1.ADT (abstract data type) 抽象数据类型 ——也就是带有某些操作的一些对象的集合.
java已经为我们很好的实现.集合的概念在Collection中得到很好的抽象。
这篇文章探讨的是实现类ArrayList.
2.话不多说,有过一点了解的都知道java中的ArrayList与LinkedList。
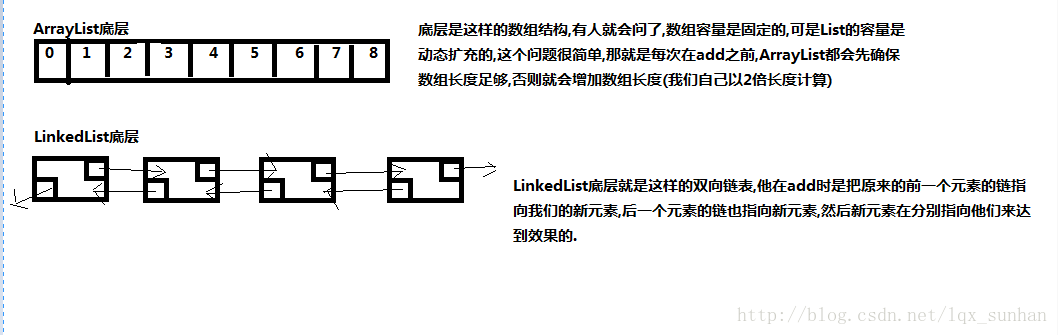
ArrayList底层是由数组实现的,有 查询快增删慢 的特点.
LinkedList底层是由链表实现的,有 查询慢增删快 的特点.
但是这些都很抽象,为什么他们会有这样的特点.我用幅图来简单解释下
ArrayList一些特性描述
- 新增时会在必要的时候扩大数组容量
- 插入一个元素时,会把插入的索引位置及以后的元素都往后挪一位(这也是影响效率的主要原因)
- 删除元素时同插入,把删除位置索引以后的元素都往前挪一位
- 另外一些异常检测我没有自己实现,比如大家可以试试,使用增强for循环或者iterator遍历集合时对集合作修改操作会报ConcurrentModificationException.
代码实现
- 实现Iterable接口(这样才能使用iterator方法)
public class MyArrayList<T> implements Iterable {
...
}- 一些初始值
/**
* 这是默认的数组大小
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 底层的数组
*/
private Object[] theArray;
/**
* 所有元素的总长度(注意不是数组的长度,而是元素的个数)
* 比如调一次add方法,theSize为1,在调一次,theSize为2
*/
private int theSize;- 构造方法
/**
* 无参构造,以默认大小调用有参构造
*/
public MyArrayList(){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
/**
* 以给定的大小初始化数组,theSize初始化0
* @param capacity
*/
public MyArrayList(int capacity){
theSize = 0;
theArray = new Object[capacity];
}- 一些简单的方法
// 简单返回theSize
public int size(){
return theSize;
}
// 返回index对应的元素值
public T get(int index){
return (T) theArray[index];
}
// 得到元素t的对应索引值
public int indexOf(T t){
for(int i = 0; i < size(); i++){
if(theArray[i] == t){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}重点代码
- 确保数组容量的方法以及add方法
/**
* 确保数组的容量
*/
private void ensureCapacity(){
if(size() == theArray.length){
// 如果数组长度已经等于元素的个数,则将数组长度*2,加1是为了size()为0的情况
theArray = Arrays.copyOf(theArray, size() * 2 + 1);
}
}
// 默认的add,则会在数组尾部添加元素
public boolean add(T t){
return add(t, size());
}
// 带索引的add
public boolean add(T t, int index){
// 确保容量
ensureCapacity();
// 如果不是在数组尾部添加
if(index != size()){
// 插入索引开始的元素都向后移动一位
for(int i = size() - 1; i >= index; i--){
theArray[i + 1] = theArray[i];
}
// System.arraycopy(theArray, index, theArray, index + 1, size() - index); 上面代码可以用这句代替,System.arraycopy用法
/**
* 第一个参数 源数组
* 第二个参数 原数组拷贝的起始位置
* 第三个参数 准备拷贝的目标数组
* 第四个参数 准备拷贝的目标数组的拷贝起始位置
* 第五个参数 拷贝的长度
* 所以这个方法就实现以上代码的功能
*/
theArray[index] = t;
} else {
// 在数组最后添加元素,则不需要移动数组里的元素
theArray[index] = t;
}
theSize++;
return true;
}- iterator的实现类(是ArrayList的内部类)
private class MyIterator<T> implements Iterator<T>{
// 当前元素的索引
private int current;
// 返回元素的索引,没有值时为-1(比如调用一次next后,current会自增,而lastIndex就指刚返回那个元素的索引)
private int lastIndex = -1;
public MyIterator(){
current = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
// 判断是否还有下一个元素
return current != size();
}
@Override
public T next() {
// 获取下一个元素(return之前记录索引)
lastIndex = current++;
return (T) theArray[lastIndex];
}
@Override
public void remove() {
// 删除调用MyArrayList内部的删除,把current恢复到上一个元素
