数组函数(这里的回调函数中的index和arr都可以省略,回调函数后有参数是设置调整 this指向的,这里暂时不使用)
- 方法目录名称:
forEach()
map() —— 更新数组
filter()、includes()、find()、findIndex() —— 筛选(删除)数组
some()、every() —— 判断数组
reduce() —— 叠加数组 - arr.forEach()
1、遍历数组全部元素,利用回调函数对数组进行操作,自动遍历数组.length次数,且无法break中途跳出循环。- 因此不可控,所以该方法不支持 return(返回值)的输出操作,很难(return)操作成新数组,新值,
- 示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
arr.forEach(function(item,index){
console.log(item);
});
- arr.map() —— 更新数组
1.创建一个新数组;
2.原数组保持不变;
3.return(返回值)的是什么就会输出什么样的新数组。
4.回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身);
5.使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作。- 示例:
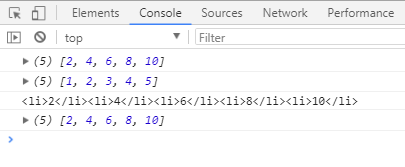
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var newArr = arr.map(function(item,index){
return item*2 ; // 操作更新数组
})
console.log(newArr); // 打印新数组
console.log(arr); // 打印原数组,map()没有改变原数组
var newArr2 = newArr.map(function(item,index){
return `<li>${item}</li>` ;
// ES6语法,模版字符串,波浪号键,变量使用${}
// ["<li>NaN</li>", "<li>NaN</li>", "<li>NaN</li>", "<li>NaN</li>", "<li>NaN</li>"]
})
console.log(newArr2.join('')); // 数组.join(),把数组每一项连接起来,形成字符串string
console.log(newArr); // 打印数组,map()没有改变原数组
arr.filter()、includes()、find()、findIndex() —— 筛选数组
- 一、arr.filter()
1.创建一个新数组;
2.原数组保持不变;
3.输出的是判断为true的数组元素形成的新数组
4.回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身);
5.使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作。- 示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var newArr = arr.filter(function(item,index){
return item>2&&item<5 ; // 根据判断为true来遍历循环添加进新数组
})
console.log(newArr); // 打印新数组
console.log(arr);
- 二、arr.includes()
- 只是判断数组是否含有某值,不用return,不用回调函数,输出一个 true或false 无用
- 示例:
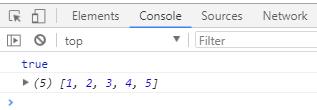
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr.includes(5); // 不用回调函数,且是完全匹配才行如原数组是55则flase(实用性不如正则)
console.log(new1);
console.log(arr);
- 三、arr.find()
1、不创建新数组;
2、原数组保持不变;
3、一旦判断条件结果为 true 则跳出循环输出符合条件的数组元素;
4、回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身);
5、使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作。- 示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr.find(function(item,index){
return item>2&&item<5 ;// 当遍历循环到判断到一个为true则跳出循环,输出当前数组元素,不再循环
})
var new2 = arr.find(function(item,index){
return item.toString().indexOf(5)>-1 ;// 把当前数组元素转为字符串,则可index()>-1判断是否含有某字符
})
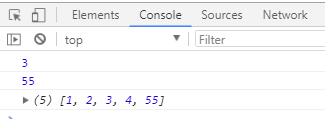
console.log(new1);// 打印操作后的结果
console.log(new2);// 打印是否含有某字符(用正则会更好,这里学习使用一下)
console.log(arr);// 打印原数组,find()没有改变原数组
- 四、arr.findIndex() —— 与 find() 相同
1.不创建新的数据;
2.原数组保持不变;
3.输出的是一旦判断为 true 则跳出循环输出符合条件的数组元素排列;
4.回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身)
5.使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作
