullable CrudMethodMetadata metadata;
public SimpleJpaRepository(JpaEntityInformation<T, ?> entityInformation, EntityManager entityManager) {
Assert.notNull(entityInformation, "JpaEntityInformation must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(entityManager, "EntityManager must not be null!");
this.entityInformation = entityInformation;
this.em = entityManager;
this.provider = PersistenceProvider.fromEntityManager(entityManager);
}
public SimpleJpaRepository(Class<T> domainClass, EntityManager em) {
this(JpaEntityInformationSupport.getEntityInformation(domainClass, em), em);
}
public void setRepositoryMethodMetadata(CrudMethodMetadata crudMethodMetadata) {
this.metadata = crudMethodMetadata;
}
@Nullable
protected CrudMethodMetadata getRepositoryMethodMetadata() {
return metadata;
}
protected Class<T> getDomainClass() {
return entityInformation.getJavaType();
}
private String getDeleteAllQueryString() {
return getQueryString(DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING, entityInformation.getEntityName());
}
private String getCountQueryString() {
String countQuery = String.format(COUNT_QUERY_STRING, provider.getCountQueryPlaceholder(), "%s");
return getQueryString(countQuery, entityInformation.getEntityName());
}
@Transactional
public void deleteById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
delete(findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new EmptyResultDataAccessException(
String.format("No %s entity with id %s exists!", entityInformation.getJavaType(), id), 1)));
}
@Transactional
public void delete(T entity) {
Assert.notNull(entity, "The entity must not be null!");
em.remove(em.contains(entity) ? entity : em.merge(entity));
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "The given Iterable of entities not be null!");
for (T entity : entities) {
delete(entity);
}
}
@Transactional
public void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "The given Iterable of entities not be null!");
if (!entities.iterator().hasNext()) {
return;
}
applyAndBind(getQueryString(DELETE_ALL_QUERY_STRING, entityInformation.getEntityName()), entities, em)
.executeUpdate();
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAll() {
for (T element : findAll()) {
delete(element);
}
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAllInBatch() {
em.createQuery(getDeleteAllQueryString()).executeUpdate();
}
public Optional<T> findById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
Class<T> domainType = getDomainClass();
if (metadata == null) {
return Optional.ofNullable(em.find(domainType, id));
}
LockModeType type = metadata.getLockModeType();
Map<String, Object> hints = getQueryHints().withFetchGraphs(em).asMap();
return Optional.ofNullable(type == null ? em.find(domainType, id, hints) : em.find(domainType, id, type, hints));
}
protected QueryHints getQueryHints() {
return metadata == null ? NoHints.INSTANCE : DefaultQueryHints.of(entityInformation, metadata);
}
@Override
public T getOne(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
return em.getReference(getDomainClass(), id);
}
public boolean existsById(ID id) {
Assert.notNull(id, ID_MUST_NOT_BE_NULL);
if (entityInformation.getIdAttribute() == null) {
return findById(id).isPresent();
}
String placeholder = provider.getCountQueryPlaceholder();
String entityName = entityInformation.getEntityName();
Iterable<String> idAttributeNames = entityInformation.getIdAttributeNames();
String existsQuery = QueryUtils.getExistsQueryString(entityName, placeholder, idAttributeNames);
TypedQuery<Long> query = em.createQuery(existsQuery, Long.class);
if (!entityInformation.hasCompositeId()) {
query.setParameter(idAttributeNames.iterator().next(), id);
return query.getSingleResult() == 1L;
}
for (String idAttributeName : idAttributeNames) {
Object idAttributeValue = entityInformation.getCompositeIdAttributeValue(id, idAttributeName);
boolean complexIdParameterValueDiscovered = idAttributeValue != null
&& !query.getParameter(idAttributeName).getParameterType().isAssignableFrom(idAttributeValue.getClass());
if (complexIdParameterValueDiscovered) {
// fall-back to findById(id) which does the proper mapping for the parameter.
