一、DataFrame
1、其他语言也有DataFrame
ptyhon pandas R
局限性:单机
2、Datasets(1.6版本之后) and DataFrames
DataSet:
(1)有利于RDD基于SparkSQL,优化执行引擎
(2)构建JVM对象使用函数式算子
(3)DataSet的API面向Scala、Java
DataFrames:
(1)是一个DataSet
(2)被组织成列,可以理解为一张表
(3)Java,Scala,python,R
(4)DataSet的一个类型
3、发展历史
SchemaRDD<1.3
===>
DataFrame<1.6
====>
DataSet
4、DataFrame vs RDD


相同点:
(1)都是分布式的数据集
(2)都是collection
(3)都有数据处理等API接口
不同点:
(1)DF有schema
(2)DF比RDD更详细,性能更好
二、DataFrame代码实现
1、入口点SparkSession
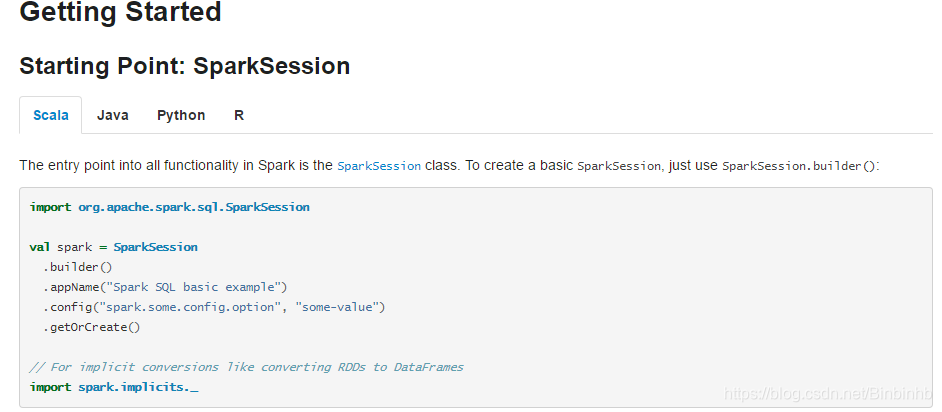
val spark = SparkSession
.builder()
.appName("Spark SQL basic example")
.config("spark.some.config.option", "some-value")
.getOrCreate()2、版本不同入口点的历史
Spark SQL入口点
<2:SQLContext HiveContext
>=2:SparkSession
3、DF读
(1)读:官网
val df1 = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
=format().load(path)
所以标准写法:
val df = spark.read.format("json").load("")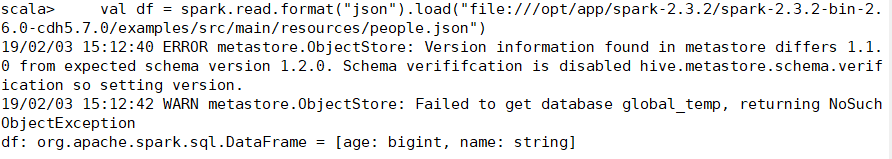
打印schema信息:

(2)显示DF内容
/**
* Displays the top 20 rows of Dataset in a tabular form. Strings more than 20 characters
* will be truncated, and all cells will be aligned right.
*
* @group action
* @since 1.6.0
*/
def show(): Unit = show(20)
(3)DF的select用法,需要哪一列就取哪一列
单个参数:

多个参数:


第二种写法:

df.select('name).show()
(4)其他方法:
// This import is needed to use the $-notation
import spark.implicits._
// Print the schema in a tree format
df.printSchema()
// root
// |-- age: long (nullable = true)
// |-- name: string (nullable = true)
// Select only the "name" column
df.select("name").show()
// +-------+
// | name|
// +-------+
// |Michael|
// | Andy|
// | Justin|
// +-------+
// Select everybody, but increment the age by 1
df.select($"name", $"age" + 1).show()
// +-------+---------+
// | name|(age + 1)|
// +-------+---------+
// |Michael| null|
// | Andy| 31|
// | Justin| 20|
// +-------+---------+
// Select people older than 21
df.filter($"age" > 21).show()
// +---+----+
// |age|name|
// +---+----+
// | 30|Andy|
// +---+----+
// Count people by age
df.groupBy("age").count().show()
// +----+-----+
// | age|count|
// +----+-----+
// | 19| 1|
// |null| 1|
// | 30| 1|
// +----+-----+4、DF创建一个视图,便于直接用SQL操作

