1.配置文件pom,一定要使用2.4以上的,2.4默认请求方式是json,会导致getmapping设置参数类型对对象时,swaggerui界面不能指定为其他类型,反正就是各种坑,不建议用
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
2.使spring管理swaggerui配置
package org.liping.springribbon; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder; import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors; import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors; import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo; import springfox.documentation.service.Contact; import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType; import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2; @Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class Swagger2 { //swagger2的配置文件,这里可以配置swagger2的一些基本的内容,比如扫描的包等等 @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo()) .select() //为当前包路径 .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("org.liping.springribbon")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build(); } //构建 api文档的详细信息函数,注意这里的注解引用的是哪个 private ApiInfo apiInfo() { return new ApiInfoBuilder() //页面标题 .title("Spring Boot Swagger2 ui") //创建人 .contact(new Contact("liping1", "https://home.cnblogs.com/u/keepMoveForevery/", "")) //版本号 .version("1.0") //描述 .description("API 描述") .build(); } }
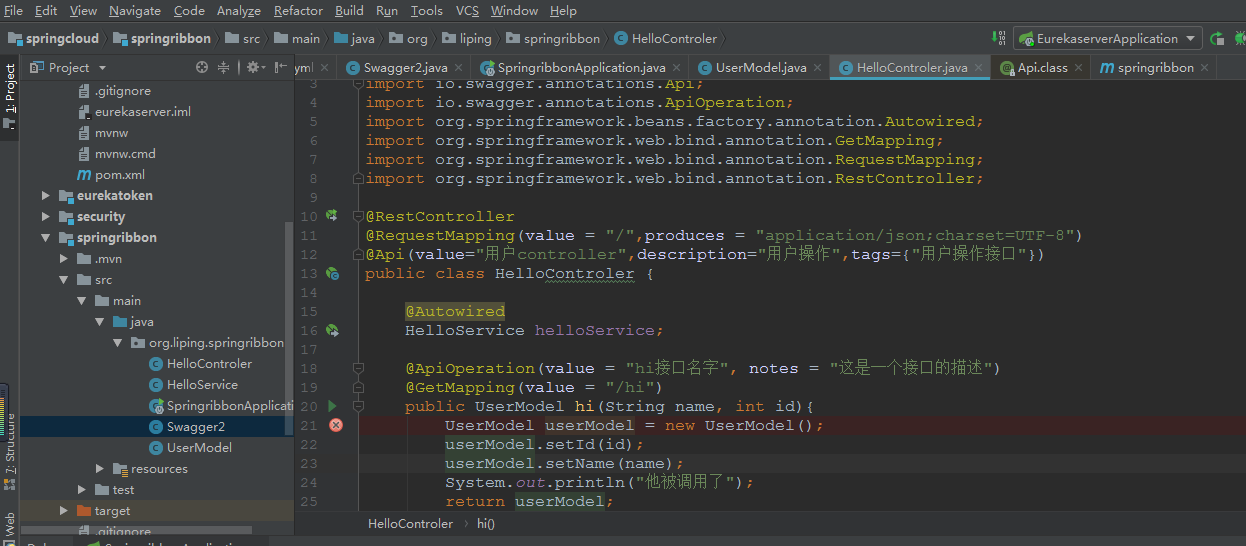
3.在自己的Controler加入swagger-ui注解开启测试
package org.liping.springribbon;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/",produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
@Api(value="用户controller",description="用户操作",tags={"用户操作接口"})
public class HelloControler {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@ApiOperation(value = "hi接口名字", notes = "这是一个接口的描述")
@GetMapping(value = "/hi")
public UserModel hi(String name, int id){
