1. Map接口概述
Collection集合的特点是每次对单个对象进行保存,如果现在要进行一对对象(偶对象)的保存就只能使用Map集合来完成,即Map集合中会一次性保存两个对象,且这两个对象的关系:key=value结构。这种结构最大的特点是可以通过key找到对应的value内容。
Map接口定义:
public interface Map<K,V>
- 此接口中的常用方法有:
①put(K key, V value):向Map中追加数据
②get(Object key):根据key取得value,如果没有返回null
③keySet():把key返回成集合,所以Map里面key不能重复
④values():把所有值返回成Collection,所以value可以重复
⑤entrySet():把Map集合变成Set集合
Map本身是一个接口,要使用Map需要通过子类进行对象实例化。它的常用子类有如下四个:HashMap、Hashtable、TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap。
2. HashMap子类
package com.bittech;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "C");
map.put(3, "JavaScript");
map.put(4, "C++");
map.put(5, "Python");
map.put(6, "SQL");
map.put(null, "SQL");
//key不能重复,但是可以为 null;value可以重复,也可以为null
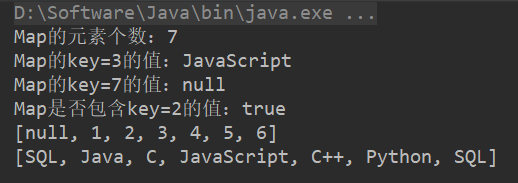
System.out.println("Map的元素个数:"+map.size());
System.out.println("Map的key=3的值:"+map.get(3));
System.out.println("Map的key=7的值:"+map.get(7));
System.out.println("Map是否包含key=2的值:"+map.containsKey(2));
System.out.println(map.keySet());
System.out.println(map.values());
}
}
- 以此推出
Map的遍历方式有以下几种:
package com.bittech;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "C");
map.put(3, "JavaScript");
map.put(4, "C++");
map.put(5, "Python");
map.put(6, "SQL");
map.put(null, "SQL");
System.out.println("Map的遍历方式:");
for(Integer key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + map.get(key));
}
System.out.println("----------");
for(String value : map.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("----------");
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("----------");
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> iterator = entries.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
-
HashMap和简单Java类的运用:
在上述使用Map集合的时候使用的都是系统类作为key(Integer,String等)。实际上用户也可采用自定义类作为key。这个时候一定要记得覆写Object类的hashCode()与equals()方法。
package com.bittech;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
class Person implements {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private transient String password;
public Person(String name, Integer age, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.password = password;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return name.equals(person.name) &&
age.equals(person.age) &&
password.equals(person.password);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, password);
}
}
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
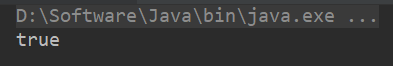
Map<Person, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(new Person("Jack", 22, "123"), "hello Jack");
System.out.println(map.containsKey(new Person("Jack", 22, "123")));
}
}
3. Hashtable子类
package com.bittech;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestHashtable {
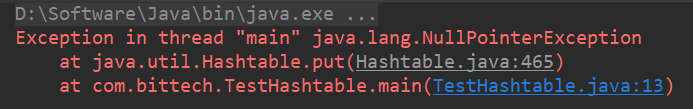
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new Hashtable<>();
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(2, "C");
map.put(null, "PHP");
map.put(8, null);
System.out.println(map);
}
}
请解释HashMap与Hashtable的区别:
① HashMap推出版本JDK1.2,Hashtable推出版本JDK1.0。
② HashMap异步处理,性能高;Hashtable同步处理,性能低。
③ HashMap非线程安全,Hashtable线程安全。
④HashMap中,key和value都可以为null,key不能重复,value允许重复;Hashtable中,key和value都不能为null,否则会出现NullPointerException,同样key不能重复,value允许重复。
4. TreeMap子类
TreeMap是一个可以排序的Map子类,它是按照Key的内容排序的。
package com.bittech;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
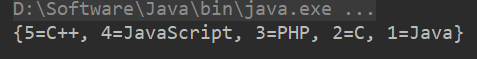
public class TressMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2)*-1;
}
});
map.put(1, "Java");
map.put(3, "PHP");
map.put(5, "C++");
map.put(2, "C");
map.put(4, "JavaScript");
System.out.println(map);
}
}