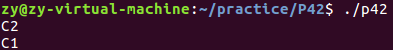
父进程创建两个子进程,子进程通过管道向父进程传递消息。父进程先读子进程1的,再读子进程2的。
1 #include <sys/wait.h> 2 #include <sys/types.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <cstdlib> 6 #include <signal.h> 7 #include <string> 8 using namespace std; 9 int flag; 10 void foo (int signo) { 11 flag = 0; 12 } 13 int main() { 14 int fp[2]; 15 pid_t pid1, pid2; 16 string InPipe; 17 string OutPipe; 18 while ( pipe(fp) < 0 ); 19 if ( (pid1 = fork()) < 0 ) { 20 cout << "pid1 error" << endl; 21 return -1; 22 } 23 if (pid1 == 0) { 24 flag = 1; 25 signal(16, foo); 26 while(flag); 27 close(fp[0]); 28 InPipe = "C1"; 29 write(fp[1], InPipe.c_str(), InPipe.length()+1); 30 sleep(1); 31 exit(0); 32 } 33 else { 34 if ( (pid2 = fork()) < 0 ) { 35 cout << "pid2 error" << endl; 36 return -1; 37 } 38 if (pid2 == 0) { 39 flag = 1; 40 signal(17, foo); 41 while(flag); 42 close(fp[0]); 43 InPipe = "C2"; 44 write(fp[1], InPipe.c_str(), InPipe.length()+1); 45 sleep(1); 46 exit(0); 47 } 48 else { 49 sleep(5); 50 char c = '0'; 51 close(fp[1]); 52 kill(pid1, 16); 53 waitpid(pid1, 0, 0); 54 OutPipe.clear(); 55 while (read(fp[0], &c, 1) && c != '\0') 56 OutPipe += c; 57 cout << OutPipe << endl; 58 kill(pid2, 17); 59 waitpid(pid2, 0, 0); 60 OutPipe.clear(); 61 c = '0'; 62 while (read(fp[0], &c, 1) > 0 && c != '\0') 63 OutPipe += c; 64 cout << OutPipe << endl; 65 exit(0); 66 } 67 } 68 return 0; 69 }
发送信号告诉两个子进程向管道写数据,等到子进程结束,再从管道读取。
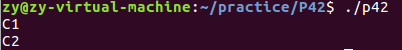
把L52,L53分别和L58,L59互换,就实现了先读进程1,再读进程2。