return findById(id).isPresent();
}
query.setParameter(idAttributeName, idAttributeValue);
}
return query.getSingleResult() == 1L;
}
public List<T> findAll() {
return getQuery(null, Sort.unsorted()).getResultList();
}
public List<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids) {
Assert.notNull(ids, "The given Iterable of Id's must not be null!");
if (!ids.iterator().hasNext()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (entityInformation.hasCompositeId()) {
List<T> results = new ArrayList<T>();
for (ID id : ids) {
findById(id).ifPresent(results::add);
}
return results;
}
ByIdsSpecification<T> specification = new ByIdsSpecification<T>(entityInformation);
TypedQuery<T> query = getQuery(specification, Sort.unsorted());
return query.setParameter(specification.parameter, ids).getResultList();
}
public List<T> findAll(Sort sort) {
return getQuery(null, sort).getResultList();
}
public Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable) {
if (isUnpaged(pageable)) {
return new PageImpl<T>(findAll());
}
return findAll((Specification<T>) null, pageable);
}
public Optional<T> findOne(@Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
try {
return Optional.of(getQuery(spec, Sort.unsorted()).getSingleResult());
} catch (NoResultException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
public List<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
return getQuery(spec, Sort.unsorted()).getResultList();
}
public Page<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable) {
TypedQuery<T> query = getQuery(spec, pageable);
return isUnpaged(pageable) ? new PageImpl<T>(query.getResultList())
: readPage(query, getDomainClass(), pageable, spec);
}
public List<T> findAll(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Sort sort) {
return getQuery(spec, sort).getResultList();
}
@Override
public <S extends T> Optional<S> findOne(Example<S> example) {
try {
return Optional.of(
getQuery(new ExampleSpecification<S>(example), example.getProbeType(), Sort.unsorted()).getSingleResult());
} catch (NoResultException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
@Override
public <S extends T> long count(Example<S> example) {
return executeCountQuery(getCountQuery(new ExampleSpecification<S>(example), example.getProbeType()));
}
@Override
public <S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example) {
return !getQuery(new ExampleSpecification<S>(example), example.getProbeType(), Sort.unsorted()).getResultList()
.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public <S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example) {
return getQuery(new ExampleSpecification<S>(example), example.getProbeType(), Sort.unsorted()).getResultList();
}
@Override
public <S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort) {
return getQuery(new ExampleSpecification<S>(example), example.getProbeType(), sort).getResultList();
}
@Override
public <S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable) {
ExampleSpecification<S> spec = new ExampleSpecification<>(example);
Class<S> probeType = example.getProbeType();
TypedQuery<S> query = getQuery(new ExampleSpecification<>(example), probeType, pageable);
return isUnpaged(pageable) ? new PageImpl<>(query.getResultList()) : readPage(query, probeType, pageable, spec);
}
public long count() {
return em.createQuery(getCountQueryString(), Long.class).getSingleResult();
}
public long count(@Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
return executeCountQuery(getCountQuery(spec, getDomainClass()));
}
@Transactional
public <S extends T> S save(S entity) {
if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) {
