1.1 构造方法
构造方法是一种特殊的方法,专门用于构造/实例化对象,形式:
[修饰符] 类名(){
}
构造方法根据是否有参数分为无参构造和有参构。
1.1.1 无参构造
无参构造方法就是构造方法没有任何参数。构造方法在创建对象(new Dog())调用,无参构造方法中一般用于给属性赋值默认值。
public class Dog{
String name;
int health;
int love;
String strain;
public Dog(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
health = 100;
love = 0;
}
…
}
如果开发中没有定义无参构造方法,jvm默认给类分配一个无参构造,形如:
public Dog(){
}
1.1.2 有参构造
当构造/实例化一个对象时,可以向构造方法中传递参数,这样的构造方法称为有参构造。形如:
[修饰符] 类名(Type arg1,Type arg2,…){
// 初始化代码
}
1.1.2.1 局部变量和成员变量优先级
如果在一个作用域中,局部变量和成员变量同名,局部变量的优先级更高。
| public class Dog{ String name; int health; int love; String strain; public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ name = name; health = health; love = love; strain = strain; } } |
优化后
| public class Dog{ String name; int health; int love; String strain; /* public Dog(){ System.out.println("构造方法"); health = 100; love = 0; } */ public Dog(String _name,int _health,int _love,String _strain){ name = _name; health = _health; love = _love; strain = _strain; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+name); System.out.print(",健康值"+health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+love); System.out.println(",我是一只"+strain); } } |
有参构造和无参构造是方法重载关系。
方法重载:方法重载是指在一个类中定义多个同名的方法,但要求每个方法具有不同的参数的类型或参数的个数。调用重载方法时,Java编译器能通过检查调用的方法的参数类型和个数选择一个恰当的方法。
1.1.2.2 有参构造常见问题
如果一个类提供了有参构造方法,jvm不在给类默认分配无参构造。
| public class Dog{ String name; int health; int love; String strain; /* public Dog(){ System.out.println("构造方法"); health = 100; love = 0; } */ public Dog(String _name,int _health,int _love,String _strain){ name = _name; health = _health; love = _love; strain = _strain; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+name); System.out.print(",健康值"+health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+love); System.out.println(",我是一只"+strain); } } |
| Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.name = name; dog.health = 100; dog.love = 0; dog.strain = strain; |
| |
总结:
在开发过程中,如果开发者提供了有参构造方法,一定要习惯性的提供无参构造。
1.2This关键字(上)
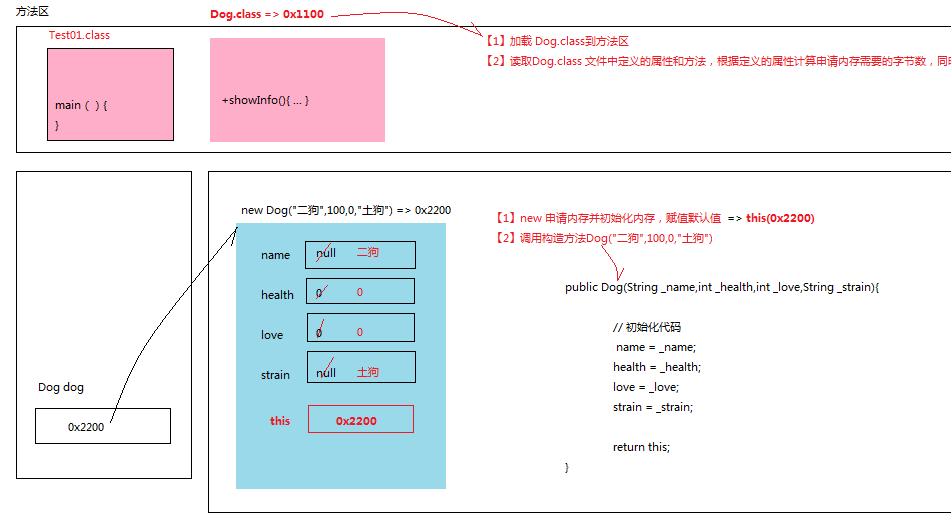
1.1.1 对象初始化内存图
| |
this 是一个关键字,表示对象本身,本质上this中存有一个引用,引用对象本身。
this用于访问本对象属性,同时解决局部变量和成员变量同名的问题。
| public Dog2(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ System.out.println("this:"+this); this.name = name; this.health = health; this.love = love; this.strain = strain; } |
| public class Test04{ public static void main(String[] args){ Dog2 dog = new Dog2("二狗",100,0,"土狗"); System.out.println("dog:"+dog); dog.showInfo(); } } |
通过打印this中的引用,可以看出对象dog和this指向同一内存。
一般而言,dog用于类的外部,this用于类的内部。因为类的内部根本不知道dog变量名的存在。
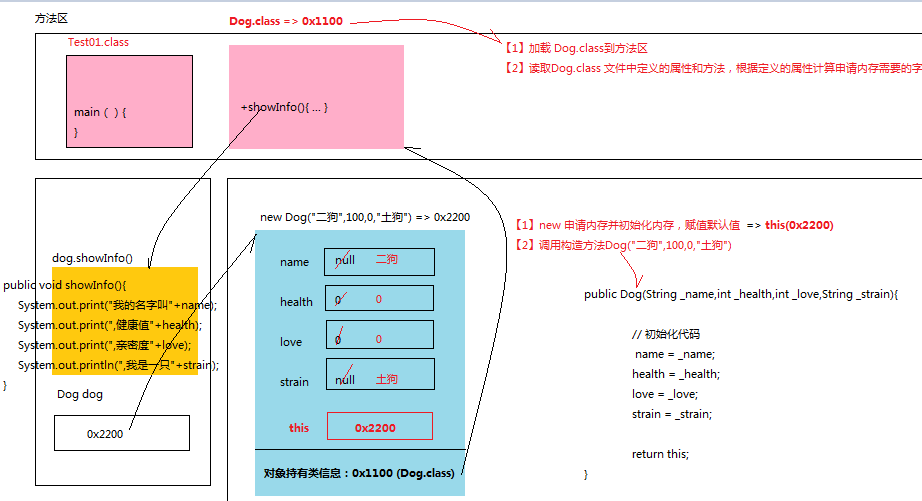
1.2.2 方法的调用内存图
| |
优化方法代码
| public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+this.name); System.out.print(",健康值"+this.health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+this.love); System.out.println(",我是一只"+this.strain); } |
1.3 static
需求:统计汽车工厂生成了多少量车?
ð 统计工厂生成了多少量汽车的功能应该放到类功能上,不应该属于某个对象。
ð 声明一个变量用于统计个数,这个变量应该被类的实例共享。
ð 被类的实例共享的区域在方法区(Car.class)
ð 用static关键字声明这样的变量
static 关键字表示静态,可以修改变量,也可以修饰方法。
1.3.1 静态变量
static 修饰的变量称为静态变量/静态属性,形式
| static 类型 变量名称 [= 初始值] |