current = lastIndex;
MyArrayList.this.remove(current);
}
}- 删除的代码
/**
* 删除指定元素
*/
public boolean remove(T t){
int i = indexOf(t);
// 需要向前移动的元素数量
int numMoved = size() - i - 1;
System.arraycopy(theArray, i + 1, theArray, i, numMoved);
theArray[--theSize] = null;
return true;
}
/**
* 删除指定索引元素
*/
public T remove(int index){
T element = (T) theArray[index];
// 下面代码同样可以用System.arraycopy(...)代替
for(int i = index; i < size() - 1; i++){
theArray[i] = theArray[i + 1];
}
theArray[--theSize] = null;
return element;
}最后上一个完整代码
public class MyArrayList<T> implements Iterable {
/**
* default capacity
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* the array
*/
private Object[] theArray;
/**
* the current size
*/
private int theSize;
/**
* the parameterless constructor
*/
public MyArrayList(){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
/**
* the parameter constructor
* @param capacity
*/
public MyArrayList(int capacity){
theSize = 0;
theArray = new Object[capacity];
}
public boolean add(T t){
return add(t, size());
}
public boolean add(T t, int index){
// 确保容量
ensureCapacity();
if(index != size()){
// 插入索引开始的元素都向后移动一位
// for(int i = size() - 1; i >= index; i--){
// theArray[i + 1] = theArray[i];
// }
System.arraycopy(theArray, index, theArray, index + 1, size() - index);
theArray[index] = t;
} else {
// 在数组最后添加元素,则不需要移动数组里的元素
theArray[index] = t;
}
theSize++;
return true;
}
public T get(int index){
return (T) theArray[index];
}
public int indexOf(T t){
for(int i = 0; i < size(); i++){
if(theArray[i] == t){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public boolean remove(T t){
int i = indexOf(t);
// 需要向前移动的元素数量
int numMoved = size() - i - 1;
System.arraycopy(theArray, i + 1, theArray, i, numMoved);
theArray[--theSize] = null;
return true;
}
public T remove(int index){
T element = (T) theArray[index];
for(int i = index; i < size() - 1; i++){
theArray[i] = theArray[i + 1];
}
theArray[--theSize] = null;
return element;
}
/**
* 确保数组的容量
*/
private void ensureCapacity(){
if(size() == theArray.length){
// 数组容量已经等于list的容量 加1是为了size()为0的情况
theArray = Arrays.copyOf(theArray, size() * 2 + 1);
}
}
public int size(){
return theSize;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new MyIterator();
}
private class MyIterator<T> implements Iterator<T>{
// 当前元素的索引
private int current;
// 返回元素的索引
private int lastIndex = -1;
public MyIterator(){
current = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != size();
}
@Override
public T next() {
lastIndex = current++;
return (T) theArray[lastIndex];
}
@Override
public void remove() {
// int index = current - 1;
current = lastIndex;
MyArrayList.this.remove(current);
}
}
}