em.persist(entity);
return entity;
} else {
return em.merge(entity);
}
}
@Transactional
public <S extends T> S saveAndFlush(S entity) {
S result = save(entity);
flush();
return result;
}
@Transactional
public <S extends T> List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities) {
Assert.notNull(entities, "The given Iterable of entities not be null!");
List<S> result = new ArrayList<S>();
for (S entity : entities) {
result.add(save(entity));
}
return result;
}
@Transactional
public void flush() {
em.flush();
}
@Deprecated
protected Page<T> readPage(TypedQuery<T> query, Pageable pageable, @Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
return readPage(query, getDomainClass(), pageable, spec);
}
protected <S extends T> Page<S> readPage(TypedQuery<S> query, final Class<S> domainClass, Pageable pageable,
@Nullable Specification<S> spec) {
if (pageable.isPaged()) {
query.setFirstResult((int) pageable.getOffset());
query.setMaxResults(pageable.getPageSize());
}
return PageableExecutionUtils.getPage(query.getResultList(), pageable,
() -> executeCountQuery(getCountQuery(spec, domainClass)));
}
protected TypedQuery<T> getQuery(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable) {
Sort sort = pageable.isPaged() ? pageable.getSort() : Sort.unsorted();
return getQuery(spec, getDomainClass(), sort);
}
protected <S extends T> TypedQuery<S> getQuery(@Nullable Specification<S> spec, Class<S> domainClass,
Pageable pageable) {
Sort sort = pageable.isPaged() ? pageable.getSort() : Sort.unsorted();
return getQuery(spec, domainClass, sort);
}
protected TypedQuery<T> getQuery(@Nullable Specification<T> spec, Sort sort) {
return getQuery(spec, getDomainClass(), sort);
}
protected <S extends T> TypedQuery<S> getQuery(@Nullable Specification<S> spec, Class<S> domainClass, Sort sort) {
CriteriaBuilder builder = em.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<S> query = builder.createQuery(domainClass);
Root<S> root = applySpecificationToCriteria(spec, domainClass, query);
query.select(root);
if (sort.isSorted()) {
query.orderBy(toOrders(sort, root, builder));
}
return applyRepositoryMethodMetadata(em.createQuery(query));
}
@Deprecated
protected TypedQuery<Long> getCountQuery(@Nullable Specification<T> spec) {
return getCountQuery(spec, getDomainClass());
}
protected <S extends T> TypedQuery<Long> getCountQuery(@Nullable Specification<S> spec, Class<S> domainClass) {
CriteriaBuilder builder = em.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Long> query = builder.createQuery(Long.class);
Root<S> root = applySpecificationToCriteria(spec, domainClass, query);
if (query.isDistinct()) {
query.select(builder.countDistinct(root));
} else {
query.select(builder.count(root));
}
// Remove all Orders the Specifications might have applied
query.orderBy(Collections.<Order> emptyList());
return em.createQuery(query);
}
private <S, U extends T> Root<U> applySpecificationToCriteria(@Nullable Specification<U> spec, Class<U> domainClass,
CriteriaQuery<S> query) {
Assert.notNull(domainClass, "Domain class must not be null!");
Assert.notNull(query, "CriteriaQuery must not be null!");
Root<U> root = query.from(domainClass);
if (spec == null) {
return root;
}
CriteriaBuilder builder = em.getCriteriaBuilder();
Predicate predicate = spec.toPredicate(root, query, builder);
if (predicate != null) {
query.where(predicate);
}
return root;
}
private <S> TypedQuery<S> applyRepositoryMethodMetadata(TypedQuery<S> query) {
if (metadata == null) {
return query;
}
LockModeType type = metadata.getLockModeType();
TypedQuery<S> toReturn = type == null ? query : query.setLockMode(type);