df.createOrReplaceTempView("people")
val sqlSF = spark.sql("select * from people")
sqlSF.show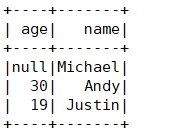
三、SparkSQL与RDD交互(重要)
1、RDD转换成数据集的方法
Spark SQL支持将现有的RDDs转换为数据集的两种不同方法。第一种方法使用反射来推断包含特定类型对象的RDD的架构。
创建数据集的第二个方法是通过一个编程接口,该接口允许您构造一个模式,然后将其应用到现有的RDD。
2、反射Inferring the Schema Using Reflection
info.txt ==> DataFrame
package com.HBinz.spark.Spark.sql.day02
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
object SparkSQLApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder()
.appName("SparkSQLApp")
.master("local[2]")
//.enableHiveSupport() //支持Hive
.getOrCreate()
//通过调用spark的sparkcontext方法来将文本文件转换成RDD
val info = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\infos.txt")
//println(info.count())
//info.collect().foreach(println)
//TODO...
/*思路
RDD转成DataFrame
3行数据===>3条记录
*/
//读取每一行记录采用逗号分割,分割出来的是数组,然后把每一行的数组给他作用到Info类里面去
import spark.implicits._
val infoDF = info.map(_.split(",")).map(x=>Info(x(0).toInt,x(1),x(2).toInt)).toDF()
infoDF.show()
//SQL的方式展示infoDF
infoDF.createOrReplaceTempView("T_info")
spark.sql("select * from T_info").show()
spark.stop()
}
//这个类有RDD信息,我们要把RDD套进这个Info里面,将schame信息定义在case class里面
case class Info(id:Int,name:String,age:Int)
}3、旧版本的转DF,翻开官网1.6.1版本

(1)只支持21字段,超过的限制就要使用自定义class来实现Product

总结:
schame信息通过case class来指定的。
4、
When case classes cannot be defined ahead of time (for example, the structure of records is encoded in a string, or a text dataset will be parsed and fields will be projected differently for different users), a DataFrame can be created programmatically with three steps.
Create an RDD of Rows from the original RDD;
Create the schema represented by a StructType matching the structure of Rows in the RDD created in Step 1.
Apply the schema to the RDD of Rows via createDataFrame method provided by SparkSession.
如果不能提前定义case classes(例如,记录的结构编码在一个字符串中,或者一个文本数据集将被解析,字段将因用户的不同而不同而不同),可以分三个步骤以编程方式创建数据框架。
1、从原来的RDD创建行的RDD;
2、创建一个schema,这个schema使用;

StructType:1到n个StructField
3、通过由SparkSession提供的createDataFrame方法将模式应用到行的RDD。
官网的实现代码:
val info = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\infos.txt")
//println(info.count())
//info.collect().foreach(println)
val rowRDD = info
.map(_.split(","))
.map(attributes => Row(attributes(0), attributes(1), attributes(2)))
val schemaString = "id name age"
//将row字段拆出来通过map方法遍历行的名字,类型,和是否允许空值
val fields = schemaString.split(" ")
.map(fieldName => StructField(fieldName, StringType, nullable = true))
val schema = StructType(fields)
val infoDF2 = spark.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
infoDF2.show()4、优化
由于StringType的类型不可知的,像官网这样操作,字段类型不可控。因此需要优化:
//生产上的做法:
//转行RDD
//.trim(),去两端空格
val info = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\infos.txt")
.map(_.split(",")).map(x => Row(x(0).trim.toInt,x(1),x(2).trim.toInt))
//自定义StructType,每个StructField自定义类型,类型要跟行RDD每一列的类型相匹配。
val infoFields = StructType(
Array(
StructField("id",IntegerType,true),
StructField("name",StringType,true),
StructField("age",IntegerType,true)
)
)
val infoDF2 = spark.createDataFrame(info, infoFields)
infoDF2.show()
如果报错:

就是行RDD和StructField的类型没对上。
四、SparkSQL实践
需求:
将student.data转成DF
1、分析数据源结构

(1)“|”分割
需要转义"\\|"
(2)email长度大于20,需要自定义长度
![]()
查看文件行长度wc -l student.data
默认20行列,和true(超出20行列的不显示)
studentInfo.show(false)即可
(3)空跟null的处理
(4)case class 要在调用的方法的作用域之外(坑)
2、原代码
//TODO..
val info = spark.sparkContext.textFile("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\LearningNote\\BigData\\lesson43\\资料\\student.data")
import spark.implicits._
val studentInfo = info.map(_.split("\\|")).map(x=>Student(x(0).toInt,x(1),x(2),x(3))).toDF()
studentInfo.show(false)
}
case class Student(id:Int,name:String,phone:String,email:String)
}
3、拓展
(1)head()方法,打印前N条记录
studentInfo.head(5).foreach(println)

(2)frist()方法,打印第1条记录
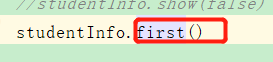
![]()
![]()
3、.select("")字段错误报错易读
studentInfo.select("id","nama")
4、.filter(),条件过滤SparkSQL
studentInfo.filter("id>5").show(false)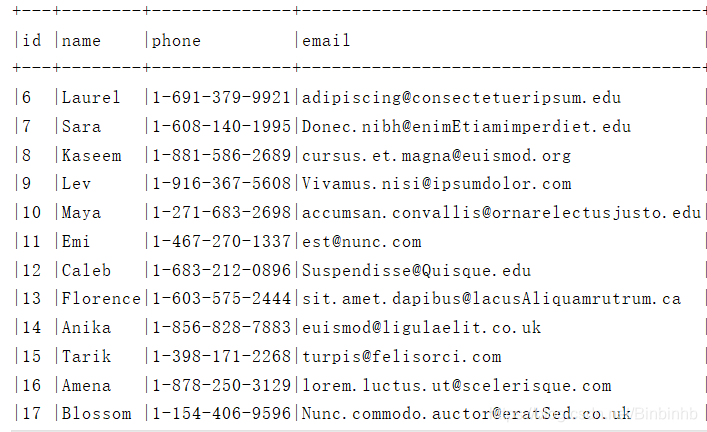
5、UDF内置函数SUBSTER
studentInfo.filter("SUBSTR(name,0,1) = 'M'").show(false)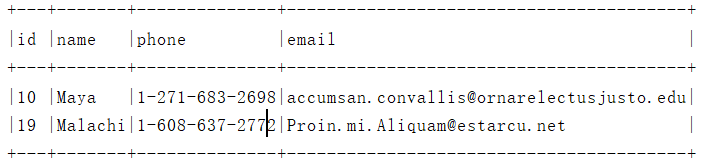
等于
studentInfo.filter("name like 'M%'").show(false)6、排序
.sort()

studentInfo.sort($"name".desc).show()
studentInfo.sort($"name".desc,$"id".desc).show(25,false)
7、修改列名
student.select($"name".as("new_name"))
8、join
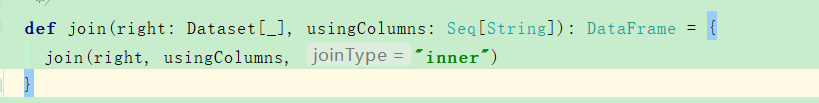

studentInfo.join(studentInfo2,studentInfo.col("id")===studentInfo2.col("id"),"inner")
.show(26,false)9、分组
文件格式输出为json,以年龄分组,保存到桌面output文件夹里
infoDF.write.format("json").partitionBy("age").save("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\output")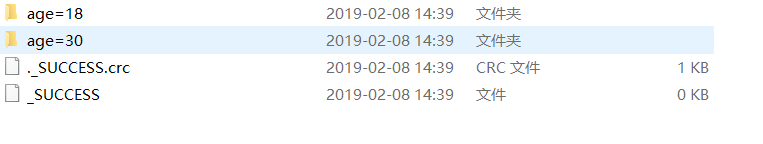
30岁有两个