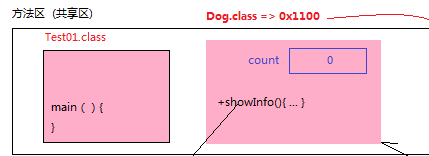
被static修饰的变量称为静态变量,归类所有,分配在方法区(共享区)中的静态区,可以被类的实例共享访问。
| |
静态变量归类所有,也叫类变量,访问方式:
[1] 类名.静态变量(推荐)
[2] 对象.静态变量
| public class Car{ String brand; String type; float price; static int count = 0; public Car(){ Car.count++; } public Car(String brand,String type,float price){ this.brand = brand; this.type = type; this.price = price; Car.count++; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("车辆信息:"); System.out.println("品牌:"+this.brand); System.out.println("型号:"+this.type); System.out.println("价格:"+this.price); System.out.println("我是第"+Car.count+"辆车"); } } |
| public class Test01{ public static void main(String[] args){ Car car1 = new Car("奔驰","漏油GL300",66); car1.showInfo(); Car car2 = new Car("奔驰","漏油GL400",66); car2.showInfo(); System.out.println(Car.count); System.out.println(car1.count); System.out.println(car2.count); } } |
类中包含静态成员(静态变量和静态方法)和实例成员(实例变量和实例方法)
1.3.2 静态方法
static 修饰的方法称为静态方法,形式
| [修饰符] static 返回值类型 方法名(arg…){ |
静态方法归类所有,调用形式
[1] 类名.方法名() (推荐)
[2] 对象.方法名()
1.3.3 静态方法访问非静态成员
| public class Car{ String brand; String type; float price; static int count = 0; public Car(){ Car.count++; } public Car(String brand,String type,float price){ this.brand = brand; this.type = type; this.price = price; Car.count++; } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("车辆信息:"); System.out.println("品牌:"+this.brand); System.out.println("型号:"+this.type); System.out.println("价格:"+this.price); System.out.println("我是第"+Car.count+"辆车"); } public static int getCarCount(){ // 在静态方法中访问实例变量 // System.out.println("品牌:"+brand); //showInfo(); //this.showInfo(); return Car.count; } } |
总结
[1]实例方法可以访问静态成员。
[2]静态方法不能访问非静态成员。
1.3.4 类加载机制
Car car = new Car(…);
当实例化一个对象时,jvm首先把Car.class加载到方法区
[1]读取Car.class 根据声明的成员变量计算申请内存需要的字节数
[2]读取Car.class 中的静态成员,给静态变量分配空间并初始化。
new Car 申请内存得到一个car对象,此时才有对象的空间。showInfo才可以通过car对象调用。
1.3.5 小结
| |
1.4 代码块(B)
代码块通过{}声明,根据其位置可以分为普通代码块、静态代码块、构造代码块、同步代码块(多线程讲解)
1.4.1 普通代码块
普通代码块一般存在于方法或者类、方法等的定义中,普通代码块形成一个作用域。
| public class Test03{ public static void main(String[] args){ int count_1 = 10; // 普通代码块 { int count_2 = 20; //System.out.println("count_1:"+count_1); //System.out.println("count_2:"+count_2); } // error System.out.println("count_2:"+count_2); } } |
1.4.2 构造代码块
构造代码块位于类中。构造代码块在构造方法前执行。构造一个对象执行一次。
| public class Person{ String name; int age; // 构造代码块 { System.out.println("构造代码块"); } public Person(){ System.out.println("构造方法"); } public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } } |
1.4.3 静态代码块
静态代码块位于类中,归类所有,用static修饰。在类加载时执行,在构建多个对象时只执行一次。
| public class Person{ String name; int age; static{ System.out.println("静态代码块"); } public Person(){ System.out.println("构造方法"); } public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } } |
总结
静态代码块一般用于初始化静态资源,构造代码块一般用于初始化实例成员。
1.5 封装
封装:将类的某些信息隐藏在类内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问。
封装的步骤
[1]属性私有化
[2]提供公共的设置器和访问器
[3]在设置器和访问器中添加业务校验逻辑
