本文参考了时光如刀的博客。https://blog.csdn.net/marshal_zsx/article/details/80225854
1、概述
本文从Linux内核启动开始分析,uboot部分只粗略讲解下。同时基于Mstar 平台系统。Android 8.0 Linux4.9.9。
Uboot:上电后通过汇编指令加载uboot引导程序,uboot将内核镜像从ROM 拷贝RAM后并加载。
Linux 启动过程中生成了三个重要的进程:idle进程(pid=0)、init进程(pid=1),kthreadd进程(pid = 2)。这三个进程是Linux内核的基 础,后面的所有进线程都是基于这个三个进程创建的。
idle进程是Linux系统第一个进程,也是init进程,kthreadd进程的父进程。
init进程是用户空间的第一个进程,也是用户空间所有进程的父进程。
kthreadd进程是内核一个守护进程,也是内核所有线程的父进程。
2、idle进程
idle进程的启动是有汇编编写的。文件是Kernel\arch\arm64\kernel\head.S
#ifdef CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE
tst x23, ~(MIN_KIMG_ALIGN - 1) // already running randomized?
b.ne 0f
mov x0, x21 // pass FDT address in x0
mov x1, x23 // pass modulo offset in x1
bl kaslr_early_init // parse FDT for KASLR options
cbz x0, 0f // KASLR disabled? just proceed
orr x23, x23, x0 // record KASLR offset
ldp x29, x30, [sp], #16 // we must enable KASLR, return
ret // to __primary_switch()
0:
#endif
b start_kernel //b 跳转 start_kernel函数其中 b 跳转的意思。 程序跳转到 Kernel\include\linux\start_kernel.h头文件中,该头文件对应实现的 Kernel\init\main.c
asmlinkage __visible void __init start_kernel(void)
{
....
rest_init();
}asmlinkage 表示调用函数参数是否从寄存器传递,__init 表示函数初始化阶段,会被加载到 .init.text段。初始化完成后会被释放。不占用内存。
start_kernel 做了许多初始化,最后跳转到rest_init.在rest_init()中会创建init和kthreadd进程。
3、rest_init
rest_init函数也定义在Kernel\init\main.c中
/* inline修饰的函数类型参数会被内联优化,
noinline修饰的函数类型参数不会被内联优化.*/
static noinline void __ref rest_init(void)
{
int pid;
#if (MP_CACHE_DROP==1)
int pid_kthre_drop_cache;
struct sched_param para;
struct task_struct *p;
int srch_retval;
#endif
RCU (Read-Copy Update)是一种同步机制,是对读写锁的优化。
rcu_scheduler_starting(); //启动RCU机制,用于多核同步
/*
* We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
* the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
* we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
*/
/* kernel-thread 创建init进程,pid=1,
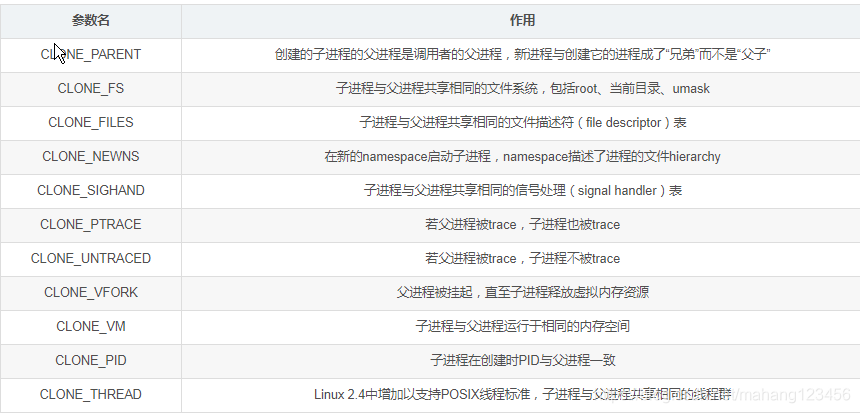
CLONE_FS 表示子进程和父进程共享相同的文件系统,包括root,当前目录,umask,CLONE_SIGHAND,
子进程与父进程共享相同的信号处理(signal handler)表*/
kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);//创建init进程
/*numa_default_policy 定义在Kernel\mm\mempolicy.c中*/
numa_default_policy();//默认NUMA内存访问策略
/*CLONE_FILES 子进程与父进程共享相同的文件描述符(file descriptor)表*/
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);//创建kthreadd进程
#if (MP_CACHE_DROP==1)
pid_kthre_drop_cache=kernel_thread(kthre_drop_cache, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
rcu_read_lock();
srch_retval = -ESRCH;
p = pid_kthre_drop_cache ? find_task_by_vpid(pid_kthre_drop_cache) : current;
if (p != NULL)
{
srch_retval = (p->policy == SCHED_FIFO || p->policy == SCHED_RR)?1:0;
para.sched_priority=srch_retval;
//use default and set min
srch_retval = sched_setscheduler(p, p->policy, ¶);
}
rcu_read_unlock();
#endif
rcu_read_lock();//rcu读上锁