applyQueryHints(toReturn);
return toReturn;
}
private void applyQueryHints(Query query) {
for (Entry<String, Object> hint : getQueryHints().withFetchGraphs(em)) {
query.setHint(hint.getKey(), hint.getValue());
}
}
private static long executeCountQuery(TypedQuery<Long> query) {
Assert.notNull(query, "TypedQuery must not be null!");
List<Long> totals = query.getResultList();
long total = 0L;
for (Long element : totals) {
total += element == null ? 0 : element;
}
return total;
}
private static boolean isUnpaged(Pageable pageable) {
return pageable.isUnpaged();
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static final class ByIdsSpecification<T> implements Specification<T> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final JpaEntityInformation<T, ?> entityInformation;
@Nullable ParameterExpression<Iterable> parameter;
ByIdsSpecification(JpaEntityInformation<T, ?> entityInformation) {
this.entityInformation = entityInformation;
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.Specification#toPredicate(javax.persistence.criteria.Root, javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaQuery, javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaBuilder)
*/
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
Path<?> path = root.get(entityInformation.getIdAttribute());
parameter = cb.parameter(Iterable.class);
return path.in(parameter);
}
}
private static class ExampleSpecification<T> implements Specification<T> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final Example<T> example;
ExampleSpecification(Example<T> example) {
Assert.notNull(example, "Example must not be null!");
this.example = example;
}
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
return QueryByExamplePredicateBuilder.getPredicate(root, cb, example);
}
}
}
从源码我们可以看出,SimpleJpaRepository在类级别定义了@Transactional(readOnly=true),而在和save、delete相关的操作重写了@Transactional属性,此时readOnly属性是false,其余查询操作readOnly仍然为true。
8.4.6 Spring Boot的事务支持
1.自动配置的事务管理器
在使用JDBC作为数据访问技术的时候,Spring Boot为我们定义了PlatformTransactionManager的实现DataSourceTransactionManager的Bean;配置见org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration类中的定义:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(
DataSourceProperties properties) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(
this.dataSource);
if (this.transactionManagerCustomizers != null) {
this.transactionManagerCustomizers.customize(transactionManager);
}
return transactionManager;
}
在使用JPA作为数据访问技术的时候,Spring Boot为我们定义了一个PlatformTransactionManager的实现JpaTransactionManager的Bean;配置见org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaBaseConfiguration.class类中的定义:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
if (this.transactionManagerCustomizers != null) {
this.transactionManagerCustomizers.customize(transactionManager);
}
return transactionManager;
}
2. 自动开启注解事务的支持
Spring Boot专门用于配置事务的类为:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,此配置类于JpaBaseConfiguration和DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration。
而在DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration配置里还开启了声名式事务的支持,代码如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ JdbcTemplate.class, PlatformTransactionManager.class })
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
public class DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
static class DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final TransactionManagerCustomizers transactionManagerCustomizers;
DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration(DataSource dataSource,