UserModel userModel = new UserModel();
userModel.setId(id);
userModel.setName(name);
System.out.println("他被调用了");
return userModel;
}
@ApiOperation(value = "hi1接口名字")
@RequestMapping(value = "/hi1")
public UserModel hi1(UserModel userModel){
UserModel userModel1 = new UserModel();
userModel1 = userModel;
System.out.println("他被调用了1"+ userModel.getId());
return userModel1;
}
}
下面是我用来做测试测对象代码
package org.liping.springribbon; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty; public class UserModel { @ApiModelProperty(value="id",name="id",required=true) private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "UserModel{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
就这么简单,其他一些属性自行百度
下面是代码结构以及执行结果
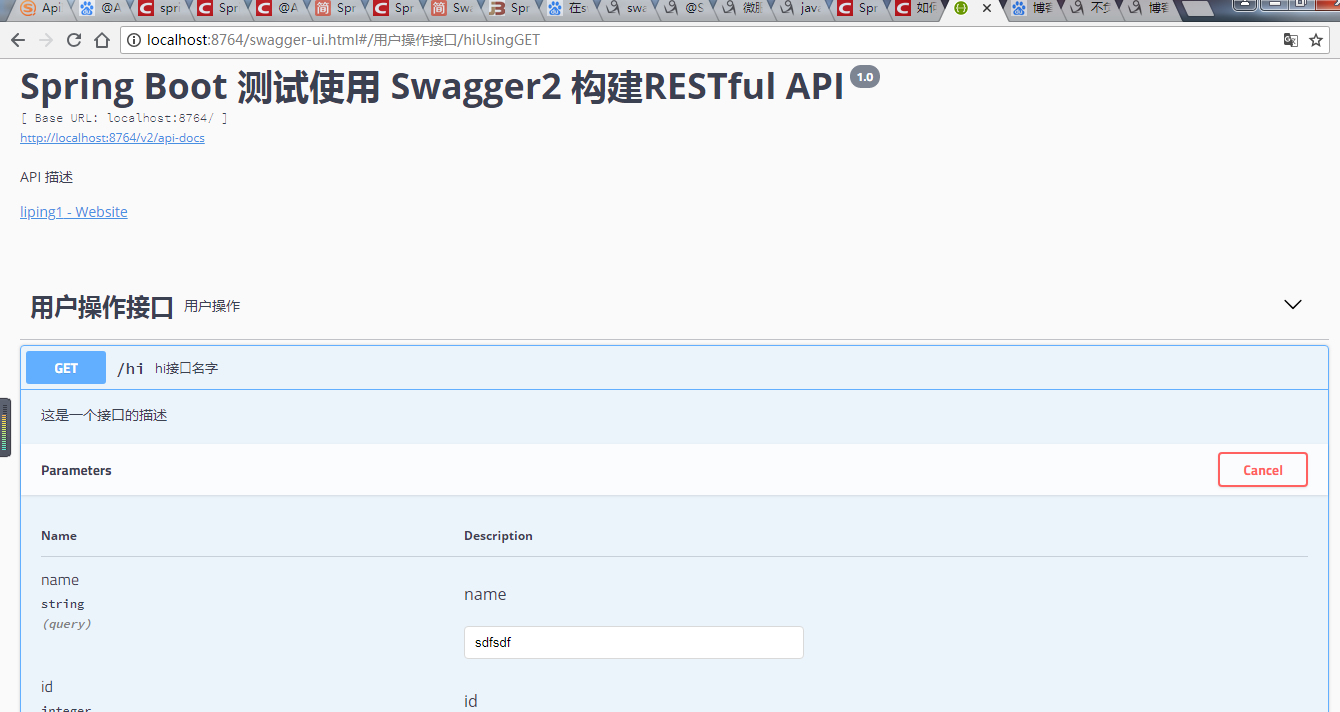

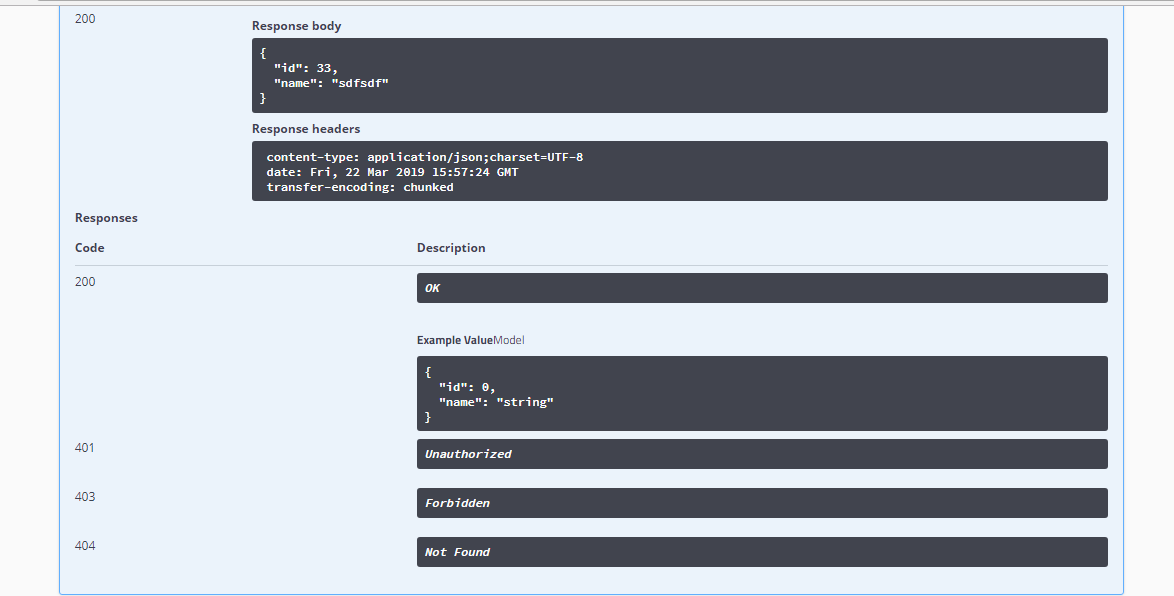
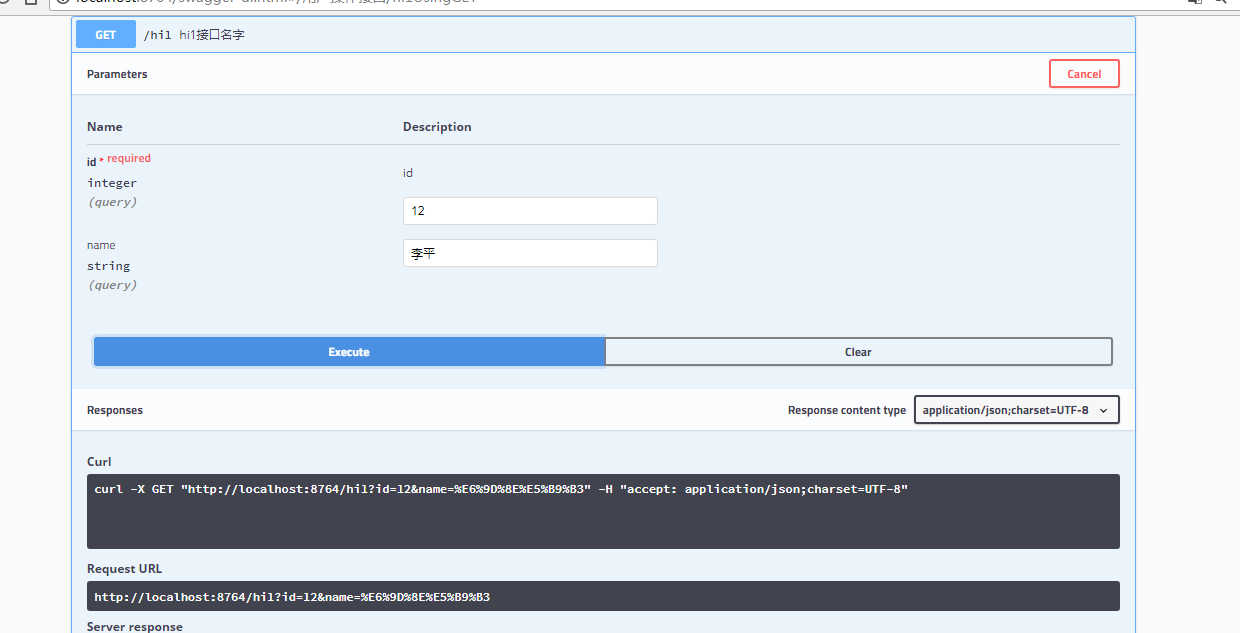
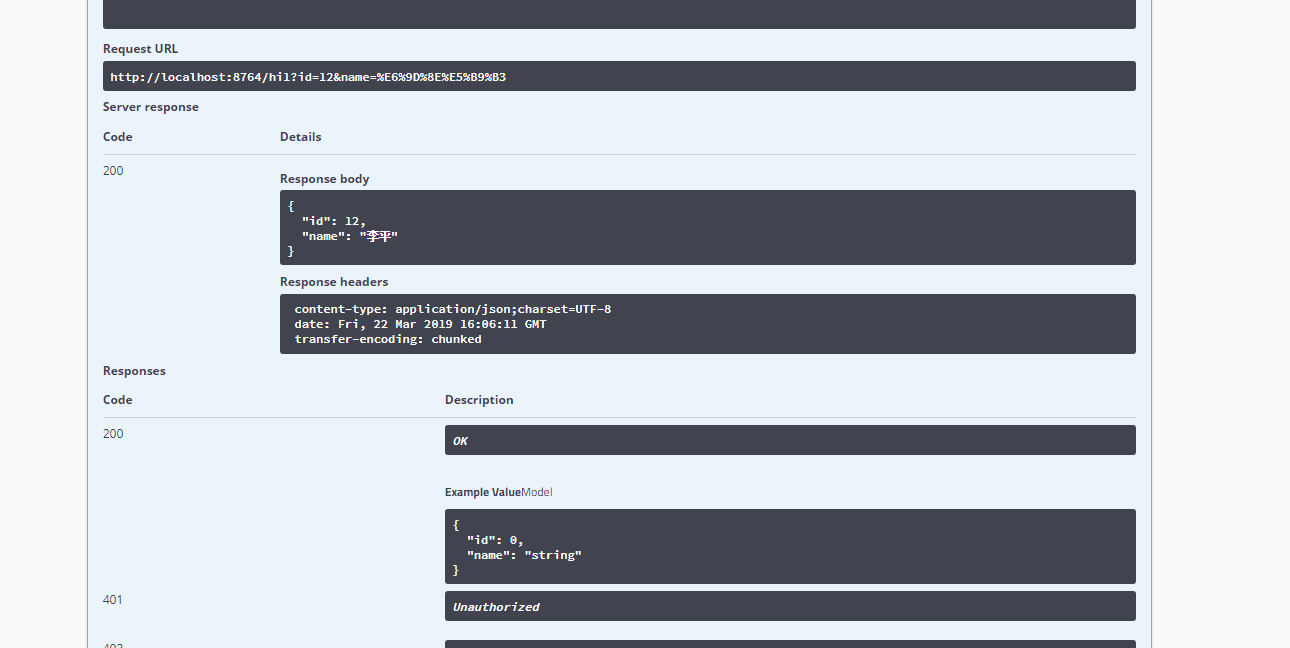
最后是代码结构