栈也是一个list,所以任何能实现list的方法都可以实现栈.所以ArrayList和LinkedList都可以实现栈,关于ArrayList和LinkedList的实现,可以看我的另外两篇博客:
LinkedList: http://blog.csdn.net/lqx_sunhan/article/details/79043644
ArrayList: http://blog.csdn.net/lqx_sunhan/article/details/79037602
我们这里选择手动实现栈
一种底层由数组实现,也就是和ArrayList差不多的思路.
一种底层由链表实现,也就是和LinkedList差不多的思路.
栈其实就是一种简单的数据结构,他也叫后进先出(Last In First Out)表.
图解:
基本操作如下:
- push 进栈
- pop 出栈
top 查看栈顶元素
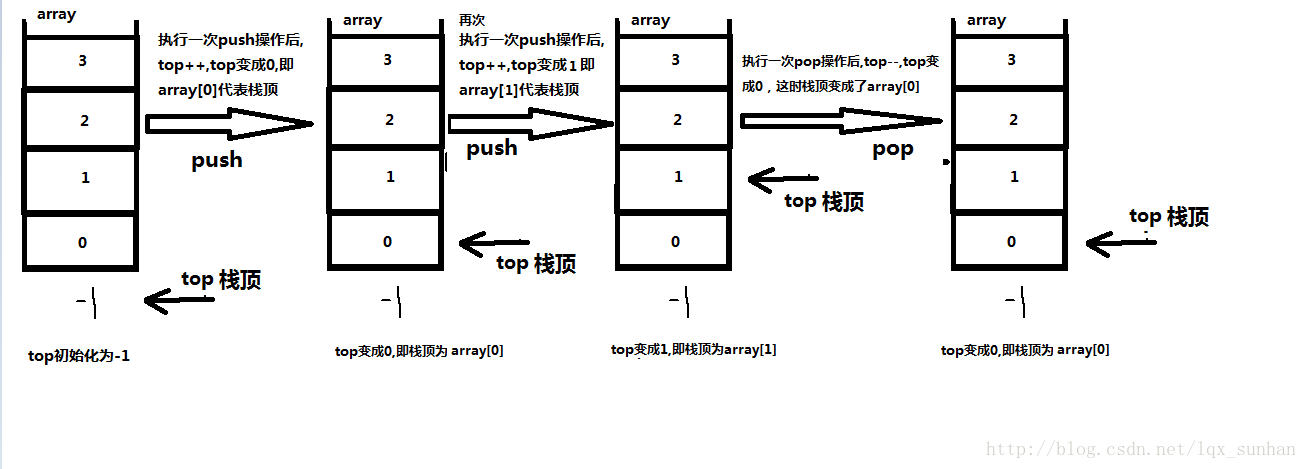
数组实现
图:
数组实现栈和实现ArrayList差不多的思路,不过我们这里固定栈的大小,如果你想,也可以动态扩充容量.我们有初始化的变量:
top = -1 代表栈顶
theArray底层的数组,容量自己定
theSize栈内元素数量push操作:
top++
theArray[top] = 元素
theSize++pop:
theArray[top] = 返回的元素
top- -
上面两个操作的顺序很重要,我们要先将栈顶元素拿到,然后再top- -
theSize++
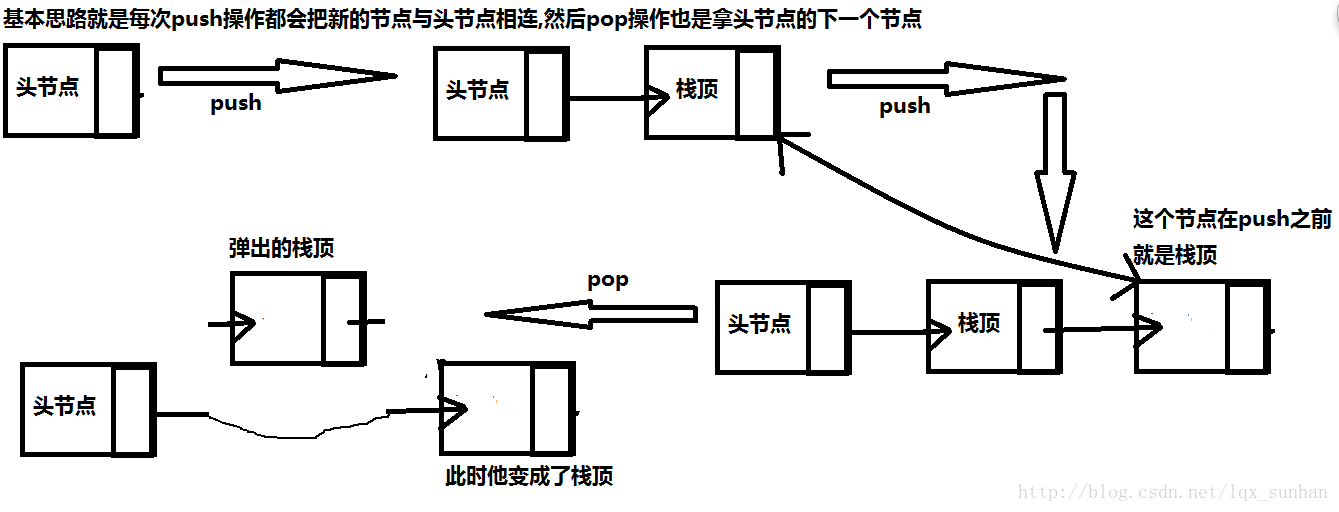
关于链表实现,其实就是一根单向链表,每次进栈和出栈都拿第一个节点的元素就可以达到效果,图:
基本思路就这样了,接下来我们上代码
底层由数组实现:
public class MyStackArray<T> {
private T[] data;
private int theSize;
private int top;
public MyStackArray(){
data = (T[]) new Object[10];
theSize = 0;
top = -1;
}
public boolean push(T t) {
if(top == data.length - 1){
throw new RuntimeException("栈已满!");
}
data[++top] = t;
theSize++;
return true;
}
public T pop(){
if(theSize == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("没有任何数据了!");
}
T element = data[top];
// 为了能让gc回收废弃的资源
data[top] = null;
top--;
theSize--;
return element;
}
public int size(){
return theSize;
}
}底层由链表实现(是单向链表):
public class MyStackLink<T> {
/**
* 这个类代表一个节点
* next代表这个节点连接的下一个节点
* element是这个节点的元素
*
* @param <T>
*/
private static class Node<T> {
private Node next;
private T element;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Node next, T element) {
this.next = next;
this.element = element;
}
}
private Node begin;
private int theSize;
public MyStackLink(){
begin = new Node(null, null);
theSize = 0;
}
public boolean push(T t){
Node node = new Node(begin.next, t);
begin.next = node;
theSize++;
return true;
}
public T pop(){
if(theSize == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("没有任何数据了!");
}
Node current = begin.next;
T element = (T) current.element;
theSize--;
begin.next = current.next;
current = null;
return element;
}
public T top(){
return (T) begin.next.element;
}
public int size(){
return theSize;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return theSize == 0;
}
}