示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr.findIndex(function(item,index){
return item>2&&item<5 ;// 当遍历循环到判断到一个为true则跳出循环,输出当前数组元素序列,不再循环
})
var new2 = arr.findIndex(function(item,index){
return item.toString().indexOf(5)>-1 ;// 把当前数组元素转为字符串,则可index()>-1判断是否含有某字符
})
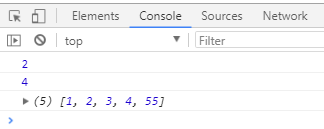
console.log(new1);// 打印操作后的结果
console.log(new2); // 打印是否含有某字符(用正则会更好,这里学习使用一下)
console.log(arr);// 打印原数组,findIndex()没有改变原数组
- arr.some()、event() —— 判断数组
此方法不常用 - 一、some()
1.不创建新的数组;
2.原数组保持不变;
3.一旦判断结果为 true 则马上跳出循环并 return 成true;
4.回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身);
5.用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作。- 示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr.some(function(item,index){
return item>2&&item<5 ;// 判断出一个符合条件则跳出循环并输出true
})
var new2 = arr.some(function(item,index){
return item>5 ;// 判断出数组全部元素都不符合条件则输出flase
})
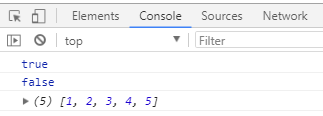
console.log(new1);
console.log(new2);
console.log(arr);
- 二、every()— —与some相反
1、不创建新数组;
2、原数组保持不变;
3、输出的是判断为false则马上跳出循环并return成false;
4、回调函数参数,item(数组元素)、index(序列)、arr(数组本身);
5、使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作。
示例:
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr.every(function(item,index){
return item>2&&item<5 ;// 判断出一个不符合条件则跳出循环并输出flase
})
var new2 = arr.every(function(item,index){
return item<10 ;// 判断出数组全部元素都符合条件则输出true
})
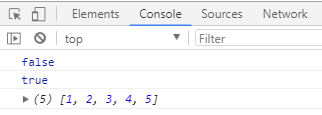
console.log(new1);
console.log(new2);
console.log(arr);
- reduce()— —叠加数组
(不一定在数学意义上的叠加计算,这里叠加指的是:可以利用前遍历操作的结果到下一次遍历使用,重复叠加使用下去)。- 1、创建一个新数组;
- 2、原数组保持不变;
- 3、输出的是 return 叠加什么就输出什么 新数组;
- 4、回调函数参数:
- pre(第一次为数组第一项,之后为上一操作的结果)
- next(数组的下一项)
- index(next项的序列)
- arr(数组本身)
回调函数后的改变第一项参数。(不影响原数组)
- 5、使用return操作输出,会循环数组每一项,并在回调函数中操作
示例:
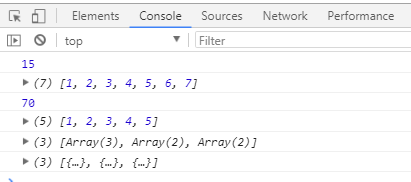
//求和计算
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
var new1 = arr1.reduce(function(sum,next,index){
return sum+next ;
/*
*第一次:pre-->1 next-->2 index-->1
*遍历计算return得结果为pre+next=1+2=3
*第二次:pre-->3 next-->3 index-->2
*遍历计算return得结果为pre+next=3+3=6
*第三次:pre-->6 next-->4 index-->3
*遍历计算return得结果为pre+next=6+4=10
*第四次:pre-->10 next-->5 index-->4
*遍历计算return得结果为pre+next=10+5=15
*/
})
//扁平化数组
var arr2 = [[1,2,3],[4,5],[6,7]] ;
var new2 = arr2.reduce(function(pre,next,index){
return pre.concat(next); //前数组拼接后数组 .concat()
})
//对象数组叠加计算
var arr3 = [{price:10,count:1},{price:15,count:2},{price:10,count:3}];
var new3 = arr3.reduce(function(pre,next,index){
return pre+next.price*next.count;
//当需要对第一项进行操作时,后面pre使用上一项操作结果,不再需要操作
//所以当需要操作第一项的时候,利用reduce(callbreak(){},往数组第一项前添加一项,如:0)
},0) //在原数组第一项添加为0,不改变原数组,则可不操作第一项
console.log(new1);
console.log(new2);
console.log(new3);
console.log(arr1);// 普通数组
console.log(arr2);// 多重数组
console.log(arr3);// 对象数组