// 获取kthreadd的进程描述符,期间需要检索进程pid的使用链表,所以要加锁
kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
rcu_read_unlock();//rcu读解锁
//complete和wait_for_completion是配套的同步机制,跟java的notify和wait差不多,
// 之前kernel_init函数调用了wait_for_completion(&kthreadd_done),这里调用complete就是通
知kernel_init进程kthreadd进程已创建完成,可以继续执行
complete(&kthreadd_done);//kthreadd创建完成
/*
* The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
* at least once to get things moving:
*/
init_idle_bootup_task(current);//加载当前idle进程
schedule_preempt_disabled(); //idle进程请求调度,init进程运行并禁止抢占
/* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE); //调用cpu_idle_loop使的idle进程进入自己的事件循环
}rest_init创建了俩个重要的进程 init进程和kthreadd进程。下面对rest_init中调用各个方法的解析
3.1、rcu_scheduler_starting
定义在Kernel\kernel\rcu\tree.c中
void rcu_scheduler_starting(void)
{
/*WARN_ON则是调用dump_stack,打印堆栈信息,不会OOPS num_online_cpus当前启动的CPU数*/
WARN_ON(num_online_cpus() != 1);
WARN_ON(nr_context_switches() > 0);//进程切换的次数。
rcu_test_sync_prims();//测试等待rcu同步?
rcu_scheduler_active = RCU_SCHEDULER_INIT;//启动rcu机制
rcu_test_sync_prims();
}rcu_scheduler_starting()就是启动RCU机制
3.2、kernel_thread
定义在 Kernel\kernel\fork.c中
/*kernel_thread 首先调用copy_process创建新进程,wake_up_new_task将进程放入运行队列中启动新进程.
int (*fn)(void *)函数指针,void *arg函数参数,unsigned long flags 创建进程标志位。
*/
pid_t kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void *arg, unsigned long flags)
{
return _do_fork(flags|CLONE_VM|CLONE_UNTRACED, (unsigned long)fn,
(unsigned long)arg, NULL, NULL, 0);
}3.3、numa_default_policy
定义在 Kernel\mm\mempolicy.c中
/* Reset policy of current process to default */
void numa_default_policy(void)
{
do_set_mempolicy(MPOL_DEFAULT, 0, NULL);//设置NUMA系统内存方位MPOL_DEFAULT策略
}3.4 kernel_init 和 kthreadd
kernel_init定义在 Kernel\init\main.c中
kthreadd定义在Kernel\kernel\kthread.c
kernel_init 和kthreadd进程是最重要的俩个进程,kernel_init是用户空间的第一个进程,kthreadd是内核所有线程的父进程。下一篇详细介绍这俩个进程。
3.5rcu_read_lock & rcu_read_unlock
定义在kernel\include\linux\rcupdate.h RCU(Read-Copy Update)是数据同步的一种方式,在当前的Linux内核中发挥着重要的作用。RCU主要针对的数据对象是链表,目的是提高遍历读取数据的效率,为了达到目的使用RCU机制读取数据的时候不对链表进行耗时的加锁操作。这样在同一时间可以有多个线程同时读取该链表,并且允许一个线程对链表进行修改(修改的时候,需要加锁)
static inline void rcu_read_lock(void)
{
__rcu_read_lock();
__acquire(RCU);
rcu_lock_acquire(&rcu_lock_map);
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_is_watching(),
"rcu_read_lock() used illegally while idle");
}
static inline void rcu_read_unlock(void)
{
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_is_watching(),
"rcu_read_unlock() used illegally while idle");
__release(RCU);
__rcu_read_unlock();
rcu_lock_release(&rcu_lock_map); /* Keep acq info for rls diags. */
}
3.6find_task_by_pid_ns
定义在Kernel\kernel\pid.c
task_struct叫进程描述符,这个结构体包含了一个进程所需的所有信息,它定义在kernel\include\linux\sched.h文件中。
它的结构十分复杂,本文就不重点讲了,可以参考Linux进程描述符task_struct结构体详解
/*
* Must be called under rcu_read_lock().