| public class Dog{ // 【1】private 私有的,对外不可见 private String name; private int health; private int love; private String strain; // 【2】提供公共的设置器(setter)和访问器(getter) public void setName(String name){ // 【3】逻辑校验 if(name.equals("")){ System.out.println("姓名不能为空."); }else{ this.name = name; } } public String getName(){ return this.name; } public void setHealth(int health){ if(health < 0){ System.out.println("健康值不合法."); this.health = 0; }else{ this.health = health; } } public int getHealth(){ return this.health; } public void setLove(int love){ if(love < 0){ System.out.println("亲密度不合法."); this.love = 0; }else{ this.love = love; } } public int getLove(){ return this.love; } public void setStrain(String strain){ if(strain.equals("")){ System.out.println("品种不能为空."); }else{ this.strain = strain; } } public String getStrain(){ return this.strain; } public Dog(){ } public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ this.setName(name); this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); this.setStrain(strain); } public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+this.name); System.out.print(",健康值"+this.health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+this.love); System.out.println(",我是一只"+this.strain); } } |
1.6 This关键字(下)
this表示对象本身。
[1] this调用属性
[2] this调用方法
| public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ this.setName(name); this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); this.setStrain(strain); // showInfo(); this.showInfo(); } |
[3] this调用本类的构造方法,形式
| this(arg1,arg2,…) |
| public Dog(){ } public Dog(String name,int health,int love){ this.setName(name); this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); } public Dog(String name,int health,int love,String strain){ //this.setName(name); //this.setHealth(health); //this.setLove(love); // this调用本类的其他构造方法 // System.out.println("test"); this(name,health,love); this.setStrain(strain); // showInfo(); //this.showInfo(); } |
| |
注意:this调用其他构造方法必须写到构造方法的第一句。
1.7 静态常量
在程序运行过程中,如果一个量的值不会发生改变,可以把该量声明为静态常量,用static final修饰。
| public class Penguin{ private String name; private int health; private int love; private String gender; static final String SEX_MALE = "雄"; static final String SEX_FEMALE = "雌"; public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public String getName(){ return this.name; } public void setHealth(int health){ if(health>100 && health<1){ this.health = 60; System.out.println("健康值必须在1-100之间,默认为60"); }else{ this.health = health; } } public int getHealth(){ return this.health; } public void setLove(String love){ this.love = love; } public int getLove(){ return this.love; } public void setGender(String gender){ this.gender = gender; } public String getGender(){ return this.gender; } public Penguin(){ } public Penguin(String name,String gender){ this.setName(name); this.setGender(gender); } public Penguin(String name,int health,int love,String gender){ this(name,gender); this.setHealth(health); this.setLove(love); } public void showInfo(){ System.out.print("我的名字叫"+name); System.out.print(",健康值"+health); System.out.print(",亲密度"+love); System.out.println(",性别"+gender); } } |
| public class Test02{ public static void main(String[] args){ Penguin penguin = new Penguin("大脚",100,0,Penguin.SEX_MALE); } } |