版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/u014303647/article/details/88360244
在muduo里经常看到生产者消费者模型,所以用互斥锁和条件变量实现了一些。
一些tips:如果使用循环的话,生产者和消费者线程个数应该相等,这样才能做到供需平衡。
还有对于pthread_cond_wait这个函数的讲解,为什么要传递两个参数进去呢?比较好奇的是为什么传递互斥锁变量上去,因为在调用pthread_cond_wait的时候,会先对互斥锁变量mutex进行解锁,然后当前面的条件变量满足以后,会重新获得互斥锁。
还有就是pthread_create传递参数的用法,写个小的错误实例。
先上传一份有问题的代码:
#include<pthread.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t notEmpty = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t notFull = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int top ,bottom;
const int MAX = 5;
void* produce(void* arg)
{
int thread_number = *(int*)arg;
for(int i = 0; i< MAX*2; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while((top+1)%MAX == bottom)
{
cout << "the area is full,please consume" <<endl;
pthread_cond_wait(¬Full, &mutex);
}
top = (top+1) % MAX;
cout << "pthread " << thread_number << " produce, "<<"now top is " << top <<endl;
pthread_cond_signal(¬Empty);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void* consume(void* arg)
{
int thread_number = *(int*)arg;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX*2; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(top % MAX == bottom)
{
cout << "the area is empty"<<endl;
pthread_cond_wait(¬Empty, &mutex);
}
bottom = (bottom+1)%MAX;
cout << "pthread " << thread_number << " consume, " << "now bottom is " << bottom <<endl;
pthread_cond_signal(¬Full);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t pid[MAX-1];
top = 0;
bottom = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX-1; i++)
{
if(i%2 == 0) pthread_create(&pid[i], NULL, produce, &i);
else pthread_create(&pid[i], NULL, consume, &i);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < MAX-1; i++)
pthread_join(pid[i], NULL);
return 0;
}
看一下运行结果有点意外:
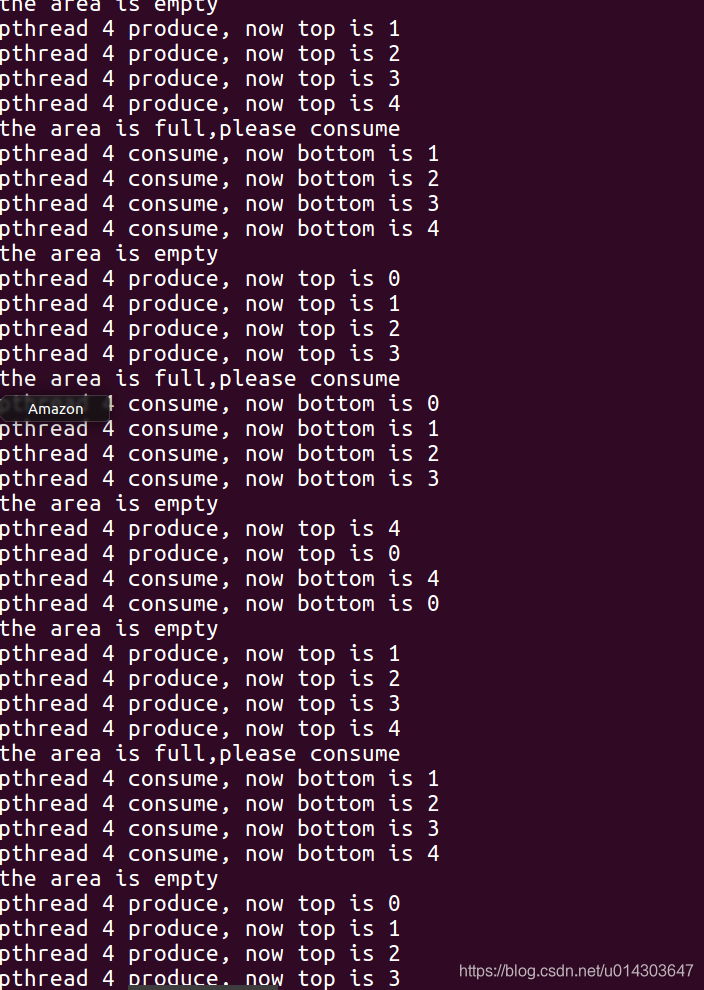
为什么所有的线程的号码都是4呢,
你看我们传递的是i的地址,但是运行的太快,所以最后i的地址的值变为4,然后初始化函数都没来得及执行
所以我们应该传递一个地址里的值不会变的值进去。
更新后的代码:
#include<pthread.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t notEmpty = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t notFull = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int top ,bottom;
const int MAX = 5;
void* produce(void* arg)
{
int thread_number = *(int*)arg;
for(int i = 0; i< MAX*2; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while((top+1)%MAX == bottom)
{
cout << "the area is full,please consume" <<endl;
pthread_cond_wait(¬Full, &mutex);
}
top = (top+1) % MAX;
cout << "pthread " << thread_number << " produce, "<<"now top is " << top <<endl;
pthread_cond_signal(¬Empty);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void* consume(void* arg)
{
int thread_number = *(int*)arg;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX*2; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while(top % MAX == bottom)
{
cout << "the area is empty"<<endl;
pthread_cond_wait(¬Empty, &mutex);
}
bottom = (bottom+1)%MAX;
cout << "pthread " << thread_number << " consume, " << "now bottom is " << bottom <<endl;
pthread_cond_signal(¬Full);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t pid[MAX-1];
top = 0;
bottom = 0;
int thread_number[MAX-1];
for(int i = 0; i < MAX-1; i++) thread_number[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX-1; i++)
{
**int* t = thread_number + i;**
if(i%2 == 0) pthread_create(&pid[i], NULL, produce, t);
else pthread_create(&pid[i], NULL, consume, &i);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < MAX-1; i++)
pthread_join(pid[i], NULL);
return 0;
}

这样就可以了!
总之,生产者消费者模型学到的东西不少!