*/
struct task_struct *find_task_by_pid_ns(pid_t nr, struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
RCU_LOCKDEP_WARN(!rcu_read_lock_held(),//必须rcu_read_lock加锁
"find_task_by_pid_ns() needs rcu_read_lock() protection");
return pid_task(find_pid_ns(nr, ns), PIDTYPE_PID);
}
struct task_struct *pid_task(struct pid *pid, enum pid_type type)
{
struct task_struct *result = NULL;
if (pid) {
struct hlist_node *first;
first = rcu_dereference_check(hlist_first_rcu(&pid->tasks[type]),
lockdep_tasklist_lock_is_held());
if (first)
result = hlist_entry(first, struct task_struct, pids[(type)].node);
}
return result;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pid_task);
struct pid *find_pid_ns(int nr, struct pid_namespace *ns)
{
struct upid *pnr;
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(pnr,
&pid_hash[pid_hashfn(nr, ns)], pid_chain)
if (pnr->nr == nr && pnr->ns == ns)
//container_of()的作用就是通过一个结构变量中一个成员的地址找到这个结构体变量的首地址
return container_of(pnr, struct pid,
numbers[ns->level]);
return NULL;
}
find_task_by_pid_ns根据pid在hash表中找到task_struct.
3.7init_idle_bootup_task
定义在Kernel\kernel\sched\core.c.
void init_idle_bootup_task(struct task_struct *idle)
{
idle->sched_class = &idle_sched_class;//设置进程的调度器类为idle_sched_class
}Linux依据其调度策略的不同实现了5个调度器类, 一个调度器类可以用一种或者多种调度策略调度某一类进程, 也可以用于特殊情况或者调度特殊功能的进程.其所属进程的优先级顺序为stop_sched_class -> dl_sched_class -> rt_sched_class -> fair_sched_class -> idle_sched_class
可见idle_sched_class的优先级最低,只有系统空闲时才调用idle进程
3.8schedule_preempt_disabled
定义在Kernel\kernel\sched\core.c.中
/**
* schedule_preempt_disabled - called with preemption disabled
*
* Returns with preemption disabled. Note: preempt_count must be 1
*/
void __sched schedule_preempt_disabled(void)
{
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();//开启内核抢占
schedule();//主动调度,让出cpu
preempt_disable();//关闭内核抢占
}schedule_preempt_disabled 禁止内核抢占时调用。
3.9cpu_startup_entry
定义在 Kernel\kernel\sched\idle.c
void cpu_startup_entry(enum cpuhp_state state)
{
/*
* This #ifdef needs to die, but it's too late in the cycle to
* make this generic (arm and sh have never invoked the canary
* init for the non boot cpus!). Will be fixed in 3.11
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
/*
* If we're the non-boot CPU, nothing set the stack canary up
* for us. The boot CPU already has it initialized but no harm
* in doing it again. This is a good place for updating it, as
* we wont ever return from this function (so the invalid
* canaries already on the stack wont ever trigger).
*/
boot_init_stack_canary();
#endif
/只有在x86这种non-boot CPU机器上执行,该函数主要用于初始化stack_canary的值,用于防止栈溢出
arch_cpu_idle_prepare();
cpuhp_online_idle(state);//进行idle前的准备工作
cpu_idle_loop();/进入idle进程的事件循环
}4.小结
idle进程(pid=0)是Linux 内核的第一个进程,创建了init和threadd俩个进程,同时做一些初始化。idle开启无限循环。对进程调度。下一篇会对init threadd俩个进程进行详细介绍。