ObjectProvider<TransactionManagerCustomizers> transactionManagerCustomizers) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.transactionManagerCustomizers = transactionManagerCustomizers
.getIfAvailable();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(
DataSourceProperties properties) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(
this.dataSource);
if (this.transactionManagerCustomizers != null) {
this.transactionManagerCustomizers.customize(transactionManager);
}
return transactionManager;
}
}
}
所以在Spring Boot中,无须显示开启使用@EnableTransactionManagement注解。
8.4.7 实战
在实际使用中,使用Spring Boot默认的配置就能满足我们绝大多数需求。在本节的实战里,我们将演示如何使用@Transactional使用异常导致数据回滚和使用异常让数据不回滚。
1.新建Spring Boot项目
新建Spring Boot 项目,依赖为JPA(spring-boot-starter-data-jpa)和Web(spring-boot-starter-web)。
项目信息
groupId:com.wisely
arctifactId:ch8_4
package:com.wisely.ch8_4
添加Oracle JDBC驱动,并在application.properties配置相关属性,与上例保持一致。
2.实体类
package com.wisely.ch8_4.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(Long id, String name, Integer age, String address) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
3.实体类Repository
package com.wisely.ch8_4.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.entity.Person;
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<Person, Long> {
}
4. 业务服务Service
(1)服务接口:
package com.wisely.ch8_4.service;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.entity.Person;
public interface DemoService {
public Person savePersonWithRollBack(Person person);
public Person savePersonWithoutRollBack(Person person);
}
(2)服务实现
package com.wisely.ch8_4.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.entity.Person;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.repository.PersonRepository;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.service.DemoService;
@Service
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService{
@Autowired
PersonRepository personRepository; //可以直接注入我们的PersonRepository的Bean。
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor= {IllegalArgumentException.class}) //使用rollbackFor属性,指定特定异常时,数据回滚
public Person savePersonWithRollBack(Person person) {
Person p = personRepository.save(person);
if(person.getName().equals("凌梦之")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("凌梦之已存在,数据将回滚"); //硬编码手动触发异常
}
return p;
}
@Override
@Transactional(noRollbackFor= {IllegalArgumentException.class}) //使用@Transactional注解的noRollbackFor属性,指定特定异常时,数据不回滚
public Person savePersonWithoutRollBack(Person person) {
Person p = personRepository.save(person);
if(person.getName().equals("凌梦之")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("凌梦之虽然已存在,数据将不会回滚");
}
return p;
}
}
5.控制器
package com.wisely.ch8_4.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.entity.Person;
import com.wisely.ch8_4.service.DemoService;
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
DemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping("/rollback")
public Person rollback(Person person) { //测试回滚情况
return demoService.savePersonWithoutRollBack(person);
}
@RequestMapping("/norollback")
public Person noRollback(Person person) { //测试不回滚情况
return demoService.savePersonWithoutRollBack(person);
}
}
6.运行
为了更清楚地理解回滚,我们以debug启动程序。并在DemoServiceImpl的savePeersonWithRollBack方法打上断点。
(1)回滚
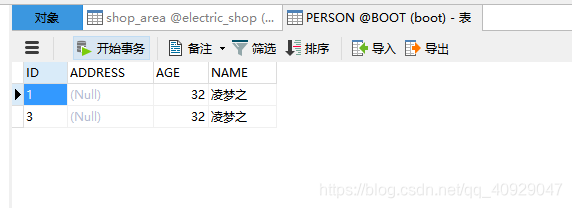
访问http://localhost:8080/rollback?name=凌梦之&age=32,调试至savePersonWithRollBack方法,如图
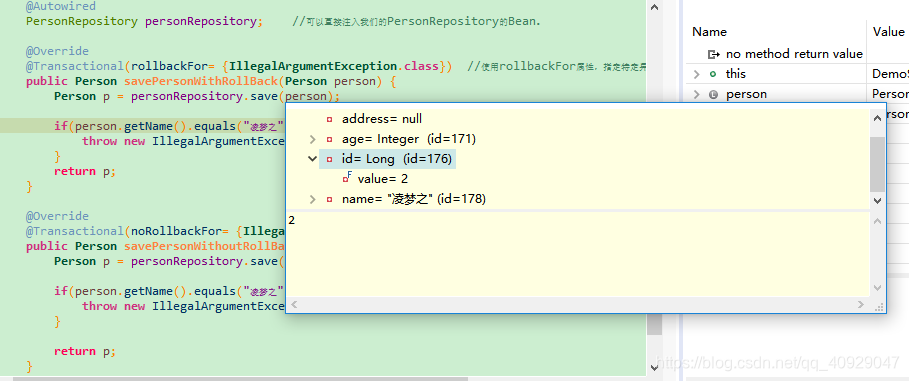
我们可以发现数据已保存且获得id为2.继续执行抛出异常,将导致数据回滚,如图
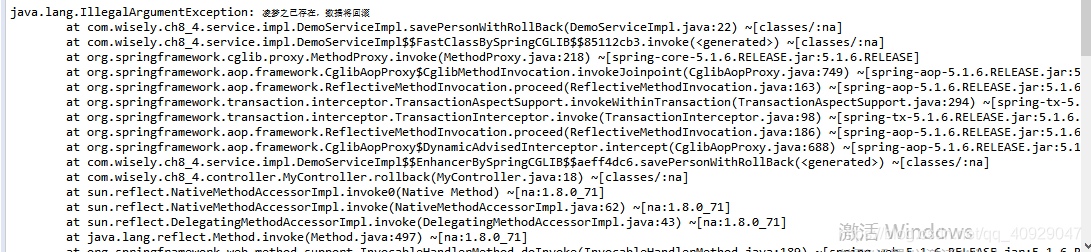
我们查看数据库,并没有新增数据,如图
(2)不回滚
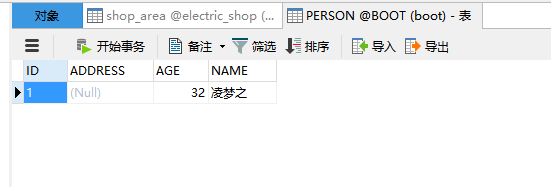
访问http://localhost:8080/norollback?name=凌梦之&age=32,虽然我们也抛出了异常,如图
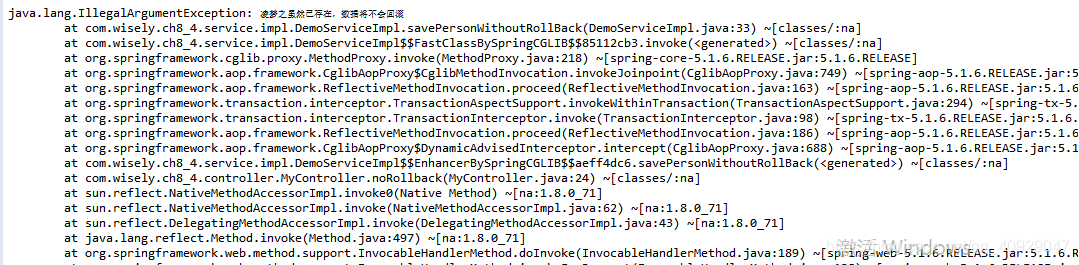
查看数据库发现数据并没有回滚,且数据库还新增了一条记录,如图