B. Jzzhu and Sequences
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Jzzhu has invented a kind of sequences, they meet the following property:
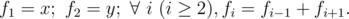
You are given x and y, please calculate fn modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Input
The first line contains two integers x and y (|x|, |y| ≤ 109). The second line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·109).
Output
Output a single integer representing fn modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
Copy
2 3 3
output
Copy
1
input
Copy
0 -1 2
output
Copy
1000000006
Note
In the first sample, f2 = f1 + f3, 3 = 2 + f3, f3 = 1.
In the second sample, f2 = - 1; - 1 modulo (109 + 7) equals (109 + 6).
题意:定义一个序列fn,f[1]=x,f[2]=y,f[n]=f[n-1]-f[n-2](n>2),求这个序列的第n(n<=1e9)项mod1e9+7。
思路:明显是类似于斐波那契数列的矩阵快速幂。
矩阵为,前两项特判即可,注意取模。
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1002;
ll mo=1000000007;
ll n,a,b;
struct node
{
ll n,m,a[7][7];
void init()
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i][i]=1;
}
};
node mul(node aa,node bb,ll n,ll m,ll k)
{
node cc;
cc.n=n;
cc.m=k;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<k;j++)
{
ll x=0;
for(int k=0;k<m;k++)
{
x+=aa.a[i][k]*bb.a[k][j]%mo;
x=(x+mo)%mo;
}
cc.a[i][j]=x;
}
}
return cc;
}
node power(node a,ll m)
{
node d;
d.n=d.m=a.n;
d.init();
while(m)
{
if(m&1) d=mul(d,a,d.n,d.m,a.m);
m>>=1;
a=mul(a,a,a.n,a.n,a.n);
}
return d;
}
ll poww(ll a,ll n)
{
ll sum=1;
while(n)
{
if(n&1) sum=sum*a%mo;
n>>=1;
a=a*a%mo;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int T,cas=1,fg;
while(scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&n)!=EOF)
{
a=(a+mo)%mo;
b=(b+mo)%mo;
if(n==1)
{
printf("%lld\n",a%mo);
continue;
}
else if(n==2)
{
printf("%lld\n",b%mo);
continue;
}
node x;
x.n=2;x.m=2;
memset(x.a,0,sizeof(x.a));
x.a[0][0]=1;
x.a[0][1]=-1;
x.a[1][0]=1;
x.a[1][1]=0;
node ans=power(x,n-2);
node tmp;
tmp.n=2;
tmp.m=1;
memset(tmp.a,0,sizeof(tmp.a));
tmp.a[0][0]=b;
tmp.a[1][0]=a;
ans=mul(ans,tmp,2,2,1);
ll sum=(ans.a[0][0]+mo)%mo;
printf("%lld\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}